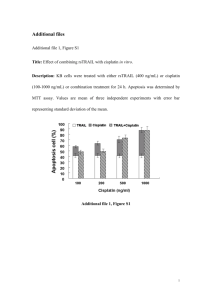
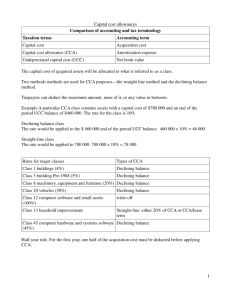
Thesis contents
advertisement

TNP- 470 as a potential adjuvant Therapy for Cholangiocarcinoma Sonexai Kidoikhammouan M.Sc. Student, Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Medicine, KKU Advisory committees: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Chaisiri Wongkham Dr. Wunchana Seubwai Dr. Atit Silsilivanit External examiners: Assoc.Prof.Dr. Sopit Wongkham Assis.Prof.Dr. Chariya Hahnvajanawong 17th August, 2012 1 Contents Introduction Hypothesis and Research questions Objectives Conceptual framework Experimental design Anticipated outcomes Research Plan 2 Introduction Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) Intrahepatic CCA (ICC) Extrahepatic CCA (ECC) 3 Epidemiology of CCA Bragazzi et al., 2011 4 CCA alternative treatments Surgery Adjuvant therapy Chemotherapy Radiation therapy 5 Surgery correlated with survival and recurrence rate in CCA patients Methods Portal vein and hepatic artery resection CCA subtype Hilar n Five-year survival rate (%) Recurrence (%) 298 42 ND Reference Igami et al., 2010 et al., However, this regimen is still giving low survival, but Guglielmi high recurrence ECC 34 20 ND 2009 rate Liver resection Liver resection ICC 45 35 30 Yedibela et al., 2009 Further more, some patients can not undergo such regimen Liver resection ICC 97 31.1 ND Palik et al. 2008 Liver resection ICC 44 63 ND DeOliveira et al. 2007 Liver resection with lymphadenectomy Hilar 26 21 27 Rea et al. 2005 Liver resection ICC 34 32 62 Casavilla et al. 1997 6 Association between response rate and median time survival using Chemotherapy n RR(%) MST (Months) Capecitabine 40 32.5 9.4 Furuse et al.,2008 Gemcitabine 40 17.5 7.6 Okusaka et al., 2006 Drug Reference Nevertheless, chemotherapy is still giving low Gemcitabine/capecitabine 45 32 Cho et al.,2005 14 response rate and median survival time Gem/cisplatin 40 28 9 Gemcitabine/5-FU 27 33 5.3 Knox et al., 2004 5-FU/FA 30 7 14.8 Malik et al., 2003 5-FU/oxaliplatin 16 56 10 Nehls et al. 2002 Irinotecan 36 8 6.1 Sanz-Altamira et al., 2002 Thongprasert et al., 2005 RR, response rate; MST, median survival time; 5-FU, 5-fl uorouracil; FA, folinic acid; 7 Radiotherapy 2-year survival was 80% and 4-year survival 30% Polistina et al. 2011 The need of targeted molecules with novel chemotherapy and adjuvant therapeutic strategies External beam radiotherapy 19.1for mo diagnosis survival timeand treatment of CCA patients are increasing nowadays Jiang et al., 2010 Survival time were 12.9 mo in patients who received EBRT Válek et al., 2007 EBRT; external beam radiation therapy 8 Serial analysis of gene expression(SAGE) K4 ; K3; K2D; K1; Low invasive cell s High invasive cells Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma Metastatic tumor (intrahepatic metastasis from cholangiocarcinoma primary tumor) 9 Comparison of MetAP2 expressions Normal biliary cells Hyperplastic and dysplastic bile duct epithelia Well differentiated tubular CCA Lymph node with metastatic CCA Sawanyawisuth et al., 2007 10 Comparison of MetAP2 expressions in bile duct epithelia Sawanyawisuth et al., 2007 11 Expression and association of MetAP2 in cancers Cancer Expression Clinical finding Reference in cancer Colon High Proliferation Selvakumar et al., 2009 Apoptosis Cholangiocarcinoma High Proliferation Sawanyawisuth Metastasis 2007 et Neuroblastoma High Angiogenesis Morowitz et al., 2005 Hepatocellular carcinoma High Tumor growth, Sheen et al., 2005 Metastasis Mesothelioma High Proliferation Catalano et al. ,2001 12 al., MetAP2 structure Addlagatta et al., 2005 13 How does MetAP2 work? Met 14 MetAP2 inhibitors Cell growth inhibition Anti-angiogenesis Datta et al.,2009 15 Why we choose TNP-470? TNP-470 gives high potential on antitumor activity and endothelial cell growth more than other MetAP2 inhibitors such as fumagillin, bestatine and anthranilic acid sulfonamide (Wang et al. 2008; Ingber et al., 1990) Wang et al. 2008 16 Anti-tumor activity of TNP- 470; in vitro Cell type Result Reference FU-MMT-1 cells Anti angiogenesis Naganuma et al.,2011 Endothelial cell G1 arrest Hines