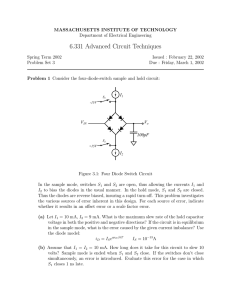
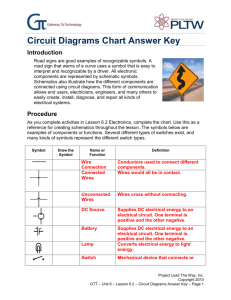
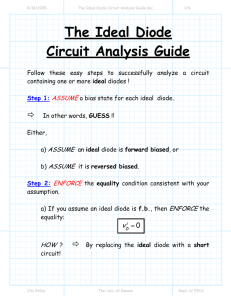
The ideal diode
advertisement

EE3+MP5: Analog elektronik Forelæser: Stig Munk-Nielsen Email: smn@et.aau.dk Lokale: Fib. 16/1.108 Litteratur: Microelectronic CIRCUITS, 6’th edition, Sedra/Smith, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-973851-9 or secondary (Microelectronic CIRCUITS, 5’th edition, Sedra/Smith, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-514252-7) 1 2 3 The ideal diode a) diode circuit symbol; b) i–v characteristic 4 The ideal diode c) equivalent circuit in the reverse direction d) equivalent circuit in the forward direction 5 The two modes of operation of ideal diodes a) An external circuit limit the forward current b) the reverse voltage 6 Circuit A Circuit B Is this circuit linear ? 7 Circuit B Circuit A 8 9 10 Figure 3.4 Circuit and waveforms for Example 3.1. 11 (a) OR gate; (b) AND gate (in a positive-logic system). 12 13 14 15 Figure 3.7 The i–v characteristic of a silicon junction diode. 16 Figure 3.8 The diode i–v relationship with some scales expanded and others compressed in order to reveal details. 17 18 Negative temperature coefficient – a problem ? 19 20 21