Power Point: Short Run Costs
advertisement

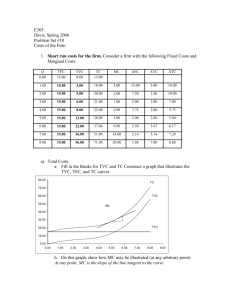
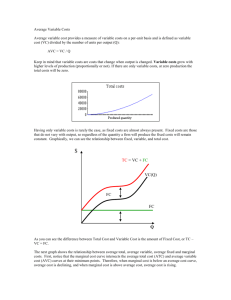
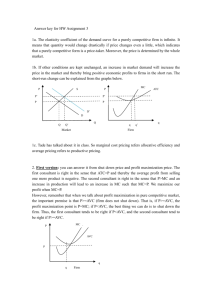
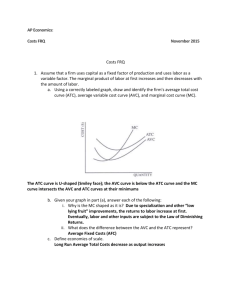
1 Interest Payments 8 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 VC MC 0 50 10.00 100 5.00 150 3.33 200 2.50 250 2.94 300 3.33 350 3.85 400 4.17 450 5.00 500 6.25 550 8.33 600 10.00 MC Increases MP MP decreases Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP Increases L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 MC Decreases From MP to MC MP 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 MP decreases Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP Increases L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 VC 0 1 50 worker10.00 = $50 2100 workers5.00 = $100 3150 workers3.33 = $150 200 2.50 250 2.94 300 3.33 350 3.85 400 4.17 450 5.00 500 6.25 550 8.33 600 10.00 Wage =$50/day MC Increases From MP to MC MC Decreases Assume that labor is the MC ONLY variable cost 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 VC MC 0 50 10.00 100 5.00 150 3.33 200 2.50 250 2.94 300 3.33 350 3.85 400 4.17 450 5.00 500 6.25 550 8.33 600 10.00 MC Increases MP MP decreases Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP Increases L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 MC Decreases From MP to MC Marginal Cost 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 $50 $50 Wage VC 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 MC $50/5=$10 10.00 5.00 $50/10=$5 $50/15=$3.3 3.33 $50/20=$2.5 2.50 $50/17=$2.9 2.94 3.33 $50/15=$3.3 $50/13=$3.8 3.85 MC Increases MP MP decreases Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP Increases L 0 5units 1 10units 2 MP 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 MC = DVC/DQ 4.17 5.00 6.25= wage/MP MC 8.33 10.00 L Q MP Wage0is the 0same 1 5MP 5 Increasing 2 15 10 3 30 15 4 50 20 5 67 17 6 82 15 7 95 13 8 107 12 9 117 10 10 125 8 Wage11is the131 same 6 Decreasing MP 5 12 136 VC MC MC= wage/MP 0 50 10.00 100 5.00 =Decreasing 150 3.33 MC 200 2.50 250 2.94 300 3.33 350 3.85 400 4.17 =Increasing 450 5.00 MC 500 6.25 550 8.33 600 10.00 MC Increases MP decreases MC Decreases MC = DVC/DQ MP Increases From MP to MC 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 VC MC 0 50 10.00 100 5.00 150 3.33 200 2.50 250 2.94 300 3.33 350 3.85 400 4.17 450 5.00 500 6.25 550 8.33 600 10.00 MC Increases MP MP decreases Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP Increases L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 MC Decreases From MP to MC MP Diminishing Returns to Labor When the MPset is at in its Maximum MC Labor L0 MP MC Diminishing Returns to Labor The MC is setatinits Minimum Q0 Units of Output From VC to TC: add FC L Q MP VC MC FC TC MC 50,000 50,000 0 0 0 1 5 5 50 10.00 50,000 10.00 2 15 10 100 5.00 50,000 5.00 3 30 15 150 3.33 50,000 3.33 4 50 20 200 2.50 50,000 2.50 5 Total 67 cost 17 of250 2.94 2.94 6 producing 82 15 zero 300 3.33 3.33 TC = FC + VC units = 50,000 7 95 13 350 3.85 3.85 50,000 = FC + VC 8 107 12 400 4.17 4.17 50,000 = FC +0 cost of 9 Variable 117 10 