RIP version 1&2
Revised by Chakchai So-In, Ph.D.
chakso@kku.ac.th
http://www.facebook.com/people/Chakchai-So-In/1293159947
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
1
Agenda
History of RIP (v1, v2, ng)
RIPv1 Encapsulation and message format
RIPv1 Operation and Configuration
RIPv1 Verification and Troubleshooting
RIPv1 vs. RIPv2
RIPv1 Limitation
RIPv2 Configuration
RIPv2 Verification and Troubleshooting
Summary
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
2
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
3
RIPv1 (Characteristics)
-A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol
-Class A : 255.0.0.0 (1.0.0.0-126.255.255.255)
-Class B : 255.255.0.0 (128.0.0.0-191.255.255.255)
-Class C : 255.255.255.0 (192.0.0.0-233.255.255.255)
-Does not send subnet masks in routing updates
-Metric = hop count
-Routes with a hop count > 15 are unreachable
-Updates are broadcast every 30 seconds
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
4
RIPv1 (Encapsulated Message)
RIPv1
RIP Characteristics
-A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol
-Metric = hop count
-Routes with a hop count > 15 are unreachable
-Updates are broadcast every 30 seconds
Encapsulated RIPv1 Message
-Frame Header : Broadcast (MAC Dest.) / Sending Interface
(Src.)
RIPv1 (RIPv1 Message)
RIP Message Format
RIP header - divided into
3 fields
-Command field
-Version field
-Must be zero
Route Entry - composed
of 3 fields
-Address family
identifier
-IP address
-Metric
RIPv1 Operation (2 message types)
-Request message :
-This is sent out on startup by each RIP enabled interface
-Requests all RIP enabled neighbors to send routing table
-Response message
-Message sent to requesting router containing routing table
Click here to show animation
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
7
RIP : Example
z
w
x
A
y
D
B
C
Destination Network
w
y
z
x
….
Next Router
Num. of hops to dest.
A
B
B
--
….
2
2
7
1
....
Routing/Forwarding table in D
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
8
RIP : Example (cont.)
Dest
w
x
z
….
Next hops
- 1
- 1
C 4
… ...
Advertisement
from A to D
z
w
x
A
y
D
B
C
Destination Network
w
y
z
x
….
Next Router
Num. of hops to Dest.
A
B
BA
-….
2
2
75
1
....
Routing/Forwarding table in D
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
9
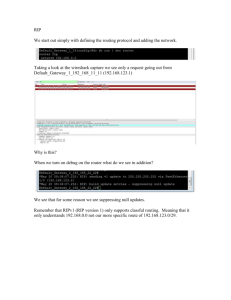
RIPv1 (Administrative Distance – AD)
RIPv2 AD = 120
RIPv1 (Simple Configuration)
To enable RIP enter:
-Router rip at the global configuration prompt
-Prompt will look like R1(config-router)#
Specifying Networks
-Use the network command to:
-Enable RIP on all interfaces
-Advertise this network in RIP updates
RIPv2 AD = 120
5 Subnets + 3 Routers
RIPv1 (Verification & Troubleshooting)
Commands:
#show ip route
#debug ip rip
#show ip protocols
RIPv1 (Verification & Troubleshooting) cont.
Commands:
#show ip route
#debug ip rip
#show ip protocols
RIPv1 (Passive Interface)
-Used to prevent a router
from sending updates
through an interface
-Example:
Router(configrouter)#passive-interface
interface-type interfacenumber
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
14
RIPv1 (Automatic Route Summarization - ASR)
Boundary Routers:
-RIP automatically summarizes classful
networks
-Boundary routers summarize RIP subnets
from one major network to another.
Modified Scenario:
-Three classful networks are used:
172.30.0.0/16
192.168.4.0/24
192.168.5.0/24
-The 172.30.0.0/16 network is
subnetted into three subnets:
172.30.1.0/24
172.30.2.0/24
172.30.3.0/24
RIPv1 (ASR)
2 rules govern RIPv1 updates:
-If a routing update and the
interface it’s received on belong to
the same network (match subnet
mask) then
-The subnet mask of the
interface is applied to the network
in the routing update
If a routing update and the
interface it’s received on belong to
a different network then
-The classful subnet mask
of the network is applied to the
network in the routing update.
