Chapter 10: Quality Management Systems
advertisement

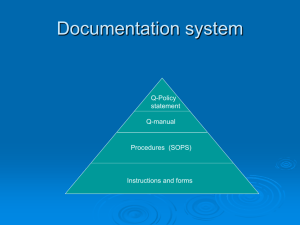
Chapter 10: Quality Management Systems Jennifer Sadorus Heather Heller What’s ISO? International Organization for Standardization Provide international standards for products and services Facilitates services worldwide exchange of goods and What We Need to Know 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Basics of ISO Benefits Requirements Documentation Procedures How to Implement ISO How to do an Internal Audit How to Register Getting to Know ISO Found in 1946 – Geneva, Switzerland 90 Member Countries ANSI – USA Representative ISO Technical Committee (TC) 176 Developed the International Standards for Quality in 1987 ISO 9000, 9001 & 9004 Benefits of ISO Registration Global competitiveness Maintain or increase market shares Secondary benefits for the supplier Decrease in scrap, rework and nonconformities at final inspection Increase in product reliability Improved time to market, on-time delivery and throughput Decrease in the cost of poor quality measured but external forces Requirements Scope Normative References Terms and Definitions Quality Management System (QMS) Management Responsibilities Resource Management Product or Service Realization Measurement, Analysis and Improvement 1st Three Requirements INFORMATION ONLY Scope Normative Reference Terms and Definitions Requirements Activity The Other 5 Requirements 5 - MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY 6 - RESOURCE MANAGEMENT 4 - QMS COUNTINUAL IMPROVEMENT 8 - MEASUREMENT, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT CUSTOMER SATISFACTION INPUT REQUIREMENTS 7 - PRODUCT REALIZATION OUTPUT PRODUCT MODEL OF A PROCESS-BASED QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 4 – Quality Management System (QMS) Identify the process Determine the process sequence Set methods for effective operation and control of process Ensure availability of resources and information for the process Monitor, measure and analyze the process Continually improve the process Document Quality policies, manuals, procedures… Set controls for documents and maintain records of conformance 5 – Management Responsibility Commitment Customer Focus Quality Policy Planning – Quality Objectives and QMS Define Responsibilities, Authorities and Communication Review 6 – Resource Management Provision of Resources Human Resources Infrastructure Work Environment 7 – Product Realization Plan Customer Related Design and Develop Purchasing Production and Service Provision Control of Monitoring and Measuring Devices 8 – Measure, Analyze and Improve Monitor and Measure Control of Nonconforming Product Analysis of Data Improvement Documentation Activity Form 4 Groups of 3 Documentation POLICY PROCEDURE WORK INSTRUCTIONS OR PRACTICES RECORDS OR PROOF BREAK! Implementation Top Management Commitment Appoint the Management Representative Awareness Appoint an Implementation Team Training Time Schedule Select Element Owners Review the Present System Write the Documentation Install the New System Internal Audit Management Review Pre-Assessment Registration Implementation Activity Internal Audits Objectives Does actual performance conform to documented QMS? Initiate corrective action to deficiencies Follow up on noncompliance items from previous audits Provide continued improvement through feedback Encourage possible improvements by thinking about the system How To Do An Internal Audit Auditor Techniques Trained in auditing principles and procedures Objective, honest and impartial Good communicator, listener and observer Examination of documents Observation of activities Interviews Procedure Pre-Audit Meeting Audit Timetables, what is being audited, review requirements Determine how well the system has been implemented and maintained Closing Meeting Present a summary including nonconformities, corrective action and decide on follow-up Audit Activity Form 2 Groups Two Ways to be ISO Certified 2-Party System Customer audits the supplier’s quality system 3-Party System Registrar audits and certifies a supplier’s quality system Registration Select a Registrar Qualifications and experience Certificate recognition Registration process Time and cost constraints Auditor qualifications Registration Process Application for Registration Document Review Pre-Assessment Assessment Registration Follow-up Surveillance What We Now Know 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Basics of ISO Benefits Requirements Documentation Procedures How to Implement ISO How to do an Internal Audit How to Register Resources ISO Homepage http://www.iso.org/iso/home.htm ISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group: Non Conformity handout www.iso.org/tc176/iso9001auditingpracticesgroup Common Sense Consulting: Process Assessment and Audit Worksheet http://www.schnauber.com/free-stuff.html National Food Service Management Institute: United States Department of Agriculture http://sop.nfsmi.org/HACCPBasedSOPs.php