World Religions
advertisement

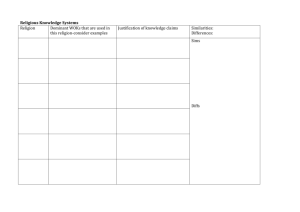
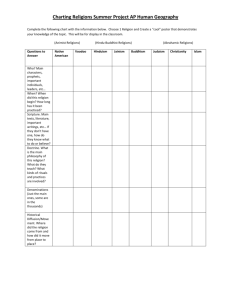
World Religions Explaining the Unexplainable Relationship with a Deity ◦ Deity – god figure Expression of Goodness Sacred Frame of Mind Moral Exchange of Power Ethical Practice Set of Beliefs and Practices What is Religion? Atheistic - no deity Monotheistic - one deity Polytheistic - multiple deities Pantheistic - everything is deity Animism – ancestors become spiritual forces Henotheism – believing in many gods, but one of them is supreme Types of Religions Belief in Supernatural Sacred/Secular Divide Communal/Individual Rituals Moral/Ethical Code Communication with Divine Mythical (sacred) stories Social Organizations Promise of Inner Peace/Harmony Offer future hope Propagate themselves ◦ Myth – story that attempts to explain the reality of the world in which a person lives Attributes of Religions Give Answers Address Morality Offer Control Provide Society, Structures, and Values Give Meaning to Existence Show guidance of how to live Function of Religion Adherent - looking from the inside Opponent - from outside to prove against Scholar - from inside to understand Seeker - from the middle with intent to follow or not follow Perspectives of Religion Began to view religion from outside in 1500’s Why Religious Studies? ◦ Understand new cultures in travel ◦ Modernity (worldview of reason and rational explaining) Responses to Religions: ◦ Exclusivism – only ours is right ◦ Inclusivism – ours is true, but others could be right too ◦ Pluralism – every religion has truth ◦ Universalism – all willed be “saved” History of Religious Studies French Wars of Religion (Cath./Protest.) ◦ French diplomat - peacemaker ◦ Didn’t believe Christians could solve war Wrote “Colloquium” ◦ Best religion is closest to Adam and Eve ◦ Earliest religion is the best religion ◦ Concerned with the best version of Christianity Jean Bodin (1530-1596) Lived during 30 Years War (Cath./Prot.) Diplomat ◦ Seek religion accepted by majority Found common religious themes: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ One God God is Worshipped Virtue is Key Repent of Sins Afterlife Consequences Edward Herbert (1582-1648) Studied myths and rituals of other groups ◦ “Primitive Mind” seeks to explain nature Gods are in control A basic mind cannot handle complexity, so a simple concept must be presented (gods) ◦ Concludes that religion will be trumped by Science ◦ Because religion was an attempt to explain reality, science is the ultimate way in which one explains reality Brenard Fontenelle (1657-1757) Scottish Empiricist (no instinctual knowledge) ◦ No spiritual realm “Natural History of Religion” ◦ Sources of Religion: ◦ 1) Nature’s Power ◦ 2) Anthropomorphism – assigning human characteristics to a deity “No progression in religion” David Hume (1711-1776) “Religion is the opiate of the masses” Focused on the Economic Aspect ◦ Have’s and Have Not’s Divides Social Functions: ◦ Sub-Structure - physical needs ◦ Super Structure - arts, philosophy, religion History Is between Workers and Owners Religion is the Owners’ attempt to calm the Workers Karl Marx (1818-1883) Founder of Sociology ◦ Sociology – the study of personal interactions and the systems of those interactions Religions based on Social Behavior Looks at Totemism ◦ Sacred things are related to society ◦ Totem is unifying mark ◦ Religions worship themselves Emile Durkheim (1858-1917) Founder of Psychoanalytical Technique “Totem and Taboo” ◦ Monotheistic religion arises from mythical and primal murder of father figure “Future of an Illusion” ◦ Religion is a coping mechanism ◦ Religion is illusion of wish-fulfillment ◦ Religion forces neurosis (deal with issues) Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) 1) 2) 3) 4) Naturalism Animism Ghost Theory Totemism 4 Theories of Origins Naturalism – the idea that worship originated with the fact that nature is unexplainable, and therefore worthy of worship Max Muller ◦ Humans are in awe of nature ◦ Lightening, Rain, Fire, etc. ◦ Religion is personification of nature Naturalism Animism – the idea that religion originated because all things had a spirit that must be controlled Edward Burnett Taylor ◦ “everything is inhabited by a spirit” Religion is interaction between human and spirit Many spirits but few gods Worship is control of unique spirits Animism Ghost Theory – the idea that religion originated by seeing spirits/ghosts in a dream state, thus the people’s spirit still exists Herbert Spencer ◦ People are confused by Real and Dreams You see dead people in dreams ◦ Ghosts must be alleviated Leads to ancestor worship ◦ Therefore, we are surrounded Ghost Theory Totemism – religion originated by means of communities needing to control their worlds and sacrificing to the group’s icon/mascot W. Robertson Smith ◦ Religion begins with sacred animal ◦ In times of need, sacrifice the animal Origin of sacrifice system ◦ Tribes have different animals as unifying Totemism Indigenous - originating locally ◦ Traditional, aboriginal, tribal, primal, native, oral, non-literate Common Features ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Oral/Spoken Religion Connection to the Land Life and Sacred Connected Time is a Circle Seasonal and Generational Cycles Taboo – a rule that forbids a specific behavior Indigenous Religions Relationship to Spirits ◦ Presence of Supreme Being ◦ Unseen Powers (human-like, nature, ancestors) Kinship to Creation ◦ Everything has spirit ◦ Earth as Mother (land is sacred) ◦ All creatures are kin (brother bear…) Indigenous Religions Relationship with Power ◦ Sacred Sites Places have higher concentration of power ◦ Sacred Objects Power built through sacred practices Ritual objects retain power ◦ Women= mysterious and dangerous Indigenous Religions Spiritual Specialists ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Storyteller - maintain oral tradition Instrumentalist - communication with spirits Sacred Dancers - make unseen visible (hula) Shaman - heals phys/psych/spirit problems Techniques: herbs, sweat bath, massage Divination – the act of determining the past, present, and future will of the god(s) Prayer, and chanting Altered Consciousness (drum, sing, drink, drugs, etc.) Indigenous Religions Group Rituals ◦ Rites of Passage (birth, manhood, womanhood, etc.) ◦ Rituals of Survival (hunting, feasting, etc.) ◦ Rituals of Purification (marriage, errors, etc.) Individual Rituals ◦ Seek Visions ◦ Vision Quest Indigenous Religions