et al., 2010 B16F10 melanoma Fetal mouse bone cell Wanget al.,2008 Vasculature disruption Wijngaarden et al., 2010 Anti angiogenesis B16F10 (murine melanoma) Induction apoptosis Okrój et al.,2006 Human pancreatic Growth inhibition Hotz et al., 2001 17 Anti - tumor activity of TNP- 470; in vitro; animal model Cell type Result Reference Human uterine carcinosarcroma Tumor growth Naganuma et al.,2011 Human gioblastoma Tumor growth Yao et al., 2010 Proliferation Murine neuroblastoma Chesler, et al.,2007 Apoptosis Sarcoma Human Wilms tumor cells Tumor growth Antiangiogenesis Kanamori et al.,2007 Huang et al.,2004 18 Effect of TNP- 470 in clinical trial Cancer type Dose (mg/m2) n RR(%) Solid tumor (lung, sarcoma, thymoma) 60 17 24 Tran et al., 2004 Lung cancer 60 32 33 Herbst et al., 2002 10-70 38 ND Dezube et al.,1998 9.3 -71.2 18 ND Kudelka et al.,1998 Renal carcinoma 60 33 3 Stadler et al.,1999 Prostate 71 33 ND Stadler et al.,1994 Kaposi’s sarcoma Cervical cancer Reference RR; response rate ND, no determine 19 Hypothesis Suppression of MetAP2 activity by TNP-470 can inhibit proliferation, migration/invasion and enhance anti-tumor activity of chemotherapeutic drugs in CCA cell lines. 20 Research questions 1. Does supplementation of TNP-470 inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of CCA cell lines? 2. What is molecular mechanism by which TNP-470 affects the proliferation, migration and invasion of CCA cell lines? 3. Can supplementation of TNP-470 enhances the antitumor activity of chemotherapeutic drugs in CCA cell lines? 21 Objectives 1. To determine the effect of TNP470 on proliferation, migration and invasion of CCA cell lines. 2. To identify the molecular mechanism by which TNP470 affects proliferation, migration and invasion of CCA cell lines. 3. To explore the possibility of using TNP470 as an adjuvant therapy of CCA. 22 Conceptual framework Background Cancers with high expression of MetAP2 High proliferation High metastasis Enhance Angiogenesis MetAP2 inhibitors 23 Conceptual framework (cont) Hypothesis CCA cell lines high expression of MetAP2 MetAP2 inhibitor: TNP-470 ? High proliferation ? High metastasis ? Enhance chemotherapeutic drug 24 Experimental design Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - Flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic drug response Chemotherapeutic sensitizin (5-FU, Cisplatin, Doxorubicin and Ge Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (Casepase3, Bax, Bcl-2, p38 ) Genes related to metastasis (c-Myc, MMP2 , MMP9) Anticipated outcomes TNP-470 and its combination with chemotherapeutic drugs will be the basic knowledge for treatment of CCA patient in the future Part of this thesis outcome will be presented in a national/international scientific conference At least one publications in an international journal are expected 26 Research plans 2011 Activities Apr - Jun 1 2 Jul-Sep 2013 Oct-Dec Jan-Mar Literature review MetAP2 expression in CCA cell lines 3. Proposal examination 4. Investigation of MetAP2 functions on metastasis of CCA * Cell proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion assays 5. Investigation of underlying mechanism by which MetAP2 play roles in the particular function cell cycle and apoptosis analysis Determine molecular gene 6. Data analysis and thesis writing 7. Manuscript preparation 8. Thesis defense * Pilot study 28 Expression of CCA cell line 4.5 MetAP2 expression level (2-ΔCt) 4 3.55 3.5 2.928 3 2.5 2 1.328 1.042 1.5 1.205 1.00 0.892 1 0.5 0 M055 M139 M156 M213 M214 KKU100 MMNK1 29 Effect of TNP-470 on CCA cells proliferation 30 Effect of TNP-470 on CCA cell migration KKU - M213 KKU - M214 Vehicle TNP - 470 (1.25 µg/ml) 31 Effect of TNP-470 on CCA cell invasion KKU - M213 KKU - M214 Vehicle TNP - 470 (1.25 µg/ml) 32 Determination molecular mechanism Expression level (2-ΔCt) KKU-M213 1 1 0.91 0.8 0.6 Vehicle 0.4 0.2 0.1 TNP-470 0.19 0.054 0.011 0 MMP2 MMP9 VCAM1 KKU-M214 Expression level (2-ΔCt) 0.054 0 C-MYC 1 1 0.8 0.6 Vehicle 0.4 0.2 0 0.27 0.178 TNP-470 0.00032 0.044 0.0078 0.0016 0.0024 MMP2 MMP9 VCAM1 C-MYC 33 Acknowledgements 34 Thank you very much 35 Structure of fumagillin and TNP-470 Ingber et al., 1990 36 SAGE process 1. Isolate the mRNA of an input sample. 