1. Ante-natal Screening
advertisement

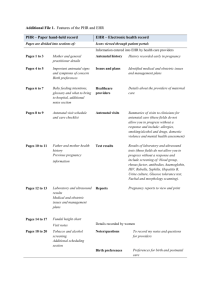
HIGHER HUMAN BIOLOGY Unit 2 Physiology and Health 1. Ante-natal Screening Recap • What are the two categories of contraception? • Give examples of physical methods? • What is the basis of chemical contraception? What I need to know • What is the purpose of antenatal screening? • What are the two types of ultrasound scan? • What are dating scans and chemical tests used to • • • • • • estimate? What are anomaly scans used for? What are biochemical tests and what are they for during pregnancy? Name two antenatal screening methods. What are the advantages and disadvantages of the two methods? What is a karyotype and what are they used to determine? What is the Rhesus antibody and what are the risks associated with this antigen during pregnancy? What is the purpose of antenatal screening? • Antenatal screening is carried out to monitor the health of a pregnant woman and her fetus • Antenatal screening identifies the risk of a disorder so that further tests can be carried out and a prenatal diagnosis given What are the two types of ultrasound scan? • Dating scan • Anomaly Scan What are dating scans used to determine? • Carried out at 12 weeks • Along with other chemical tests used to estimate how old the fetus is i.e. stage of pregnancy • Also used to estimate the due date What are anomaly scans used for? • Carried out at 20 weeks • Used to determine any abnormalities in the development of the fetus • Also used to estimate risk of Down’s Syndrome Biochemical tests • Many physiological changes occur during pregnancy • Biochemical tests are used to monitor these changes in order to highlight problems should they occur Tests Include • Blood analysis to detect blood Detect hypertension a pre-cursor to preeclampsia type (Rhesus) • Hormone concentrations (HCG) • Thyroid (hyperthyroidism) liver and kidney function • Glucose analysis (gestational diabetes) False positives • HCG increases up to week 10 then decreases in normal pregnancy • With a Down’s syndrome pregnancy HCG levels remain high throughout • False positive results • Human chorionic would be created if a gonadotrophin levels in blood sample was normal pregnancy taken at week 10 Diagnostic Screening • These are procedures • They include: used to diagnose, without doubt, disorders associated with the developing fetus • Offered if routine tests have highlighted problem or woman belongs to high risk category • Amniocentesis • Chorionic villus sampling Diagnostic testing Amniocentesis • • • • • Carried out at 18 weeks Less risk of miscarriage Amniotic fluid removed Karyotype produced Decision to proceed/terminate Chorionic villus sampling • • • • • Carried out at 8 weeks Higher risk of miscarriage Placental cells removed Karyotype produced Decision to proceed/terminate How tests are used – Assessing risk of Down’s syndrome Step 1 – woman’s age/history • Does she belong to high risk group Step 2 – Blood analysis • Alpha-fetoprotein concentration • Levels are normal if within 0.5 – 2.49 • Low levels (less than 0.4) can indicate high risk of Down’s syndrome • Baby may not have Down’s syndrome even in high risk How tests used – Down’s syndrome diagnosis Step 3a –Amniocentesis offered • If high risk indicated amniocentesis is offered to confirm diagnosis Step 3b – Nuchal translucency Rhesus Antibody Blood test Analysis Second pregnancy • Mother Rhesus negative • If the baby is Rhesus (no antigen for rhesus on her blood cells) • Causes problems if she is carrying a Rhesus positive baby • Mother becomes sensitised after birth and produces Rhesus antibodies positive • Rhesus antibodies from mother cross placenta and attack red blood cells • Baby born severely anaemic • Prevention – Rhesus negative expectant mothers given Rhesus antibody injections Activities • Make notes, summary on ante-natal screening procedures • Testing your Knowledge Qs • p146 No’s 1-4