Critical Pedagogy and the Live Client Clinic
advertisement

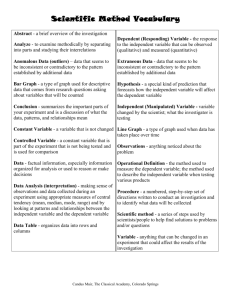
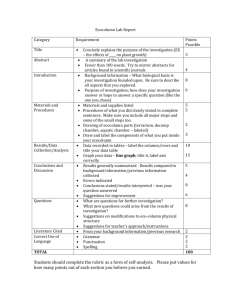
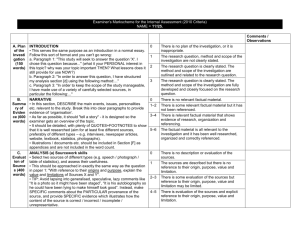
Dr. Robert Schehr Department of Criminology and Criminal Justice “Education” as an empty signifier “Education” as hegemony Apple, Bourdieu, Bowles and Gintis, MacLeod, Kennedy, Jessop, Foucault, Farber, Dewey “School is a system reproducing steering mechanism whose curriculum and teaching methods are designed to advance the interests of the status quo” (Schehr) Foucault – “Schools create docile bodies.” Farber – “Schools teach you by pushing you around, by stealing your will, by making timid square apathetic slaves out of you – authority addicts.” Difference between “learning” and “education” (Moliterno) Learning can happen anywhere Education consists of designed, managed, and guided experience ▪ Experiential education proceeds through the process of synthesis whereby students are exposed to the theory of an activity; they experience the activity; they reflect on the relationship between the theory and the experience and synthesize the two; they form a new or modified theory; they test it by experience, and so on. “a willingness to enter conversation about ideas, taking a position in openness that can still be altered given additional information; a commitment to keep relationships affirming, even as disagreements over theory occur; and a willingness to ask value questions about information application” (Arnett). Privileges learning by doing Engagement with human beings and texts. Bain – we learn best when: We are trying to solve problems we find intriguing, beautiful, or important We are able to do so in a challenging yet supportive environment in which we can feel a sense of control over our own education We can work collaboratively We believe that our work will be considered fairly and honestly We can try, fail, and receive feedback Identify and diagnose a problem Generate alternative solutions and strategies Develop a plan of action Implement a plan Identify and formulate legal issues Formulate relevant legal theories Evaluate legal theory Know the nature of legal rules and institutions Know of and have the ability to use legal research tools Determine the need for factual investigation Plan a factual investigation strategy Organize information Assess the perspective of the recipient of information Use effective communication techniques Develop in students fundamental knowledge and skill, especially academic knowledge base and research Provide students with the capacity to engage in complex practice Enable students to learn to make judgments under conditions of uncertainty Teach students how to make learn from experience Introduce students to professional community Form students able and willing to engage public service. Established in February of 2002 Actual Innocence Live Client Clinic – New Civil Rights movement Have reviewed nearly 400 cases 8 student investigators, 3 attorneys, 1 private investigator Professional development training Case review and investigation Changes to local, state and federal due process and crime scene investigation Professional Development Includes: Causes of WC Case Analysis and Briefing ARS Post-Conviction Statutes – Filing PCR Interviewing Skills (Role Play) Forensic analysis (DNA, fingerprinting, etc.) How to locate people Crime Scene Investigation Declarations and Affidavits Clemency Petitions Capital v. Non-capital strategy Recent Death Penalty Case – Donald Beaty Donald Beaty. Convicted in 1985 of rape – homicide. Presently serving time on Arizona’s death row. Case contains 3,000 pages of trial transcripts. Five NAJP students are working this case.