Albert Einstein
advertisement

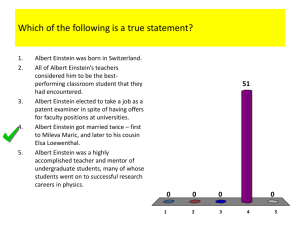
Albert Einstein 1879-1955 Brief history • Albert Einstein was born in Ulm, in Wittenberg Germany, on March 14, 1879 • At the age of fifteen he quit high school and followed his family to Italy where they had moved their failing electro technical • he entered the Swiss Federal Polytechnic School in Zurich in 1896 to be trained as a teacher in physics and mathematics. • In 1901 he finally gained his diploma, and got Swiss citizenship. • He was unable to find a teaching post, so he accepted a position as technical assistant in the Swiss patent office. • In 1905 Einstein wrote four fundamental papers. The first paper says that light must sometimes behave like a stream of particles with discrete energies, quanta. • The second paper showed an experimental test for the theory of heat and proof of the existence of atoms. • And his third paper was written to a central puzzle for physicists of the day describing the connection between electromagnetic theory and ordinary motion. He solved it using the principle of relativity. • The fourth showed that mass and energy are the same thing, mass-energy (E=mc2). Albert Einstein Accomplishments • In 1908 Albert was appointed as a Privatdozent in Berne. • In 1909 he became the Professor Extraordinary of Zurich school. • in 1911 he also became the Professor of Theoretical Physics at Prague • In 1914 he was appointed as the Director of Kaiser Wilhelm Physical Institute and Professor in the University of Berlin • Albert Einstein went to America to get the position of Professor of Theoretical Physics at Princeton University. He became a United States citizen in 1940 and retired from his post in 1945. • After World War II, Einstein was offered the Presidency of the State of Israel, but he didn’t accept it. • Later he worked together with Dr. Chaim Weizmann in establishing the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. • He wrote a theory of gravitation in 1916 and later he published his paper on the general theory of relativity • He contributed to statistical mechanics by his development of the quantum theory of a monatomic gas. • he has also accomplished valuable work in connection with atomic transition probabilities and cosmology. • he was awarded Fellowships or Memberships of all the leading scientific academies throughout the world. • He gained numerous awards in recognition of his work, including the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London in 1925, and the Franklin Medal of the Franklin Institute in 1935. • Albert Einstein received honorary doctorate degrees in science, medicine and philosophy from many European and American universities. • During the 1920's he lectured in Europe, America and the Far East. Science Goals • Einstein works with problems of statistical mechanics that march with quantum theory and it led to an explanation of the Brownian movement of molecules. • He also investigated the thermal properties of light with a low radiation density and his observations laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. Some of his Important Researches • Special Theory of Relativity (1905), • General Theory of Relativity (1916), • Investigations on Theory of Brownian Movement (1926), • The Evolution of Physics (1938). • Among his non-scientific works, About Zionism (1930) Personal life • Albert Einstein was a man that loved music and this played an important role in his life. • He married to Mileva Maric in 1903 and they had a daughter and two sons. • he divorced her in 1919 and he married his cousin, Elsa Lowenthal, who died in 1936 Resources • http://www.aip.org/history/Einstein/phisol1. html • http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/phy sics/laureates/1921/einstein-bio.html