critical thinking - Bakersfield College
advertisement

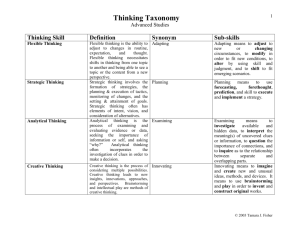
THINKING POWER Objectives • 1. Define critical thinking. • 2. State how critical thinking is essential to nursing practice. • 3. Identify strategies that will facilitate the development of critical and creative thinking skills. Successful Intelligence depends on 3 thinking skills: practical analytical THINKING SKILLS creative CRITICAL THINKING (Analytical thinking) What is it? The ability to reason More than just recall The ability to apply knowledge Being innovative Critical/Analytical thinking is: when you take in information, examine the information by asking questions about it, and then put it to use in one or more of the following ways: • • • • • Problem solving Making decisions Reasoning Opening your mind to new things Planning strategically A Path to Critical/Analytical Thinking Take in information Ask questions Use information Taking in information • This is your raw material • It involves: – – – – – Recall Input from what you hear What you see What you read What you experience Ask questions???? • ?what, when, where, why • ?What effect does this info have • ?How is this similar/different from what I know More Questions?? • ?will this information help solve a problem or make a decision • ?is this fact or opinion Questioning is the key to linking what you learn to other information Learning exercise It’s 3 am in the hospital and Ms. Avon, the nurse, sees a patient’s overhead room light on. She walks into the room and says, ”Hi, Mr. Trent, I noticed your light on. How are you doing?” The patient smiles and says. “I’m fine.” The nurse observes that there are wads of used tissues on the floor; the sheets are all twisted; Mr. Trent’s eyes are puffy and red. Conclusions • The patient is fine, is normally awake at this hour, and may have been rubbing his eyes because of his allergies • The patient is fine but can’t sleep because he napped all day. His eyes are always red and puffy • The patient is not fine but doesn't want to talk about it • The patient is not fine but doesn’t know how to ask for help. Using Information This is evident by: • What you say • What you do • What you write • What you create Using information Put what you learn to work by: Problem solving Making decisions Strategic planning Reasoning Seeing new perspectives How do we use “CT” in Nursing? • Analyzing: separating or breaking a whole into parts to discover their nature, function a relationship • Applying standards: judging according to established personal, professional, or social rules or criteria • Discriminating: recognizing differences and similarities among thing or situations and distinguishing care fully as to category or rank • Information seeking: searching for evidence, facts, or knowledge by identifying relevant sources and gathering objective, subjective historical , and current data from those sources • Logical reasoning: drawing inference or conclusion that are supported in or justified by evidence • Predicting: envisioning a plan and its consequences • Transferring knowledge: changing or converting the condition, nature, form or function of concepts among contexts SUMMARY • REMEMBER THE COMPONENTS OF CRITICAL/ANALYTICAL THINKING • IT IS A SKILL THAT TAKES PRACTICE - KEY COMPONENTS FOR NURSES 1) OBSERVATION 2) MAKING CONNECTIONS 3) QUESTIONING Bloom’s taxonomy Knowledge – remembering facts, names, events, rote recall Comprehension –putting information into your own words Application – taking learned information and using it in a new situation Analysis – examining or breaking down the parts of information Synthesis – combining pieces of information to create a larger and newer piece of information Evaluation – assessing or judging the worth of information CREATIVE THINKING • Creativity forms a bridge between analytical and practical thinking Practical thinking CREATIVITY Analytical thinking Creative Strategies • • • • Brainstorming Shift your perspective Take a risk Set the stage – Be curious – Be spontaneous 1. Information Received 2.Critical thinkers use information by applying, analyzing, synthesizing, or evaluating it. Creative thinkers are problem solvers who broadened their thinking by becoming aware of more possibilities 3.Problem solvers propose a solution based on the evidence and their examination of that evidence. 4.Creative thinkers solve problems by coming up with new and different solutions. Creative thinking: You have to do things differently if you want different results PRACTICAL THINKING • • • • This is the ‘common sense’ aspect It is developed from personal experience rather than formal or academic lessons It is putting into ‘action’ what you know there is also an emotional connection Practical Strategies • Make the most of your personal strengths • Learn from every experience – both good and bad • Apply what you learn – don’t keep repeating the same mistake