2. Extract a small chunk of sequence from a defined position of each mRNA molecule. 3. Link these small pieces of sequence together to form a long chain 4. Clone these chains into a vector which can be taken up by bacteria. 5. Sequence these chains using modern highthroughput DNA sequencers 6. Process this data with a computer to count the small sequence tags 37 Conclusion CCA is a malignant cancer, its early state for diagnosis and very poor prognosis because its low response to treatments. The need of targeted molecules with novel chemopreventive and adjuvant therapeutic strategies for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of CCA patients have been increasing in nowadays. Overexpression of MetAP2 play a crucial role in several cancers especially in CCA development . Inhibition of MetAP2 activity by its inhibitors is lethal for cancers No studies regarding effects of TNP-470 adjuvant with chemotherapeutic drugs in CCA has been reported, therefore, this effects are of our interest. 38 Pathological feature of CCA patients and expression of MetAP2 in primary tissue 39 Effect of fumagillin in CCA cells Sawanyawisuth et al., 2007 40 Effect of fumagillin on cell growth Hou et al. (2009). 41 Immune suppression in murine 42 Mass forming Blechacz et al., 2011 43 periductal-infiltrating type Blechacz et al., 2011 44 The intraductal-growth type Blechacz et al., 2011 45 Criteria for diagnosis 1. Tumor stage, 2. Tumor location 3. Growth pattern 46 Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma Diagnosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma Require histopathology and is a diagnosis of exclusion; a pathologic staging system The diagnosis of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma is often made clinically, and is aided by cytologic fluorescent in situ hybridization studies; staging systems for this subtype of cholangiocarcinoma are still evolving Diagnosis of distal extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma can usually be confirmed by cytology; stage is highly dependent upon depth of invasion of surrounding structures Blechacz et al., 2011 47 Risk factors for CCA Blechacz et al., 2011 48 CCA classification Blechacz et al., 2011 49 CCA subtype 50 Adjuvant chemoradiation therapy Adjuvant chemoradiation therapy • 5-year survival; 5-FU plus radiotherapy 35% and surgical resection alone 27% Hughes et al. 2007 51 ERK 52 Capecitabine convert to 5-FU phosphorylated 5-FU is converted to its deoxynucleoside, which inhibits DNA synthesis by blocking the functions of a key enzyme in DNA replication- thymidylate synthetase. phosphorylated and incorporated into RNA where it causes miscoding and halts protein synthesis. Side effects Vomiting Poor appetite sores in mouth, lips, or throat hair loss or thinning (may include face and body hair) diarrhea dry, flaky, cracking skin 53 Gemcitabine Gemcitabine diphosphate effectively inhibits ribonucleotide reductase inducing a depletion of cellular deoxynucleotides (dNTP). On the one hand this will inhibit DNA synthesis by lack of sufficient DNA precursors. Side effects weakness, loss of appetite, headache, cough, chills, and muscle aches); hair loss; infection (fever, chills, sore throat); 54 Irinotecan prevents DNA from unwinding by inhibition of topoisomerase 1 Side-effects The most significant adverse effects of irinotecan are severe diarrhea and extreme suppression of the immune system. Diarrhea Irinotecan-associated diarrhea is severe and clinically significant, sometimes leading to severe dehydration requiring hospitalization or intensive care unit admission. This side-effect is managed with the aggressive use of antidiarrheals such as loperamide or Lomotil with the first loose bowel movement. Immunosuppression The immune system is adversely impacted by irinotecan. This is reflected in dramatically lowered white blood cell counts in the blood, in particular the neutrophils. The patient may experience a period of neutropenia (a clinically significant decrease of neutrophils in the blood) while the bone marrow increases white cell production to compensate. 