Lecture Presentation to accompany Investment Analysis & Portfolio
advertisement

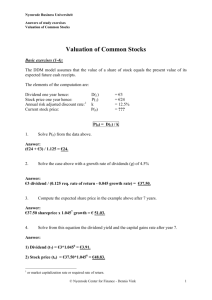
Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation Questions to be answered: • Why is it important to differentiate between company analysis and stock valuation? • What is the difference between a growth company and a growth stock? • How do we apply the two valuation approaches and the several valuation techniques to Walgreens? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • What techniques are useful when estimating the inputs to alternative valuation models? • What techniques aid estimating company sales? • How do we estimate the profit margins and earnings per share for a company? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • What factors are considered when estimating the earnings multiplier for a firm? • What two specific competitive strategies can a firm use to cope with the competitive environment in its industry? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • In addition to the earnings multiplier, what are some other relative valuation ratios? • How do you apply the several present value of cash models to the valuation of a company? • What value-added measures are available to evaluate the performance of a firm? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • How do we compute economic value-added (EVA), market value-added (MVA), and the franchise value for a firm? • What is the relationship between these value-added measures and changes in the market value of firms? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • When should we consider selling a stock? • What is meant by a true growth company? • What is the relationship between positive EVA and a growth company? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • Why is it inappropriate to use the standard dividend discount model to value a true growth company? • What is the difference between no growth, simple growth, and dynamic growth? • What is the growth duration model and what information does it provide when analyzing a true growth company and evaluating its stock? Chapter 14 - Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • How can you use the growth duration model to derive an estimate of the P/E for a growth company? • What are some additional factors that should be considered when analyzing a company on a global basis? Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • After analyzing the economy and stock markets for several countries, you have decided to invest some portion of your portfolio in common stocks • After analyzing various industries, you have identified those industries that appear to offer above-average risk-adjusted performance over your investment horizon • Which are the best companies? • Are they overpriced? Company Analysis and Stock Valuation • Good companies are not necessarily good investments • Compare the intrinsic value of a stock to its market value • Stock of a great company may be overpriced • Stock of a growth company may not be growth stock Growth Companies • Growth companies have historically been defined as companies that consistently experience above-average increases in sales and earnings • Financial theorists define a growth company as one with management and opportunities that yield rates of return greater than the firm’s required rate of return Growth Stocks • Growth stocks are not necessarily shares in growth companies • A growth stock has a higher rate of return than other stocks with similar risk • Superior risk-adjusted rate of return occurs because of market undervaluation compared to other stocks Defensive Companies and Stocks • Defensive companies’ future earnings are more likely to withstand an economic downturn • Low business risk • Not excessive financial risk • Stocks with low or negative systematic risk Cyclical Companies and Stocks • Cyclical companies are those whose sales and earnings will be heavily influenced by aggregate business activity • Cyclical stocks are those that will experience changes in their rates of return greater than changes in overall market rates of return Speculative Companies and Stocks • Speculative companies are those whose assets involve great risk but those that also have a possibility of great gain • Speculative stocks possess a high probability of low or negative rates of return and a low probability of normal or high rates of return Value versus Growth Investing • Growth stocks will have positive earnings surprises and