Value Chain Analysis and Sales Logistics
advertisement

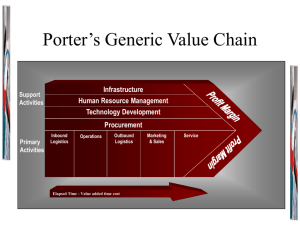
Value Chain Analysis and Sales Logistics R/3 Text Chapters 4 &5 Strategic Significance (1) – – – – “Value Chain”, the company’s activities are divided into the technologically and economically distinct activities that the company performs in doing business “Value Activities”, are nine generic activities (split in two categories: primary and support) which value is the amount that buyers are willing to pay for a product or service “Primary activities” are those involved in the physical creation of the product or service “Support activities” provide the inputs and infrastructure that allow the primary activity to take place The Value Chain Firm Infrastructure Human Resources Management Technology Development Procurement Inbound Operations Logistics Outbound Sales & Logistics Marketing Service Primary VC Activities Inbound logistics – Outbound logistics – machining, packaging, assembly, etc. Marketing & sales – collecting, order processing, delivery, etc. Operations – inventory control, vehicle scheduling, returns to supplier, etc. advertising, promotion, quoting Service – installation, repair, training VC Support Activities Procurement Technology development Human resource management Firm infrastructure Transforming the Value Chain (2) Firm Infrastructure Office Automation Human Resources Management Technology Development Work Force Planning Systems CAD Procurement EDI Inbound Operations Logistics Outbound Sales & Logistics Marketing Service Automated Warehousing Computerized ordering Equip. Maintenance Computer-Controlled Machine Automated Shipment Scheduling Mapping R/3 Text to VC External Accounting/Treasury Mgt Chapter 8 and 12 Human Resources Management Controlling Chapter 9 Chapter 10 Procurement Chapter 7 Inbound Operations Logistics Outbound Sales & Logistics Marketing Chapter 5 Service Chapter 5 Chapter 6 and 7 Chap 11 and 13 Chapter 5 Strategic Significance (2) – – Supplier VC – A company’s value chain is a system of interdependent activities A value chain for a company in a particular industry is embedded in a larger stream of activities that it is called “Value System” Firm VC Channel VC Buyer VC Linkage among activities not only connect value activities inside a company but also create interdependence between its value chain and those of its suppliers and channels Porter’s Five Forces Model Threat of new entrants Bargaining Power of Suppliers Rivalry Among Existing Competitors Bargaining Power of Buyers Threat of Substitute Products or Services Interaction between opportunities and threats Individual Company VC Every company activity can be categorized into primary or support activity – – – start with generic VC and subdivide into discrete activities categorize those activities that contribute best to a firm’s competitive advantage can compare company VC to industry VC R/3 and the VC Allows company to restructure activities on VC Business reference scenarios are structured around primary and support VC activities Text is organized around VC activities See VC examples – copier machine, AMCC, Dell computer Standard Order Handling Scenario Mailing campaign Monitor sales activity Possible customer inquiry Customer RFQ processing Order entry Delivery processing Goods issue processing Billing Possible rebate processing VC for Direct Sale to Industrial Customer Sales Support Sales inquiry/ Quotation proc Customer Outline Agreement Sales Order Shipping Credit Management Billing Personnel selection Foreign Trade Customer Rebate Processing Information System Quality Managment Transportation Warehouse Management Standard Order Handling Scenario (1) Cust mail Campaign to Be carried out Mailing Campaign processing ^ Sales activity Is to be prepared Sales activity Is agreed upon Customer Inquires about products Direct mail Campaign Is sent Customer RFQ processing XOR XOR Sales Activity processing Quotation to Be created From contract Inquiry Items rejectec Quotation to Be created From inquiry XOR Quotation Reason occurred Standard Order Handling Scenario (2) Customer Quotation Processing ^ XOR Stand Order w/o Quote ref received Stand. Order w/ref to quote received Quotation Is sent ^ Quotation Is Valid ^ Quotation Items are rejected ^ XOR XOR Standard Order Processing Framework Agreement Processing XOR Framework Agreement Is Agreed w/ref Framework Agreement is To be created Standard Order Handling Scenario (3) XOR Rejection Notice sent to customer ^ Order is released Order Confirmation sent Sales Requirements created ^ Cash Management ^ Delivery Processing XOR Delivery Cannot be created Make-to Order Production Repetitive Manufacturing Production For Lot Size Process Manufacturing Standard Order Handling Scenario (4) ^ XOR Delivery is Relevant For billing Delivery is Relevant for shipment ^ Material For quality Check is available Shipping papers Are created/ transmitted Delivery is Not relevant For shipment Shipment Is determined Quality Management COGLAS GmbH - Logistics Solutions Goods issue Is posted Transportation Planning Goods issue Processing for Stock material XOR Transportation processing Shipping Notification generated Standard Order Handling Scenario (5) Billing ^ Export papers Are created/ sent Billing doc Is released For billing Billing doc Is sent ^ Cash Management Profitability Analysis w/ Overhead cost Profitability Analysis w/ Flex. Stand costing Profitability Analysis w/ Allocation costing Profitability Analysis w/ Static stand costing Customer processing More Complex Sales Scenarios Contract handling & agreements Third party order handling Customer consignment handling Cash orders Rush orders Make-to-order Returns handling Buy/Sell Overview Requisite Catalog • Select catalog item • Send Purchase Order • Create Sales Order XML XML R/3 Buy IDoc IDoc BC B/C • Goods Receipt • ERS • A/P • Create Purchase Order Marketplace BC • Pick • Pack • Ship •Receive Order Confirmation • Create Purchase Order Confirmation • Access Marketplace via BBP BBP R/3 Sell • EFT Payment Let’s Try Some XML!