55 cisplatin these platinum complexes react in vivo, binding to and causing crosslinking of DNA which ultimately triggers apoptosis (programmed cell death) Side effects Nephrotoxicity (kidney damage) Neurotoxicity (nerve damage) Ototoxicity (hearing loss) 56 Folinic acid Folinic acid, therefore, allows for some purine/pyrimidine synthesis to occur in the presence of dihydrofolate reductase inhibition, so that some normal DNA replication and RNA transcription processes can proceed. 57 Cell cycle control 58 Regulates cell growth and Protein synthesis ϒ P67/MetAP2 α Protein synthesis β Deglycocetylation ? ϒ P67/MetAP2 P ERK1/2 β α P eIF2α Specific kinase ERK1/2 P67/MetAP2 eIF2α Specific kinase Inhibition of Cell Growth ϒ α ϒ β P α β Inhibition of Protein synthesis 59 Effect of TNP-470 on angiogenesis Naganuma et al., 2011 60 Effect of TNP-470 on mouse xenograft Yao, Zhao et al. 2010 61 Effect ofTNP-470 on cell cycle TNP-470 arrest cell cycle at G1 phase 62 Wang et al. 2008 Wang et al. 2008 63 Reversible inhibition of MetAP2 catalytic activity by A-800141 Wang et al. 2008 64 Western blot analysis of cell cycle proteins in HUVEC treated with MetAP2 inhibitors. Wang et al. 2008 65 MetAP2 inhibition results in formation of cellular GAPDH variants with an unprocessed N-terminal methionine. Wang et al. 2008 66 Effects on growth of the FU-MMT-1 xenografts Emoto et al., 2007 67 Anti-tumor effect of radiation response by combined treatment with angiogenesis inhibitor, TNP-470, in oral squamous cell carcinoma Shintani et al., 2006 68 TNP-470 promotes initial vascular sprouting in xenograft Huang et al., 2004 Malignant Progression and Blockade of Angiogenesis Hitting the mother lode of tumor angiogenesis Post-translational myristoylation: Fat matters in cellular life and death CCA Khan, S., et al., 2005 73 MetAP2 inhibitors fumagillin Target gene in cell cycle arrest Target gene in apoptosis G1 arrest cyclinE2 Bcl-2 Bcl-2 TNP-470 or AGM-1470 A-800141 Cell type reference Colorectal , Hou.L.et.al hepatocellular (2009) carcinoma Sheen,I.et.al (2005) Human Catalano,A.et.al Mesothelioma (2001) G1 arrest P53, p21, p27 p-RB cyclinE HUVEC Zhang,Y.et.al (2000) p-RB CDK/cyclin G0 arrest HUVEC Abe,J.et.al (1994) Antoine, N. et.al (1994) G1 arrest p53 and p21 p-RB human neuroblastom a BAEC Wang,J.et.al (2007) 74 MetAP2 inhibitors Target gene in cell cycle arrest Target gene in apoptosis Cell type reference A-353700 G1 arrest p-RB cyclinA Carcinoma, Wang,J.et.al Sarcoma , (2003) neuroblastoma hybrid of 1-deoxynojirimycin (DNJ) and an aryl1,2,3-triazole G1 arrest cyclin D1 ERK1/2 BAEC Zhao,Y. et.al. (2008) IDR-803, IDR-804, CKD-732 G1 arrest p21 HUVEC Chun,E.et.al (2005) PPI-2458 G1 arrest HUVEC Bainbridge, J .et.al.(2007) bovine aortic endothelial cell (BAEC) 75 MetAP2 Enzymes similarity Dissimilarity MetAP1 MetAP1 Could compensate when MetAP2 is inactive (in yeast) Play role in the G2/M phase of cell cycle Mn2+ MetAP2 inhibition leads to G1 arrest in active site MetAP2 number of key Respects ( 60-aa insert) Addlagatta et al. 2005 76 retinoblastoma protein 77 Cell cycle control 78 Criteria for choosing chemotherapeutic drugs 1. Different mechanism from cytotoxic agent 2. Side effect 3. Cost 79 Signal transduction 80 Expression of MMP-2 in bladder cancer Seiler et al., 2011 81 Expression of MMP-9 in bladder cancer Seiler et al., 2011 82 MetAP2 specific substrates 1. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) 2. cyclophilinA 83 BCL2 (B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2) antiapoptosis, through a possibly complex process; dimerization, especially with BAX; role of the BCL2 antiapoptosis members in forming complexes with caspase-9 and APAF1 (homolog of the nematode CED-4), which prevent them to initiate the protease cascade (through caspase-3 cytochrome C dependent activation and) leading to apoptosis 84 PI staining Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis Chemotherapeutic drug response - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic sensitizing (5-FU and Gemcitabine ) Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (bcl-2, p53, ) Genes