above-average risk adjusted rates of return because the stocks are undervalued • Value stocks appear to be undervalued for reasons besides earnings growth potential • Value stocks usually have low P/E ratio or low ratios of price to book value Economic, Industry, and Structural Links to Company Analysis • Company analysis is the final step in the topdown approach to investing • Macroeconomic analysis identifies industries expected to offer attractive returns in the expected future environment • Analysis of firms in selected industries concentrates on a stock’s intrinsic value based on growth and risk Economic and Industry Influences • If trends are favorable for an industry, the company analysis should focus on firms in that industry that are positioned to benefit from the economic trends • Firms with sales or earnings particularly sensitive to macroeconomic variables should also be considered • Research analysts need to be familiar with the cash flow and risk of the firms Structural Influences • Social trends, technology, political, and regulatory influences can have significant influence on firms • Early stages in an industry’s life cycle see changes in technology which followers may imitate and benefit from • Politics and regulatory events can create opportunities even when economic influences are weak Company Analysis • • • • Industry competitive environment SWOT analysis Present value of cash flows Relative valuation ratio techniques Competitive Forces • • • • • Current rivalry Threat of new entrants Potential substitutes Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of buyers Firm Competitive Strategies • Defensive strategy involves positioning firm so that it its capabilities provide the best means to deflect the effect of competitive forces in the industry • Offensive strategy involves using the company’s strength to affect the competitive industry forces, thus improving the firm’s relative industry position • Porter suggests two major strategies: low-cost leadership and differentiation Porter's Competitive Strategies • Low-Cost Strategy – The firm seeks to be the low-cost producer, and hence the cost leader in its industry • Differentiation Strategy – firm positions itself as unique in the industry Focusing a Strategy • Select segments in the industry • Tailor strategy to serve those specific groups • Determine which strategy a firm is pursuing and its success • Evaluate the firm’s competitive strategy over time SWOT Analysis • Examination of a firm’s: – Strengths – Weaknesses – Opportunities – Threats SWOT Analysis • Examination of a firm’s: – Strengths – Weaknesses – Opportunities – Threats INTERNAL ANALYSIS SWOT Analysis • Examination of a firm’s: – Strengths – Weaknesses – Opportunities – Threats EXTERNAL ANALYSIS Some Lessons from Peter Lynch Favorable Attributes of Firms 1. Firm’s product should not be faddish 2. Firm should have some long-run comparative advantage over its rivals 3. Firm’s industry or product has market stability 4. Firm can benefit from cost reductions 5. Firms that buy back shares show there are putting money into the firm Tenets of Warren Buffet • • • • Business Tenets Management Tenets Financial Tenets Market Tenets Business Tenets • Is the business simple and understandable? • Does the business have a consistent operating history? • Does the business have favorable long-term prospects? Management Tenets • Is management rational? • Is management candid with with its shareholders? • Does management resist the institutional imperative? Financial Tenets • Focus on return on equity, not earnings per share • Calculate “owner earnings” • Look for companies with high profit margins • For every dollar retained, make sure the company has created at least one dollar of market value Market Tenets • What is the value of the business? • Can the business be purchased at a significant discount to its fundamental intrinsic value? Estimating Intrinsic Value A. Present value of cash flows (PVCF) – 1. Present value of dividends (DDM) – 2. Present value of free cash flow to equity (FCFE) – 3. Present value of free cash flow (FCFF) B. Relative valuation techniques – – – – 1. Price earnings ratio (P/E) 2. Price cash flow ratios (P/CF) 3. Price book value ratios (P/BV) 4. Price sales ratio (P/S) Present Value of Dividends • Simplifying assumptions help in estimating present value of future dividends • Assumption of constant growth rate Intrinsic Value = D1/(k-g) D1= D0(1+g) Growth Rate Estimates • Average Dividend