Today*s Warm Up
advertisement

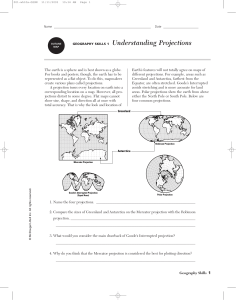
Today’s Warm Up Lines of Latitude are called _________. They run _______________ and are measured ___________. Lines of Longitude are called _________. They run _______________ and are measured ___________. Let’s Review our Homework 1. If you were going to the opening of a new amusement park, which map would you use? Why? 2. If you wanted to find out about how different counties in Texas voted on an issue, which map would you use? Why? 3. If you were planning a hike, which kinds of maps would you use? Why? This Week at a Glance Monday: 5 themes of Geography Tuesday: Maps-Continued Wednesday: Maps Thursday: Maps Friday: (Extreme Weather) Case StudyMapping Hurricane Katrina Remember! Terms: You have a vocabulary/unit snap shot at the end of this week!!! ● GIS, ● Global Position System, ● Greenwich Mean time ● International Date Line ● Latitude ● Longitude ● Map ● Map Scale ● Meridian ● Parallel ● Prime Meridian ● Projection ● Remote Sensing ● Scale ● Cartography ● Mental Map Today’s Learning Objective Today we will analyze maps for distortion using oranges, maps, and a graphic organizer. Today’s Agenda: 1. Warm-Up 2. TPO 3. Textbooks 4. Map Distortion Activity 5. Map Projections Orange World Map Instructions: You and your partner will receive a copy of a map. You must attach your world map to the ball. You may not tuck any paper under, but you may cut if you need to. Questions: What problems did you and your partner have during this activity? Warm-Up (On your Cornell Notes) Define the term distortion Thursday, September 3, 2015 AP Human Geo Warm-Up Remember! Terms: You have a vocabulary/unit snap shot at the end of this week!!! ● GIS, ● Global Position System, ● Greenwich Mean time ● International Date Line ● Latitude ● Longitude ● Map ● Map Scale ● Meridian ● Parallel ● Prime Meridian ● Projection ● Remote Sensing ● Scale ● Cartography ● Mental Map Today’s Learning Objective Today we will analyze maps for distortion using a webquest. Today’s Agenda: 1. Warm-Up 2. TPO 3. Introduction to Map Projections 4. Webquest Map Projections Map Projections ● Map Projection show the Earth (3D) on a flat (2D) surface. Map Projections ● Projecting a 3D object on a flat (2D) surface causes distortion. Map projections cause distortion in: ● ● ● ● Distance Direction Shape Area See how different South America can look depending on the map projection?! Map Projections ● There are many different map projections, and they all have different functions. Specific Types of Projections ● ● Most try to preserve at least one characteristic from being distorted (either distance, direction, shape or area). Usually, limiting distortion in one area causes more distortion in the other areas. For example… What’s wrong with this map? Web Quest ●You will be assigned a laptop. ●Using the provided websites, you will have the class period to explore each of the map projections on your handout. ●IT IS VERY IMPORTANT THAT YOU KNOW THE DISTORTIONS, ADVANTAGES, AND DISADVANTAGES FOR EACH PROJECTION!!! ●You will need to bring a completed chart to class TOMORROW!!! Closure ●Which map projection is best suited for navigation purposes? Three Main Types of Map Projections ● ● ● Cylindrical Projections Conical Projections Azimuthal Projections (flattened surface) Cylindrical Projections ● ● Show the world projected onto a cylinder, then rolled out. Good for comprehensive views of the world, but often distort the area or shape Conical Map Projections ● ● ● Show the world projected onto a cone, then rolled out. This projection significantly distorts scale, but is often true to direction Used for regional and topographical maps, not good for world maps. Azimuthal (or Planar) Projections ● ● Shows a portion of the earth projected onto a flat plane Good for polar maps, distort area in outer latitudes, less distortion in the middle (preserves shape). Mercator Map Projection ● ● ● Example of a Conical Map Projection Shows accurate direction, but distorts area. Was used as a nautical map (for people who travel by sea). Sinusoidal Projection Map ●Maintains equal area despite conformal distortion. No distortion with area, direction, and distance Peter’s Projection ● ● Cylindrical Projection Equal-area projection that de-emphasizes area exaggerations, but distorts shape Goode’s Interrupted Homolosine Projection ● ● ● ● A type of conical projection Limits area distortion “Interrupted” because it leaves out some areas and spreads others out (like Antarctica) to prevent further distortion Useful for GIS data maps and overall world maps with little disruption. Polar Projection ● ● Azimuthal (planar) projection Good for mapping the polar regions, not good for a world map. Flow Line Map Flow maps typically use lines to show the movement of people and goods between various locations. The lines are varied in width to represent the quantity of flow Mollweide Projection It is an equal-area projection designed for small-scale maps. Fuller Projection ●Maintains the accurate size and shape of landmasses ●Completely rearranges direction such that the four cardinal directions (north, south, east, and west) no longer have any meaning. Robinson Projection ●Attempts to balance several possible projection errors. ●Does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each. ●Used by National Geographic Proportional Symbols Map ●The proportional symbol technique uses symbols of different sizes to represent data associated with different areas or locations within the map. Dot Distribution/Density Map ●A dot may be used to locate each occurrence of a phenomenon. ●Where appropriate, a dot may indicate any number of entities, for example, one dot for every 100 voters. Military families in Ohio Choropleth Map ●Shows statistical data aggregated over predefined regions, such as counties or states, by coloring or shading these regions. ●For example, countries with higher rates of infant mortality might appear darker on a choropleth map. Choropleth Map Cartogram ●A cartogram is a map in which some thematic mapping variable is substituted for land area or distance. ●The geometry or space of the map is distorted in order to convey the information of this alternate variable. Cartogram Cartogram Closure! ● You run a cartography company and make customized maps for different clients. For each of the clients on your handout, determine which type of map you would create for them, and explain why that map best fits your client’s wishes. Warm-Up: Get a pencil out and prepare for you assessment. You have two minutes to study!!! Today’s Learning Objective Today we will review specific map projections and weigh their pros and cons using a gallery walk. Today’s Agenda: 1. Warm-Up: Unit Snap Shot 2. TPO 3. Gallery Walk 4. Latitude and Longitude Practice Map Projection Activity Step One: I will put you into groups of three Step Two: With you group mates, you will report to your assigned a specific map projection. Step Three: Using your notes and your blank chart, you will fill in your chart, and ADD any additional information you learned about your map projection on the poster Step Four: Once you are done, you will wait for instruction. Gallery Walk ●You will circumnavigate the room filling in the gaps from yesterday’s web quest. ●Be sure to ADD what you learned from the web quest on the poster. ●You will have two minutes at each station. ●Once you are done, you will wait for the timer to go off. Questions? Latitude and Longitude Practice You will receive a handout that will help you practice with latitude and longitude. You will turn this in either at the end of the class period or at the beginning of class tomorrow!!! Closure: Answer the following questions: ● What type of map does this image depict? ● Explain the benefits and drawbacks of this particular map projection. ● What aspects of this map is distorted?