Prenatal Testing
advertisement

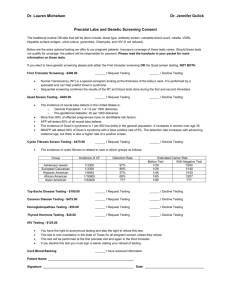
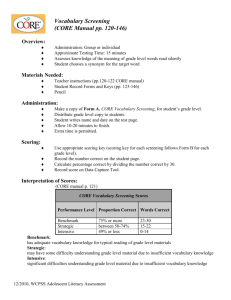
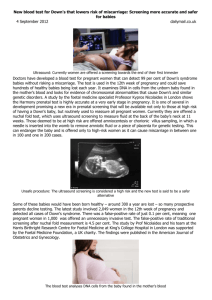
IN THE NAME OF GOD Prenatal screening E . ZAREAN Fellowship of perinatology Congenital Disorder • • • • • Genetic Chromosomal Enviromental Infection Morphogenesis defect Baseline Risk for Having a Child With a Serious Birth Defect 3-5% First and Second Trimester Screening Prenatal Testing Screening versus Diagnosis First trimester versus Second trimester Serum and/or Ultrasound Low-risk versus High-risk Women Diagnostic versus Screening (-) (+) No overlap: Positive test is abnormal Overlap: Positive test could be normal or abnormal Is Prenatal Testing for Everyone? consult • An explanation of the difference between a screening test and a diagnostic test. • Screening sensitivity and specificity compared to diagnostic testing. • Description of the performance of various screening tests . • The risks associated with prenatal diagnosis • The psychological implications of prenatal screening and diagnosis . • The implications of having a child with Down syndrome . • The detection rate of chromosomal abnormalities other than Down syndrome, and the implications of having a child with one of these abnormalities . • Information about the length of time necessary to obtain results from screening and diagnostic testing . • Information about pregnancy termination . Screening Performance: The challenge in screening is to have a test that has a high detection rate and low false positive rate. Detection Rate : (sensitivity) percentage of affecteds called screen positive by the test The higher the better! False Positive Rate : (1 – specificity) percentage of unaffecteds called screen positive by the test The lower the better! First trimester Screening Nuchal translucency Free beta HCG PAPP-A Combined NT and Serum Nuchal Translucency (NT) Amnion Skin First Trimester US – Nasal Bone Nasal bone present in a euploid fetus in the first trimester Nasal bone absent in a fetus with T21in the first trimester Nuchal Translucency (NT) Measurement “normal nuchal translucency” “increased nuchal translucency” Second trimester screening • AFP • B-HCG • Unconjucated estriol • Inhibin A Contingent First-trimester Screen High Risk Intermediate Risk Low Risk Offer CVS Quad Screen No Further Testing Offer Amino if HR Positive screen test • Most parents are anxious because they do not fully understand that most positive results are associated with a normal pregnancy outcome. • after than negative diagnostic test some anxiety related to the false-positive screening test may persist . • On the other hand, normal results may have psychological benefits for the reassured parents. • Consult : DR – FPR – Advantage – Disadvantage • Multiple pregnancy Case 1 • • • • • Age 27 8 weeks pregnant G2P1 Previous pregnancy uncomplicated Married for 5 years, healthy 3 year old daughter Case 1 • What prenatal genetic screening options would you discuss with her? – Discuss options with benefits, limitations, availability. – New screening tests may require earlier first prenatal visit . Case 1 • If she was 38…..? – Could go directly to CVS, amnio – Combined /Integrated test more accurate than age . • What might affect her decision? • Miscarriage rate . • Performance of amnio/CVS compared to sequential test. – May detect problems other than Down syndrome . • Her perception of risk/morbidity associated with Down syndrome. • Her personal/family/religious beliefs… Case 2 • Age 34 • 17 weeks pregnant • To discuss result of integrated screen. Case 2 • Results: Screening result : *** SCREEN POSITIVE*** Reason : Increased Risk of Down syndrome Down syndrome risk : 1 in 130 (at term) Risk of NTD : 1 in 7000 Comment : Down syndrome risk due to maternal age alone is 1 in 400 COMMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Down syndrome: The risk of Down syndrome is GREATER than the screening cut-off of 1 in 250 at term. If the gestational age is confirmed, counselling regarding the risks and benefits of AMNIOCENTESIS is suggested. Case 3 • • • • • • 33 years old G2P0 Miscarriage last year Trying to get pregnant for several years 14 weeks pregnant Following U/S for NT . you received report from radiologist indicating NT is elevated (4.0mm) for this gestational age • What would be important to discuss with Case 3 • she was referred for genetic counselling – Offered: • Chromosome testing • Ultrasound 18 - 20 wks & echocardiogram 20 - 22 wks – Counselled risk of miscarriage with CVS or amniocentesis. • May be even more significant for this couple in view of infertility and miscarriage High AFP • Over than 2 MOM : twin pregnancy incorrect GA ovarian tumor hepatocellular tumor IUFD low birth weight Placenta abruptio Anomaly open NTD omphalocele ( 4 MOM ) gastroschisis (10 MOM ) teratoma cystic hygroma benign obstructive uropathy fetal edema skin defect ultrasonography The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of ultrasound evaluation for the detection of NTDs were 98, 100, 100, and 99.9 percent, respectively . prenatal diagnostic procedure for fetal karyotype, rather than serum screening A previous pregnancy complicated by fetal trisomy . At least one major or two minor fetal structural anomalies in the current pregnancy . Chromosomal translocation, inversion, or aneuploidy in themselves or their partner . Future Directions First trimester US alone 3D/4D US Noninvasive Isolation of fetal DNA دستورالعمل کشوری مشاوره بايد در اولين مالقات بارداري (هفته 6تا 10 بارداري) انجام شود. درحال حاضر غربالگري جنين در سه ماهه اول بارداري توصيه مي شود .چنانچه خانم باردار پس از 13هفته و 6 روز و قبل از هفته 17بارداري مراجعه نمايد و غربالگري سه ماهه اول را انجام نداده است ،پس از مشاوره و انتخاب والدين ،غربالگري سه ماهه دوم بارداري درخواست مي شود. QUESTIONS ??