ch10
advertisement

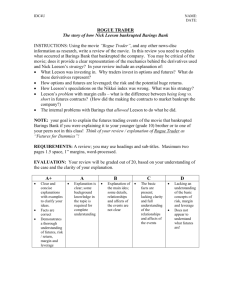
Accounting 100 Contact Details Lecturer NIT China: email: Room : Accounting 100 Accounting 100 will run as a 6 hour seminar comprising lecture and tutorial components Responsibility for learning is yours Best results are achieved by consistent work throughout the semester Accounting 100 Tutorials begin this week Attendance at the tutorial is compulsory Attempt the tutorial work each work before the tutorial session Check your answers and ask questions at the tutorial Text Books Essential Hoggett and Edwards (2003) “Accounting in Australia 5th Edition”, John Wiley & Sons Essential Hutchings G (2004) “Accounting 100 in Practice” , John Wiley & Sons Assessment Structure Mid-Semester Test Assignment One Final Exam 25% TBA 25% TBA 50% TBA You must achieve 40% or more in the exam to pass the unit What is accounting Accounting is commonly known as the language of business It is the recording, reporting and analysis of financial information and associated activities. Completion of a Curtin degree with a major in accounting qualifies for associate membership of CPA Australia (Certified Practising Accountant) or ICA (Institute of Chartered Accountants) Accounting Various types of work performed by accountants; Financial Management External Auditing Internal Auditing Taxation Liquidation/Insolvency Small Business Consultancy Law Enforcement What Accountants do Bookkeepers maintain the financial records not accountants The accountant has a supervisory role The accountant is typically involved in strategic planning and analysis An accounting background is highly regarded when competing for executive positions Career prospects in accounting Demand is extremely high for qualified accountants, particularly in Business consultancy and taxation. International opportunities. Many aspects of accounting are common throughout the world. Eg Australian CPA can convert to USA CPA Curtin double majors in accounting Accounting & Law Accounting & Taxation Accounting & Information Systems Accounting and Small Business Etc. Accounting & Finance Accounting & Banking Accounting & Accounting Technologies Accounting & Financial Planning Starting a Business Lecture Outline Options in Starting a Small Business Business Structures Common Reasons for Business Failure Getting Started The first decision you need to make is how you are going to enter the small business world. You can choose from one of three options: 1. Start your own business 2. Buy an existing business 3. Obtain a franchise Starting your own Business Benefits 1. Independence. 2. Lower Cost. 3. New start – no negative sentiment towards the business. Limitations 1. No relationship with Customers Suppliers Business may be slow for a while. 3. Problems 2. New staff New technology and equipment. Buying a Business Benefits 1. Established reputation. 2. Immediate stream of income. 3. Easier to borrow additional funds. Limitations 1. May be stuck with poor decisions made by prior owners(s). Obtain a Franchise Benefits 1. Strong Reputation. 2. Much lower risk of failure. 3. Training and support may be provided by franchise owner. 1. Limitations Lack of independence 2. 3. Must conform to franchise policies. Fees must be paid to franchise owner. Damage to reputation of franchise name. Ownership Structure Choose a form of business structure. The most common are; Sole Trader: Partnership: Company Proprietary Limited (Pty. Ltd.) Public (Ltd.) Partnership Defined The relationship between persons carrying on a business in common with a view to making a profit. Characteristics: Two or more partners Not a separate legal entity But treated as a separate accounting entity. Written or verbal Partnership Agreement Partnership Agreement A partnership agreement should contain: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Partnership Name and names of partners. Information on how profits & losses are to be shared. Conduct of the partnership affairs. Authority of each partner in contractual situations. Procedures to be followed in the event of dispute. Legal Status Partnership (Not a Separate Legal Entity) Partners/Business Company (A Separate Legal Entity) Owners Company Partnership Major Benefits 1. Easy to form 2. Minimal cost to establish 3. Limited rules and regulations Major Limitations 1. Unlimited Liability Proprietary Company Minimum – 1 Person Maximum 50 shareholders Separate legal entity Usually a family business that has been incorporated to obtain the benefits of limited liability. Starting your own Business Companies Major Benefits 1. Limited liability 2. Ability to raise more money. Major Limitations 1. Highly regulated. Introduction Rate of new business failure is extremely high. 50% of new businesses will fail in the first year, whilst 75% will fail in the first 5 years. Failure as a % of start ups. Year 1 32.3% Year 2 16.5% Year 3 10.3% Year 4 6.8% Year 5 4.5% Reasons for Business Failure Economic Environment In most cases, an