450 5.00 5.00 FC = 50,000 10 producing 125 8 zero 500 6.25 6.25 11 131 8.33 units 6= 0 550 8.33 12 136 5 600 10.00 10.00 17 Marginal Cost Cost of “the last” unit produced. – When one more unit is produced, the fixed cost does not change. – Is the cost of labor, raw materials and other variable expenses incurred when producing an additional unit. 18 Marginal Cost Formula MC = DTC/DQ D FC = 0 MC = (DFC + DVC) /DQ MC = rise/run MC is the slope of both the MC = slope and theDTC slope= of the when VC TC Because DVC one more unit is produced, we can also write: MC = DVC/DQ TC and VC have the additional exact sameVariable slope Marginal cost is the TCof and VC have the same Cost producing oneexact more unitshape L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Q MP VC MC FC TC 0 0 50,000 50,000 5 5 50 10.00 50,000 50,050 15 10 100 5.00 50,000 50,100 30 15 150 3.33 50,000 50,150 50 20 200 2.50 50,000 50,200 67 17 250 2.94 50,000 50,250 82 15 300 3.33 50,000 50,300 95 13 350 3.85 50,000 50,350 107 12 400 4.17 50,000 50,400 117 10 450 5.00 50,000 50,450 125 8 Total Cost =500 6.25 50,000 50,500 131 6 Fixed Cost +550 8.33 50,000 50,550 136 5 600 10.00 50,000 50,600 Variable Cost MC 10.00 5.00 3.33 2.50 2.94 3.33 3.85 4.17 5.00 6.25 8.33 10.00 20 L Q MP 0 0 1 5 5 2 15 10 3 30 15 4 50 20 5 67 17 6 82 15 7 95 13 8 107 12 9 117 10 10 125Cost8= Total 11 131 Fixed Cost6+ 12 136 5 Variable Cost VC MC FC TC 0 50,000 50,000 50 10.00 50,000 50,050 100 5.00 50,000 50,100 150 3.33 50,000 50,150 200 2.50 50,000 50,200 250 2.94 50,000 50,250 300 3.33 50,000 50,300 350 3.85 50,000 50,350 400 4.17 50,000 50,400 450 5.00 50,000 50,450 500 6.25 50,000 50,500 550 8.33 50,000 50,550 600 10.00 50,000 50,600 21 L Q MP VC MC FC TC MC 0 0 0 50000 50000 DQ D VC DTC 50050 1 5 5 50 50000 50 102 50 50100 5.00 15 10 100 5.00 50000 3 30 15 150 50000 50150 4 50 20 200 50000 50200 5MC can 67be 17 250 50000 50250 6calculated 82 15 300 50000 50300 =DVC/DQ 50000 50350 7 95VC 13 MC 350 using the 8or the107 12 400 50000 50400 TC MC =DTC/DQ 9 117 10 450 50000 50450 10 125 8 500 50000 50500 DQ D VC D TC 50550 11 131 6 550 50000 50 512 50 50600 10.00 136 5 600 10.00 50000 MC =DVC/DQ L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Q 0 5 15 30 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 MP 5 10 15 20 17 15 13 12 10 8 6 5 VC 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 MC 10.00 5.00 3.33 2.50 2.94 3.33 3.85 4.17 5.00 6.25 8.33 10.00 MC =DTC/DQ FC 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 50000 TC 50000 50050 50100 50150 50200 50250 50300 50350 50400 50450 50500 50550 50600 MC 10.00 5.00 3.33 2.50 2.94 3.33 3.85 4.17 5.00 6.25 8.33 10.00 Marginal Cost Tells you how the Variable cost changes as more output is produced MC =DVC/DQ It is the slope of the Variable Cost 24 Variable Cost MC MC 10 5 3.3 2.5 2.9 3.3 3.8 4.2 5 6.3 8.3 10 Slope Increase Output VC VC 0 0 50 50 100 100 150 150 200 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 Slope Decrease Starts at the Origin Q Q 0 0 5 5 15 15 30 30 50 50 67 82 95 107 117 125 131 136 Determine whether each of the following cost items, or categories would most likely be a fixed cost (FC) or a variable cost (VC). 