Confucianism, Classical Greek Philosophy

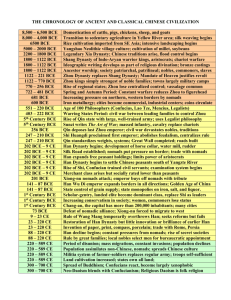
Axial (Spiritual Age) 6 th -4 th century BCE
Influential Thinkers
• Buddha
• Mahavira
• Confucius
• Laozi ?
• Socrates
• Aristotle
• Plato & other Greeks
New Religions/
Philosophical Systems
• Buddhism
• Confucianism
• Daoism
• Greek Philosophy
Zhou Dynasty & Confucianism
I. Dynasties in Chinese History
II. Zhou Dynasty
III. Confucianism
IDs: Mandate of Heaven, Duke of Zhou,
Confucius (Kong-fu-zi), d. 479 BCE, Confucian reciprocity, filial piety
Argument
Zhou Dynasty ideals and the philosophy of
Confucianism initiated the political, social and familial ideology that dominated Chinese government and society until the early 20 th century.
I. Dynasties in Chinese History
A. Unity of China under dynasty by 1100 BCE
B. Dynasties as Gov’ts & Periods in
Chinese History
Shang Dynasty (1600-1050
BCE)
Zhou Dynasty (1050-256
BCE)
Qin Dynasty (256-206
BCE)
Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220
CE)
Sui Dynasty (581-618 CE)
Tang Dynasty (618-906 CE)
Song Dynasty (960-1279)
Yuan Dynasty (1279-1368)
Ming (1368-1644)
Qing (1644-1911)
C. Shang Dynasty (ca. 1600-1050 BCE)
Union of kings & priests (diviners) in state
Religious ideas
• Ancestor worship
• Di (High God, founding ancestor of Shang family)
• Divination by oracle bones
II. Zhou Dynasty (1027 – 256 BCE)
A. Composition of 4 of 5
Chinese
Classical Texts
B. Governing Ideals
1. Mandate of Heaven
Di = Heaven
King Wen
King Wu
Mandate of Heaven
& the
Dynastic
Cycle
2. Virtuous Rulers and Ministers as
Models
• King Wu
• Duke of Zhou
• Regent
• Family
• Social order
• Strong son preference
3. Values
4. Warring States Period* (770-221
BCE)
Breakdown of unity
Lots of small states
War & anarchy
(*actually it’s divided into Eastern Zhou
Dynasty period, Spring and Autumn Period, and Warring States
Period)
Hundred Masters or Hundred Schools of Thought
Confucius
(Confucianism)
Laozi (Daoism)
III. Confucianism
Confucius (Kong-fu-zi),
551-479 BCE
The Analects
A. Ideology of Confucianism
1. Hierarchy in Human
Relationships leads to social order
a. Hierarchical Pairs
1. father-son
2. ruler-minister
3. husband-wife
4. friend-friend
5. older brother-younger brother
b. Reciprocity
• treat those above with respect
• treat those below with benevolence
2. Achieving Proper Behavior
Rectification of Names
b. Filial piety
c. ritual
• Ancestors
• “Heaven”
B. Impact of Confucianism
1. A philosophy rather than a religion
2. Subordination of
Individual to Family
3. Reshaping of Elites as Gentlemen
Officials
Gov’t service: highest status
Emphasis on education
Training in virtue
4. Virtue & Reciprocity in Gov’t.
Do not seek profit
Support agriculture
Protect common people
Argument
Zhou Dynasty ideals and the philosophy of
Confucianism initiated the political, social and familial ideology that dominated Chinese government and society until the early 20 th century.