economic downturn merely exposes entities which are over leveraged (ie have too much debt) or poorly managed. More businesses collapse during economic booms than during economic downturns. Reasons for Business Failure The overwhelming reason for business collapse is poor management. Lack of Internal Controls No Strategic Plan Inadequate Pricing Structures Poor Management Decisions Lack of Budgetary Control Overleveraged (Topic 1) (Topic 1) (Topic 2) (Topics 2 & 3) (Topic 4) (Topic 4) Reasons for Business Failure Lack of Internal Controls Internal Control Comprises all the methods and measures established to safeguard assets, ensure reliability of records, promote operational efficiency and encourage adherence to prescribed managerial policies. Internal Controls Examples of internal controls: Separation of duties. 2. Clearly established lines of responsibility. 3. Internal auditing. 4. Mechanical and electronic devises. 1. • Refer to pages 405-407 of “Accounting in Australia – 5th Edition”. Reasons for Business Failure Lack of Internal Controls Failure to implement and/or regulate internal control policies can be fatal. Barings Bank Barings Bank Leeson (novice trader) posted to Singapore in July 1992 Acted beyond his authority By 31/12/94 had accumulated losses of £208M through unauthorized trades Represented that he was making a profit Perceived as a “Star Performer” By 27/2/95 accumulated losses of £830M Discovered 23/2/95 – Barings Collapses Barings Bank The BOE report into the collapse stated: (a) the losses were incurred by reason of unauthorized and concealed trading by Leeson (b) the true position was not noticed earlier by reason of a serious failure of internal controls and managerial confusion within Barings; (c) the true position had not been detected prior to the collapse by the external auditors, supervisors or regulators of Barings. Barings Bank Collapse “The Bank regarded the controls in Barings as informal but effective. It had confidence in Baring's senior management, many of whom were longstanding Barings' employees.” Extract from the conclusion of the Bank Of England Report on the Collapse of Barings Reasons for Business Failure No Strategic Plan Strategic Plan Defined A blueprint for developing a business and provides a basis for measuring progress towards the achievement of goals. Consists of several basic steps: Mission Statement Objectives SWOT Analysis Reasons for Business Failure No Strategic Plan Strategic Plan Defined A blueprint for developing a business and provides a basis for measuring progress towards the achievement of goals. Consists of three basic steps: Mission Statement Objectives SWOT Analysis Strategic Plan Mission Statement The mission statement should focus on the one, possibly two, feature(s) that distinguishes your business from your competitors. It is designed to motivate employees so it should be brief so that employees are able to memorise the statement. Generic Mission Statement Our mission is to provide the highest quality product at the lowest price and to provide outstanding service within an aesthetically pleasing environment. Strategic Plan Objectives Characteristics (SMART) 1. Specific – Clear & Precise 2. Measurable 3. Achievable 4. Relevant 5. Time frame in which objectives should be achieved. Examples of Objectives Example of a SMART objective; We will increase sales of computers by 10% within 12 months. Example of an objective that is not SMART – Why?? We will increase customer satisfaction by 10%. Objectives Not SMART because; No time frame – when will it happen? Not specific or measurable – What is customer satisfaction & how would we precisely measure it at low cost? Strategic Plan SWOT Analysis Strengths & Weaknesses (Internal Analysis) Reviews the way in which a business operates. Management Style Resources What internal factors (over which a manager does have control) represent strengths and weaknesses. Curtin Business School 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Strengths ‘Curtin’ brand EQUIS accreditation Well Resourced. Diversity of double majors. Diversity of students. Weaknesses 1. Parking. 2. Absence from campus. Strategic Plan SWOT Analysis Opportunities & Threats (External Analysis) Review of external environment Market Regulation Competitors What external factors (over which your entity has no control) represent a threat or an opportunity. Strategic Plan SWOT Analysis Threats By identifying potential threats you can take action now to minimise or avoid these threats. Opportunities By identifying potential opportunities you can take action now to ensure that you profit from the opportunity. Curtin Business School Opportunities 1. China Market Threats 1. Reduction in govt. funding. 2. Online degrees from international universities. Lecture summary You should be able to now; Name and explain 3 business structures Explain the causes of business failure Explain the importance of a business plan List & define the elements of a business plan