Incremental Extra Homework Solution
advertisement
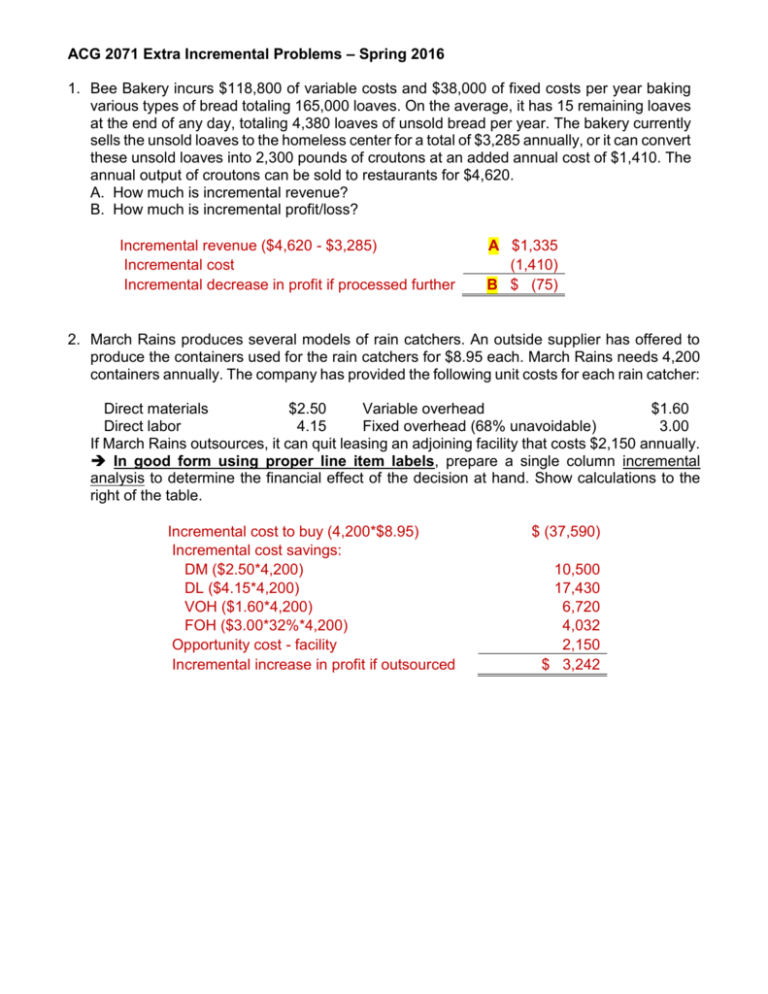
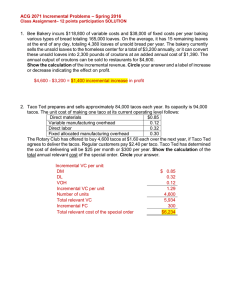
ACG 2071 Extra Incremental Problems – Spring 2016 1. Bee Bakery incurs $118,800 of variable costs and $38,000 of fixed costs per year baking various types of bread totaling 165,000 loaves. On the average, it has 15 remaining loaves at the end of any day, totaling 4,380 loaves of unsold bread per year. The bakery currently sells the unsold loaves to the homeless center for a total of $3,285 annually, or it can convert these unsold loaves into 2,300 pounds of croutons at an added annual cost of $1,410. The annual output of croutons can be sold to restaurants for $4,620. A. How much is incremental revenue? B. How much is incremental profit/loss? Incremental revenue ($4,620 - $3,285) Incremental cost Incremental decrease in profit if processed further A $1,335 (1,410) B $ (75) 2. March Rains produces several models of rain catchers. An outside supplier has offered to produce the containers used for the rain catchers for $8.95 each. March Rains needs 4,200 containers annually. The company has provided the following unit costs for each rain catcher: Direct materials $2.50 Variable overhead $1.60 Direct labor 4.15 Fixed overhead (68% unavoidable) 3.00 If March Rains outsources, it can quit leasing an adjoining facility that costs $2,150 annually. In good form using proper line item labels, prepare a single column incremental analysis to determine the financial effect of the decision at hand. Show calculations to the right of the table. Incremental cost to buy (4,200*$8.95) Incremental cost savings: DM ($2.50*4,200) DL ($4.15*4,200) VOH ($1.60*4,200) FOH ($3.00*32%*4,200) Opportunity cost - facility Incremental increase in profit if outsourced $ (37,590) 10,500 17,430 6,720 4,032 2,150 $ 3,242 3. Taco Ted prepares and sells approximately 86,000 tacos each year. Its capacity is 92,000 tacos. The unit cost of making one taco at its current operating level follows: Direct materials Variable manufacturing overhead Direct labor Fixed allocated manufacturing overhead $1.05 0.15 0.45 0.32 The Rotary Club has offered to buy 3,600 tacos at $1.75 each over the next year, if Taco Ted agrees to deliver 300 tacos to each of its monthly meetings for a year. Regular customers pay $2.40 per taco. Taco Ted has determined the cost of delivering will be $39 per month or $468 per year. Show the calculation of the total relevant cost of the special order. Circle your answer. DM ($1.05*3,600) DL ($0.45*3,600) VOH ($0.15*3,600) Delivery cost Incremental cost per unit $3,780 1,620 540 468 $6,408 4. Walkers has three product lines in its retail stores: shoes, boots, and sandals. The allocated fixed costs are based on units sold and are unavoidable. Results of June follow: Units sold Socks 800 Boots 1,200 Sandals 2,400 Total 4,400 Revenue $23,800 $30,400 $36,600 $90,800 Variable costs 13,600 13,200 16,800 43,600 Direct fixed costs 5,000 7,000 6,500 18,500 Allocated fixed costs 8,000 9,000 8,000 25,000 Net income (loss) $(2,800) $1,200 $ 5,300 $3,700 Demand of sandals is expected to increase by 12% as a result of dropping socks. In good form, prepare a single column incremental analysis of dropping socks. Label each line item respectively. Incremental revenue -socks Incremental VC savings - socks Incremental DFC savings - socks Incremental revenue -sandals (12%*36,600) Incremental VC - sandals (12%*16,800) Incremental decrease in profit if socks are dropped $ $ (23,800) 13,600 5,000 4,392 (2,016) (2,824)