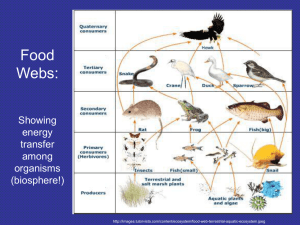
Amides
advertisement

Amides BY: Jacob Baird and Nathan Carrier Structural components -Carbonyl: Carbon pi bonded to oxygen https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/IUPAC _carbonyl_divalent_group.png Structural components continued - Nitrogen - Bonded to carbonyl - Two valence electrons for the free radicals Structural components continued - Free Radical - Any molecule or element with 1 free valence electron General Structure C- Is the base carbon O- The double bonded oxygen N- Is the nitrogen attached to the carbon R- Represents the free radicals https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2e/A mide-general.png Propanamide 3 2 1 Naming scheme • [Positions][Attachments][Family name (subtract ‘e’)][-amide (suffix)] • Ex: 2-methylpentanamide (Although double bond present not an alkene) Naming scheme continued • Positions• According to the location of the parent chain starting at carbonyl (1), or the nitrogen • Attachments onto the nitrogen are said to be at position N coming before all integers ( Not to be confused with “n”) N,N- Dimethylbutanamide 3-methylpentanamide http://chemsink.com:8080/examples/jsp/marvin/generate_ image.jsp?mol=CCCC(C)C(%3DO)N&format=png%3Aw40 0%2Ch200%2Cb32%2C%23ffffff Parent chain and naming examples http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigmaaldrich/structure9/020/mfcd00008023.eps/_jcr_content/renditio ns/mfcd00008023-medium.png Give it a try http://chemsink.com:8080/e xamples/jsp/marvin/generat e_image.jsp?mol=CCCNC(% 3DO)C(C(C)C)Br&format=p ng:w400,h200,b32,#ffffff Reaction properties • Peptide bond- A peptide bond (sometimes mistakenly called amino bond) is a covalent bond that is formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the another molecule, releasing a molecule of water. This is a a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids. The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. Via peptide guide.com http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio /enger/student/olc/art_quizzes/genb iomedia/0037.jpg Synthesis of an amide • The easiest way to make an amide is using carboxylic acids. What the reaction is using ethanoic acid and ammonium carbonate to create ammonium ethanoate, dehydrate that and you have made an amide! Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution • Hydrolysis- Is the reaction using water to break the bond or bonds of a molecule. Everyday uses • The most commonly used amide(#1) has to be acetamide! Peptide bonds in protein are necessary for life. • The second most commonly used amide would be acetaminophen which is found in many pain relievers 1)https://cdn1.sph.harvard.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2012/09/Protein.jpg 2)http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/archives/image.cfm?archiveid=150463&type=i mg&name=hydrocodone-bitartrate-and-acetaminophen-tablet-2.jpg Everyday uses continued • Formamide is used as a cryoprotectant and a gel stabilizer. Cryoprotectant is a protectant for biological tissue from freezing damage. That due to ice formation. Draw : Everyday uses continued • Phenylamide is a highly active class of fungicide specifically controlling plant pathogens of the Downy Mildews. https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c /Benzamide.svg/170px-Benzamide.svg.png Hopefully not everyday use Lysergic acid diethylamide or commonly known as LSD. Polyamides • Are polymers in which a carboxylic acid molecules and a lone amine are bonded together by amide bonds creating various types of useful substances like nylon. This is known as a condensation polymer. Inorganic amides Is an amide without the organic carbonyl compound, so the inorganic amide is just a cation attached to NH2. Not nearly as large or as important as the organic amide however. http://cdn.meme.am/instances/61290566.jpg Reference Pictures • • https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2e/Amide-general.png • http://chemsink.com:8080/examples/jsp/marvin/generate_image.jsp?mol=CCCC(C)C(%3DO)N&format=png%3Aw400%2Ch200%2Cb32 %2C%23ffffff • http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/structure9/020/mfcd00008023.eps/_jcr_content/renditions/mfcd00008023medium.png • • • • • http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/enger/student/olc/art_quizzes/genbiomedia/0037.jpg http://chemsink.com:8080/examples/jsp/marvin/generate_image.jsp?mol=CCCNC(%3DO)C(C(C)C)Br&format=png%3Aw400%2Ch200 %2Cb32%2C%23ffffff https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/IUPAC_carbonyl_divalent_group.png http://cdn.meme.am/instances/61290566.jpg https://cdn1.sph.harvard.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/30/2012/09/Protein.jpg https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c/Benzamide.svg/170px-Benzamide.svg.png http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/archives/image.cfm?archiveid=150463&type=img&name=hydrocodone-bitartrate-andacetaminophen-tablet-2.jpg References • • • • • • • • • http://science.jrank.org/pages/285/Amides.html http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/student/olc/ch20reactionsamides.html Chemguide.co.uk Chem.ucalgary.ca Ucdavis.chemwiki Dub.unl.edu Pubchem.com Sigmaaldrich.com F.R.A.C.ca Textbook resources: Organic chemistry- Joseph M.Hornback