What is a Computer Network?
advertisement
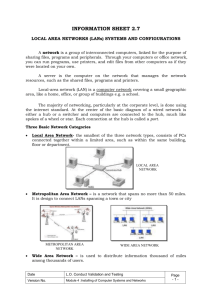
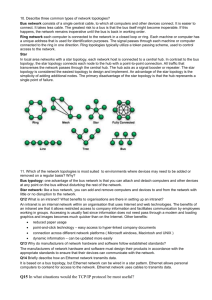
What is a Computer Network? • A computer network is a linked set of computer systems capable of sharing computer power and resources such as printers, large disk drives, CD-ROM and other databases. • There are two types of network: Local Area Network (LAN) Wide Area Network (WAN) Slide 1 Local Area Networks • A local area network is a computer network across one building or site. Printer Work Station Fileserver Network Cable Slide 2 Peer to Peer Network • This describes a very simple network structure where shared resources such as printers are available but where there are very few other facilities. • All computers on the network have similar specification and status. Slide 3 Client-Server Network • This method of network organisation requires one or more servers to which a number of clients may obtain services. • The servers act as central resource managers for the network. • A star topology is often used for this form of network. Slide 4 Network Hardware • Network hardware will include: stations servers • file, print, web passive components • cables, connections, etc active components • repeaters, hubs, switches Slide 5 Network Stations • The network station (often called the client) will normally comprise: PC Network interface card (NIC). • The NIC allows the computer to communicate with the network Network Operating Systems • eg. Windows 95/98, Windows NT, Appleshare, etc Slide 6 Network Servers • A network server is a computer which acts as a central storage point for files and applications. • Servers also act as a connection point to shared peripherals such as printers. Slide 7 Active Components • Active components are required for all but the simplest of networks. • These include: repeaters hubs switches Slide 8 Repeaters • Due to loss of signal strength it is often necessary to use a repeater to boost the signal. • A repeater is a hardware device to link together two cable segments. • The repeater amplifies the signal it receives before passing it on. Slide 9 Hubs • A hub is a device which allows the interconnection of a group of users. A hub will forward any packet of data it receives over one port from one station to all of the remaining ports. • Hubs are used in the star topology. Slide 10 Switches • A switch is “smarter” than a hub and offers more bandwidth. A switch forwards data packets only to the appropriate port for the intended recipient.The switch establishes a temporary connection between the source and the destination. Slide 11 Routers • A router receives packets of data transmitted over a network, and using their IP address, forwards them to the correct destinations over the most efficient available path. Slide 12 Network Topologies • The network topology is the theoretical arrangement of components on a network. • There are four network topologies which you need to be aware of: bus star Ring mesh Slide 13 Bus Topology • Each device is connected to a main communications line called a bus. Slide 14 Star Topology • In the star topology all stations are connected to a central node, called a hub. Slide 15 Ring Topology • Each device is connected to a ring around which signals are sent. The devices are connected to the ring via spurs, or the connection may pass through the interface card Slide 16 Mesh Topology • A mesh network is the most expensive type of network to install Slide 17 Protocols • A protocol is a standard set of rules used to ensure the proper transfer of data between devices. • In network design it is vital that a recognised protocol is used. Slide 18 TCP/IP • TCP/IP is a protocol which allows computer on different networks to communicate. • TCP/IP is a pair of protocols TCP - transmission control protocol IP Internet Protocol Slide 19 IP Addressing • Every computer station on the internetwork must have an IP address. • This IP address must be unique but is not encoded in the network interface. It is set by software in the computer. Slide 20 Internetwork Hardware • Connecting LANs together will require extra hardware: bridges routers gateways Slide 21 Bridges • A bridge acts as a link between LANs. • This will allow two LANs to appear to users as though they are a single LAN. Slide 22 Routers • A router is a device which receives data packets and sends them on via an appropriate route. • It will have a number of network interface ports to allow connection to different segments to which data packets may be directed. Slide 23 Gateways • A gateway is a link between two dissimilar networks.. • The communications between the networks are usually via public telecommunications networks. • A gateway will normally be used to connect a LAN to the Internet. Slide 24 Implications of Networks • Computer networks have developed as a result of a perceived need and as a result of economic and technical factors. • Computer networks have social, legal and ethical implications Slide 25 Economic Factors • The cost of communication technology equipment costs are continually reducing and improving features mean that more is available for the same money. • Access to expensive equipment printers and mass storage are expensive so it makes sense to share them. • Geographic spread of organsiations video-conferencing and email, etc allow organisations to cope with geographic Slide 26 isolation. Technical Factors • Adoption of Internet technology TCP/IP • Adoption of International Standards ISO OSI • Development of Communication Technology fast modems, ISDN, etc Slide 27 Social Implications • Individuals may become withdrawn from society • Personal privacy may be compromised as a result of monitoring network use • People may not have to move from rural communities to find • Home working may allow strengthening of family life (?) Slide 28 Ethical Implications • Bogus doctors could easily offer medical advice over the Internet. • Availability of unacceptable and inappropriate material within education • Antisocial, criminal, racist or other prejudiced material may be distributed freely. Slide 29 Legal Implications • Copyright law British law makes it illegal to copy someone elses copyright material. A lot of material on web pages is copyright Sometimes the breaking of this law is unwitting but in others it is deliberate (eg MP3 files of commercial recordings) Slide 30