Growth Rate n Dn 1 D0 Growth Rate Estimates • Average Dividend Growth Rate n Dn 1 D0 • Sustainable Growth Rate = RR X ROE Required Rate of Return Estimate • Nominal risk-free interest rate • Risk premium • Market-based risk estimated from the firm’s characteristic line using regression Required Rate of Return Estimate • Nominal risk-free interest rate • Risk premium • Market-based risk estimated from the firm’s characteristic line using regression R stock E(RFR) stock [E(R market ) E(RFR)] The Present Value of Dividends Model (DDM) • Model requires k>g • With g>k, analyst must use multi-stage model Present Value of Free Cash Flow to Equity FCFE = Net Income + Depreciation Expense - Capital Expenditures - D in Working Capital - Principal Debt Repayments + New Debt Issues Present Value of Free Cash Flow to Equity FCFE = FCFE1 Value Net Income k g FCFE + Depreciation Expense - Capital Expenditures - D in Working Capital - Principal Debt Repayments + New Debt Issues Present Value of Free Cash Flow to Equity FCFE1 Value k g FCFE FCFE = the expected free cash flow in period 1 k = the required rate of return on equity for the firm gFCFE = the expected constant growth rate of free cash flow to equity for the firm Present Value of Operating Free Cash Flow Discount the firm’s operating free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) at the firm’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC) rather than its cost of equity FCFF = EBIT (1-Tax Rate) + Depreciation Expense - Capital Spending - D in Working Capital - D in other assets Present Value of Operating Free Cash Flow FCFF1 Firm Value WACC g FCFF Oper . FCF1 or WACC g OFCF Present Value of Operating Free Cash Flow FCFF1 Firm Value WACC g FCFF Oper . FCF1 or WACC g OFCF Where: FCFF1 = the free cash flow in period 1 Oper. FCF1 = the firm’s operating free cash flow in period 1 WACC = the firm’s weighted average cost of capital gFCFF = the firm’s constant infinite growth rate of free cash flow gOFCF = the constant infinite growth rate of operating free cash flow An Alternate Measure of Growth g = (RR)(ROIC) where: – RR = the average retention rate – ROIC = EBIT (1-Tax Rate)/Total Capital Calculation of WACC WACC = WEk + Wdi Calculation of WACC WACC = WEk + Wdi where: WE = the proportion of equity in total capital k = the after-tax cost of equity (from the SML) WD = the proportion of debt in total capital i = the after-tax cost of debt Relative Valuation Ratio Techniques • Price Earnings Ratio D1 / E1 P / E1 kg Estimating Company Earnings Per Share • Function of – Sales forecast – Estimated profit margin Walgreens Competitive Strategies The Internal Performance • Industry Factors • Company Performance • Net Profit Margin Estimate • Computing Earnings per Share Importance of Quarterly Estimates Estimating Company Earnings Multipliers • Macroanalysis of the Earnings Multiplier • Microanalysis of the Earnings Multiplier – – – – – Comparing Dividend-Payout Ratios Estimating the Required Rate of Return Estimating the Expected Growth Rate Computing the Earnings Multiplier Estimate of the Future Value for Walgreens Additional Measures of Relative Value • Price/Book Value Ratio • Price/Cash Flow Ratio • Price-to-Sales Ratio Analysis of Growth Companies • Generating rates of return greater than the firm’s cost of capital is considered to be temporary • Earnings higher the required rate of return are pure profits • How long can they earn these excess profits? • Is the stock properly valued? Analysis of Growth Companies • Growth companies and the DDM – constant growth model not appropriate • Alternative growth models – no growth firm E = r x Assets = Dividends E 1 b E V k k E k v Analysis of Growth Companies • Long-run growth models – assumes some earnings are reinvested • Simple growth model bEmk bEm (Gross Present Value of Growth Investment s) 2 k k bEm bE ( Net Present Value of Growth Investment s) k k E bEm bE E 1 b bEm v v k k k k k Simple Growth Model (cont.) E bEm bE v k k k D bEm v k k E 1 b bEm v k k (Present value of Constant Dividend plus the Present Value of Growth Investment) E bE m 1 (Present value of Constant Earnings plus v the Present Value of Excess Earnings k k from Growth Investment) Expansion Model • Firm retains earnings to reinvest, but receives a rate of return on its investment equal to its cost of capital m = 1 so r = k E E 1 b bE E V k k k k Negative Growth Model • Firm retains earnings, but reinvestment returns are below the firm’s cost of capital • Since growth will be