Demo. Notes - Community Unit School District 200
advertisement
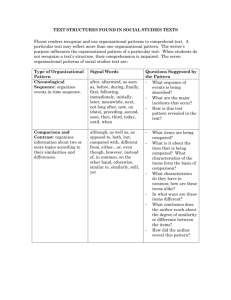
DEMONSTRATION UNIT Comm. Studies Learning Targets: I can describe the purpose of a demonstration speech. I can effectively organize my demonstration speech. WRITE STEP BY STEP INSTRUCTIONS • On how to make a grilled cheese sandwich • On how to dance the Macarena WHAT IS A DEMONSTRATION SPEECH? • Type of informative speech • Informing the audience “how to” do something • As long as you are able to present the steps of the demonstration or process speech topics • How To Make ... • How To Fix ... • How To Use ... • How To Do ... • How ... Works • How ... Is Done, Produced or Made WHY ARE WE DOING A DEMO SPEECH? Applicable to life both formally and informally Forces you into to use precise instruction Evaluate different methods of organization As an audience member you learn something from every speech! SPEECH DIFFERENCES In the introduction, you must give your audience a reason to listen. Tell them WHY the skill is valuable and what they can do with it in their own lives. Introduction: 1. Attention Getter! 2. Purpose (tell them what you are going to teach them) 3. Tell them why you choose to demonstrate this topic or how you learned this skill 4. Reason to listen (tell them why they should know how to do it. Apply it to their lives) 5. List the main points (your first main point should map out your materials) PROCESS / MAKE CONNECTIONS IN DIFFERENT WAYS Activity: Turn to your partner and explain to them how someone should drive from Wheaton North to Wheaton College. Activity: Turn to your partner and explain how someone should get from the English Resource Room to the tennis courts. PROCESS / MAKE CONNECTIONS IN DIFFERENT WAYS How did you give instruction? Directional? (Drive North) Landmarks? (Go past the nurse’s office) Gestures? (Head that way) In relation to? (You know the train tracks? Its next to that.) Literally? (Go about 1.3 miles) A combination of these?? IMPORTANCE OF PRECISE INSTRUCTION Instruction is an important (and very common) form of communication We must realize that people process and make connections in different ways. Without precise instruction people can get lost, frustrated, or complete a task incorrectly. HOW DO YOU RECEIVE INSTRUCTION BEST? How do you like to receive instruction or learn? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Auditory Visually Kinesthetically Manipulatively Combination ORGANIZATIONAL PATTERNS *Not all of these apply to Demo Speeches! TOPICAL DIVISION: Organizes a speech according to aspects, subtopics, or topics. Example: Introduction Speech Roger’s future goals… Mary’s family consists of… Michael's favorite sports… CHRONOLOGICAL DIVISION: Organizes speech according to a time sequence. Example: Historical Topics, Process or procedure topics How to cook How to change car oil History of WWII SPATIAL DIVISION: Organizes a speech according to the geography or physical structure of the subject. Example: Best for topic dealing with parts of an object or a place The parts of a gun Grocery Store Museum CAUSAL DIVISION: Organizes a speech from cause to effect, or effect to cause. Helpful when you identify / trace a condition from its causes. Also useful in persuasion Example: Recession, Medical topic disease PRO-CON DIVISION: Organizes a speech according to arguments for and against some policy, position, or action. Since it is balanced approach - easier to use in informative than persuasion . Example: Policy options, Political choices GIMMICK DIVISION: Organizes a speech according to a special memory device, such as alliteration, rhyme, or initial letters that spell a word. Example: ROYGBIV PROBLEM SOLUTION PATTERN: A pattern of organization that identifies and analyzes a problem and proposes a solution. Example: Not enough passing time/Extend school day ! ANALYZE THIS EXAMPLE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hKKKiF5AdTE PRACTICE OUTLINING THE GARDEN EXAMPLE IN YOUR PACKET