1. Labor 2. Raw materials 3. Rent for building and land 4. Advertising 5. Sales commissions 6. Shipping costs to retail outlets 7. Research and development 8. Interest expense on loans 9. Fire and theft insurance 10. Owner's required annual profit of $75,000 26 Determine whether each of the following cost items, or categories would most likely be a fixed cost (FC) or a variable cost (VC). 1. Labor VC or FC 2. Raw materials VC 3. Rent for building and land FC 4. Advertising FC 5. Sales commissions FC 6. Shipping costs to retail outlets VC 7. Research and development FC 8. Interest expense on loans FC 9. Fire and theft insurance FC 10. Owner's required annual profit of $75,000 FC 27 MC Starts at FC FC Starts at the Origin Output ATC = AVC + AFC 29 ATC =29 20 AFC =20 AVC ATC = 19 19 15 9 ATC ATC AVC =9 AVC = 15 AFC AVC 4 AFC = 4 AFC Q=2 Q=10 39 AVC, AFC, ATC 29 ATC AVC AFC 19 Distance between AFC the ATC and AVC = AFC 15 9 AFC Q=2 AFC Q=10 The Relationship between Average and Marginal costs If MC > Average Cost, the Average Cost AVC or ATC increase. AVC or ATC If MC < Average Cost, the Average Cost decrease. AVC or ATC If MC = Average Cost, the Average Cost does not increase or decrease: it is maximum. 41 ATC MC AVC MC = ATC, ATC minimum MC = AVC, AVC minimum Q MP is max MP, AP MC, AC AP is max MP AP MC AVC L AVC is min MC is min Q MC cuts the ATC and the AVC at their MINIMUM points ATC MC AVC Min ATC Min AVC Min MC: Diminishing returns to labor set in Reach Minimum at different Output levels 44 From Average Costs to Total Costs ATC = TC/Q AVC = VC/Q AFC = FC/Q Rearrange as TC =ATC x Q VC = AVC x Q FC = AFC x Q Per unit Costs ATC Cost of producing the LAST unit MC AVC MC ATC AVC ATC x Q = TC FC AVC x Q = VC TC VC AFC x Q = FC Q AFC =ATC - AVC 46 Cost of producing the120th unit 20 FC = 120*(20-10) ATC = 20 10 TC = 120*20 AFC=20 -10= 10 AVC = 10 VC = 120*10 120 For Q = 120 44 40 24 20 FC = 300*(24-20) VC = 300*20 10 50 120 TC = 300*24 300 For Q = 300 48 44 40 24 20 10 10 50 120 300 49 Use the graph in the next slide to calculate for Q = 50, Q = 120, Q = 300 1. Variable Cost 2. Total Cost 3. Average Variable Cost 4. Average Total Cost 5. Marginal Cost of the last unit 6. Fixed Cost. 7. Average Fixed Cost 50 FC= TC = TR = Q = 100 VC = AFC= ATC = AVC = MC ATC AVC 10 8 6 20 50 100 150 170 51 Calculate for Q =20,000 1. Variable Cost 2. Total Cost 3. Average Variable Cost 4. Average Total Cost 5. Fixed Cost. 6. Average Fixed Cost 12,000 11,000 10,000 ? 10,000 20,000 52 ATC = TC/Q ATC = 12,000/20,000 ATC = 0.6 TC VC 12,000 11,000 10,000 ? FC = 2,000 AFC = FC/Q AFC = 2,000/20,000 AFC = 0.1 VC = 10,000 TC = 12,000 AVC = VC/Q AVC = 10,000/20,000 AVC = 0.5 10,000 20,000 53 12,000 11,000 10,000 ? Calculate for Q =10,000 1. Variable Cost 2. Total Cost 3. Average Variable Cost 4. Average Total Cost 5. Fixed Cost. 6. Average Fixed Cost 10,000 20,000 54 12,000 ATC = TC/Q ATC = 11,000/10,000 ATC = 1.1 11,000 10,000 FC = 2,000 AVC = VC/Q AVC = 9,000/10,000 AVC = 0.9 AFC = FC/Q AFC = 2,000/10,000 AFC = 0.2 ? VC = 9,000 TC = 11,000 10,000 20,000 55