positive, but slower than it should be, the value will decline when the investors discount the reinvestment stream at the cost of capital The Capital Gain Component bEm/k b Percentage of earnings retained for reinvestment m relates the firm’s rate of return on investments and the firm’s required rate of return (cost of capital) 1 = cost of capital >1 is a true growth company Time period for superior investments Dynamic True Growth Model • Firm invests a constant percentage of current earnings in projects that generate rates of return above the firm’s required rate of return D1 V kg Measures of Value-Added • Economic Value-Added (EVA) – Compare net operating profit less adjusted taxes (NOPLAT) to the firm’s total cost of capital in dollar terms, including the cost of equity • EVA return on capital EVA/Capital • Alternative measure of EVA – Compare return on capital to cost of capital Measures of Value-Added • Market Value-Added (MVA) – Measure of external performance – How the market has evaluated the firm’s performance in terms of market value of debt and market value of equity compared to the capital invested in the firm • Relationships between EVA and MVA – mixed results Measures of Value-Added • The Franchise Factor – Breaks P/E into two components • P/E based on ongoing business (base P/E) • Franchise P/E the market assigns to the expected value of new and profitable business opportunities Franchise P/E = Observed P/E - Base P/E Incremental Franchise P/E = Franchise Factor X Growth Factor Rk G rk Growth Duration Model • Evaluate the high P/E ratio by relating P/E ratio to the firm’s rate and duration of growth • P/E is function of – expected rate of growth of earnings per share – stock’s required rate of return – firm’s dividend-payout ratio Growth Duration E’(t) = E (0) (1+G)t N(t) = N(0)(1+D)t E’(t) = E’(t) N(t) = E (0) [(1+G)t (1+D)]t E(t) E (0) (1 G D) t T E g (0) (1 G g D g ) Pg (0) T Pd 0 E a (0) (1 G a D a ) Growth Duration T E g (0) (1 G g D g ) Pg (0) T Pd 0 E a (0) (1 G a D a ) T (1 G g D g ) Pg (0)/E g (0) T Pd 0 / E a (0) (1 G a D a ) Pg (0)/E g (0) (1 G g Dg ) T ln ln Pd 0 / E a (0) (1 G a Da ) Intra-Industry Analysis • Directly compare two firms in the same industry • An alternative use of T to determine a reasonable P/E ratio • Factors to consider – A major difference in the risk involved – Inaccurate growth estimates – Stock with a low P/E relative to its growth rate is undervalued – Stock with high P/E and a low growth rate is overvalued Site Visits and the Art of the Interview • Focus on management’s plans, strategies, and concerns • Restrictions on nonpublic information • “What if” questions can help gauge sensitivity of revenues, costs, and earnings • Management may indicate appropriateness of earnings estimates • Discuss the industry’s major issues • Review the planning process • Talk to more than just the top managers When to Sell • Holding a stock too long may lead to lower returns than expected • If stocks decline right after purchase, is that a further buying opportunity or an indication of incorrect analysis? • Continuously monitor key assumptions • Evaluate closely when market value approaches estimated intrinsic value • Know why you bought it and watch for that to change Influences on Analysts • Efficient Markets • Paralysis of Analysis • Analyst Conflicts of Interest Efficient Markets • Opportunities are mostly among less well-known companies • To outperform the market you must find disparities between stock values and market prices - and you must be correct • Concentrate on identifying what is wrong with the market consensus and what earning surprises may exist Analyst Conflicts of Interest • Investment bankers may push for favorable evaluations • Corporate officers may try to convince analysts • Analyst must maintain independence and have confidence in his or her analysis Global Company and Stock Analysis Factors to Consider: – Availability of Data – Differential Accounting Conventions – Currency Differences (Exchange Rate Risk) – Political (Country) Risk – Transaction Costs – Valuation Differences The Internet Investments Online http://www.better-investing.com http://www.fool.com http://www.cfonews.com http://www.zacks.com http://www.valueline.com http://iaschicago.org http://moneycentral.msn.com/investor/home.asp End of Chapter 14 –Company Analysis and Stock Selection Future topics Chapter 15 Technical Analysis • Assumptions and Advantage • Technical Trading Rules and Indicators • Techniques and Charts