related to proliferation (ERK1/2, cyclinE, p21, Rb) Genes related to metastasis (ICAM1, ALCAM, MMP2 , MMP9) 85 SYBR Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis Chemotherapeutic drug response - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic sensitizing (5-FU and Gemcitabine ) Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (bcl-2, p53, ) Genes related to proliferation (ERK1/2, cyclinE, p21, Rb) Genes related to metastasis (ICAM1, ALCAM, MMP2 , MMP9) 86 The sulphorhodamine (SRB) assay Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis Chemotherapeutic drug response - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic sensitizing (5-FU and Gemcitabine ) Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (bcl-2, p53, ) Genes related to proliferation (ERK1/2, cyclinE, p21, Rb) Genes related to metastasis (ICAM1, ALCAM, MMP2 , MMP9) 87 Combination index Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis Chemotherapeutic drug response - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic sensitizing (5-FU and Gemcitabine ) Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (bcl-2, p53, ) Genes related to proliferation (ERK1/2, cyclinE, p21, Rb) Genes related to metastasis (ICAM1, ALCAM, MMP2 , MMP9) 88 Effect of TNP-470 in the treatment on uterine carcinosarcoma in vivo 89 Etiology Yongvanit et al. 2011 90 Wound healing 91 Information of CCA cell lines Cell lines Gender Age (years old) Histological type KKU-M055 Male 56 Poorly differentiated KKU-M139 Female 53 Squamous cell carcinoma KKU-M156 Male 68 Moderately differentiated KKU-M213 Male 58 Adenosquamous carcinoma KKU-M214 Male 52 Moderately differentiated KKU-100 Female 65 Poorly differentiated KKU-OCA17 Male 38 Well differentiated 92 TNP-470 binding Wang et al., 2003 93 MetAP2 TNP-470 Cell cycle G1 arrest p21 CyclinD Apoptosis induction Bcl-2 Casepase3 Metastasis ICAM1, ALCAM, MMP2 , MMP9 Upregulation Downregulation 94 Tentative model for role of MetAP2 in CCA development MetAP2 ERK1/2 TNP-470 Cell cycle G1 arrest p21 CyclinD Apoptosis Bcl-2 Metastasis Casepase3 MMP2/9 c-Myc Hypothesis Upregulation Downregulation 95 Tentative model for role of MetAP2 in CCA development MetAP2 ERK1/2 TNP-470 Cell cycle p21 Apoptosis CyclinD Bcl-2 Metastasis Casepase3 MMP2/9 c-Myc Hypothesis Upregulation Downregulation 96 CCA cell lines with high MetAP2 expression TNP-470 Growth n ) cycle Metastasis Cell cycle and apoptosis (flow cytometry) - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Determine the molecular mechanism (real time PCR, western blot) Cell apoptosis Enhan chemotherape Chemotherapeuti (5-FU and Gem Prolifera (MTT as Genes related to metastasis Cancers with high MetAP2 expression TNP-470 ? ? Growth ? Enhance chemo drug Metastasis - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Cell cycle and apoptosis (flow cytometry) C-Myc VCAM1 MMP2 Chemotherapeuti (5-FU and Gem MMP9 Cell apoptosis Hypothe Bcl-2 Casepase3 Upregula Downreg 98 Experimental design Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth Metastasis Chemotherapeutic drug response - Proliferation - MTT assay - Cell cycle and apoptosis - flow cytometry - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Chemotherapeutic sensitizing (5-FU and Gemcitabine ) Determine the molecular mechanism Genes related to apoptosis (bcl-2, p53, ) Genes related to cell cycle (p21, cyclinD) Genes related to metastasis (ICAM1, c-Myc, MMP2 , MMP9) 99 Conceptual framework (cont) Hypothesis CCA cell lines high expression of MetAP2 MetAP2 inhibitor: TNP-470 ? High proliferation ? High metastasis ? Enhance chemotherapeutic drug 100 Selected CCA cell lines with high expression of MetAP2 Study the effect of TNP - 470, MetAP2 inhibitor Growth n ) cycle Metastasis Cell cycle and apoptosis (flow cytometry) - Invasion assay - Migration assay - Adhesion assay Determine the molecular mechanism (real time PCR, western blot) Cell apoptosis Enhan chemotherape Chemotherapeuti (5-FU and Gem Prolifera (MTT as Genes related to metastasis High MetAP2 expression in cancer ERK1/2 TNP-470 Cell growth e G1 arrest Angiogenesis Metastasis VEGF Apoptosis Migration Invasion Adhesions