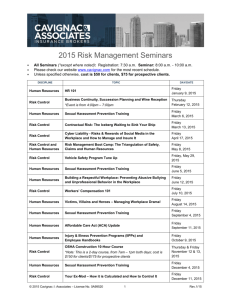
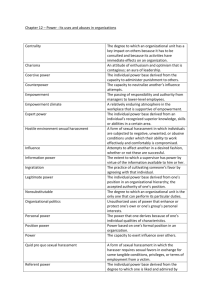
Supervisor, Teacher, and School Personnel
Responsibilities under Federal and State
Sexual Harassment Laws
Sexual Harassment
“Unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual
favors, sexually motivated physical conduct or visual
forms of harassment of a sexual nature…”
•
•
Sexual Harassment – Employment
Sexual Harassment – Students
Employment
“when submission to such conduct is either explicitly or
implicitly made a term or condition of employment or
is used as the basis for employment decisions or
when such conduct has the purpose of effect of
unreasonably interfering with an individual’s work
performance or creating an intimidating, hostile, or
offensive work environment.”
Title VII, Civil Rights Act of 1964, as Amended 1991
Students
“by an employee, by another student, or by a third
party that is sufficiently severe, persistent, or
pervasive to limit a student’s ability to participate in
or benefit from an education program or activity, or
to create a hostile or abusive educational
environment.”
Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972
State Laws
• North Carolina Employment Practices Act
• Retaliatory Employment Discrimination Act
• Torts
• Wrongful Discharge
• Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress ***
• Criminal Laws ***
•
•
•
•
Rape
Sexual Offense
Sexual Offense by School Employee
Assault
*** Individual Liability
Federal Laws
• Title VII (Discrimination in Employment)
• Title IX (Student free from Sexual Harassment)
• 42 U.S.C. § 1981 (Discrimination in Employment
Contracts)
• 42 U.S.C. § 1983 (Civil Rights Violation) ***
*** Individual Liability
Sexual Harassment in Employment
Types of Employment Based
Sexual Harassment
• Adverse Employment Action
• Hostile Work Environment
Liability for Employment
Based Sexual Harassment
Adverse Employment Action
School Board will always be liable for instances of
Employment Sexual Harassment based upon an
Adverse Employment Action.
Liability for Employment
Based Sexual Harassment
Hostile Work Environment Defenses
•
Employer exercised reasonable
care to prevent and correct
promptly any sexually harassing
behavior; and
•
That the harassed employee unreasonably failed to take
advantage of the school’s anti-harassment policies
Preventive Measures
Prohibition Against Discrimination, Harassment and
Bullying Policy Code: 1710/4021/7230: Reference
School Board Policy Manual under CCS Website
Discrimination, Harassment and Bullying Complaint
Procedure Policy Code: 1720/4015/7225: Reference
School Board Policy Manual under CCS Website
Individual Liability Concerns
• 42 U.S.C. 1983
• Intentional Infliction of
Emotional Distress
• Criminal Assault
• Disciplinary Actions
TITLE IX Sexual Harassment
Hostile environment sexual
harassment of a student by
other students, employees,
or third parties is created if
conduct of a sexual nature is
sufficiently severe, persistent,
or pervasive to limit a student’s ability to participate
in or benefit from the education program or to create
a hostile or abusive educational environment
TITLE IX Sexual Harassment
• Applies to educational institutions that receive federal
funds.
• Applies to students engaging in academic educational,
extra-curricular, athletic and any other school program.
• Take place at school facilities, bus, or other location if
sponsored by school.
• Reasonable Care to Prevent….
• Policies
• Supervisor training and education
TITLE IX Sexual Harassment
• Quid Pro Quo Sexual
Harassment
• Hostile Environment
Sexual Harassment
Liability of School for Sexual
Harassment
School always will be liable for even one instance of
sexual harassment of quid pro quo or adverse
employment action
Liability of School for Sexual
Harassment
A school will also be liable for hostile environment sexual harassment
by its employees (non quid pro quo) if:
1) The harassing employee acted with apparent authority or
2) The harassing employee was aided in carrying out the sexual
harassment of students by his or her position of authority
with the school system.
3) School also liable for non quid pro quo sexual harassment if
they knew or should have known of the harassment and
failed to take immediate and appropriate steps to remedy
known harassment.
Example: Coach threatens to bench a student unless that student agrees
to respond to his sexual advances (although the coach never follows
through on his/her threat).
Policies
Schools are required to adopt and publish grievance
procedures providing for prompt and equitable
resolution of sex discrimination complaints and to
disseminate its policy against sex discrimination.
Policies
Prohibition Against Discrimination, Harassment and
Bullying Policy Code: 1710/4021/7230: Reference
School Board Policy Manual under CCS Website
Discrimination, Harassment and Bullying Complaint
Procedure Policy Code: 1720/4015/7225: Reference
School Board Policy Manual under CCS Website
Staff-Student Relations Policy Code 4040/7310
Individual Liability
42 U.S.C. § 1983 (Civil Rights Violation)
•
Culpable Person
•
Supervisor Liability
Individual Liability
An individual can be held liable under a theory of
supervisory liability under §1983 where:
1)
The supervisor had actual or constructive knowledge that
his or her subordinate was engaged in a conduct that
posed a pervasive and unreasonable risk of sexual
harassment;
2) That the supervisor’s response to that knowledge was so
inadequate as to show deliberate indifference to or tacit
authorization of the alleged offensive practices; and
3) That there was an affirmative causal link between the
supervisor’s inaction and sexual harassment injury.
Criminal Liability
N. C. Gen. Stat §14-27.2
N. C. Gen. Stat §14-27.3
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.27.4
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.27.5
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.27.7
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.27.7A
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.33
N. C. Gen. Stat §14.202.4
First Degree Rape
Second Degree Rape
First Degree Sexual Offense
Second Degree Sexual Offense
Intercourse and Sexual Offenses
with Certain Victims
Statutory Rape
Misdemeanor Assault
Taking Indecent Liberties with a
Student
*The majority of these crimes are felony-level offenses and, for state licensed employees, carry licenserevocation penalties.