RIPv1 (Automatic Route Summarization)
-Advantages :
-The size of routing updates is reduced.
-Single routes are used to represent multiple routes.
which results in faster lookup in the routing table.
-Disadvantages:
-Discontiguous Topologies do not converge with RIPv1.
-A router will only advertise major network addresses out
interfaces that do not belong to the advertised route.
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
17
RIPv1 (Default Route)
Default Route Command:
#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1
RIPv1 (Propagating the Default Route)
Route Command:
#default-information originate
-This command is used to
specify that the router is to
originate default information, by
propagating the static default
route in RIP update.
RIPv1 vs. RIPv2 (The Difference)
-RIPv1
-A classful distance vector routing protocol (DV)
-Does not support discontiguous subnets
-Does not support VLSM
-Does not send subnet mask in routing update
-Routing updates are broadcast
-RIPv2
-A classless DV
-Next hop address is included in updates
-Routing updates are multicast
-The use of authentication is an option
-What is the same?
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
-Use of timers to prevent routing loops
-Use of split horizon or split horizon with poison reverse
-Use of triggered updates
-Maximum hop count of 15
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
20
RIPv1 (Limitation - Scenario)
Scenario :
-3 router set up
-Topology is discontiguous
-There exists a static summary
route.
-Static route information can
be injected into routing table
updates using redistribution.
-Routers 1 & 3 contain VLSM
networks
VLSM (This is sub netting the
subnet)
-Private IP addresses are on
LAN links
-Public IP addresses are used
on WAN links
-Loopback interfaces : LoX
(These are virtual interfaces
that can be pinged and added
to routing table.)
RIPv2 (VLSM Review)
-Case I : Both R1 and R3 have had the 172.30.0.0/16 network subnetted into
/24 subnets. Four of these /24 subnets are assigned.
-Case II : 172.30.200.0/24 subnet and subnetted it again, using the first four
bits for subnets and the last four bits for hosts. The result is a 255.255.255.240
mask or /28.
RIPv1 (Limitation – RR)
Route Redistribution (RR)
Command :
-Redistribution command is way to
disseminate a static route from
one router to another via a routing
protocol
R2(config-router)#redistribute
static
Verifying/ Testing Connectivity :
#show ip interfaces brief
#ping
#traceroute
RIPv1 (Limitation – no VLSM)
No VLSM supported :
-RIPv1 does not send subnet
mask in routing updates.
-RIPv1 does summarize routes to
the Classful boundary Or uses the
subnet mask of the outgoing
interface to determine which
subnets to advertise.
Example : R3 (VLSM) : class B
network 172.30.0.0/16
-172.30.100.0/24 (FastEthernet
0/0)
-172.30.110.0/24 (Loopback 0)
-172.30.200.16/28 (Loopback 1)
-172.30.200.32/28 (Loopback 2)
RIPv1 (Limitation – no CIDR)
No CIDR Support :
-Classful routing
protocols do not
support CIDR routes
that are summarized
with a smaller mask
than the classful
subnet mask.
R2 will not include the static
route in its update SO no such
route in R1.
RIPv2 (RIPv1 vs. RIPv2 Message)
RIPv2 message format is similar to RIPv1 BUT has 2 extensions
-1st extension is the subnet mask field
-2nd extension is the addition of next hop address (identify a better
next-hop address - if one exists)
RIPv2 (Configuration) – Cisco Default = RIPv1
To configure RIPv2:
-Requires using the version 2 command
-RIPv2 ignores RIPv1 updates
-To verify RIPv2 is configured:
#show ip protocols
RIPv2 (Configuration) – Auto-Summary
-RIPv2 will automatically summarize routes at major network boundaries
and can also summarize routes with a subnet mask that is smaller than the
classful subnet mask.
RIPv2 (Configuration) – no auto-summary
When using RIPv2 with automatic summarization turned off, Each subnet
and mask has its own specific entry, along with the exit interface and nexthop address to reach that subnet.
-Disabling Auto-Summary
#no auto-summary
-Verifying RIPv2 Updates
#debug ip rip
RIPv2 (VLSM)
Networks using a VLSM IP
addressing scheme :
-Use classless routing protocols to
disseminate network addresses and
their subnet masks
RIPv2 (CIDR)
CIDR uses Supernetting :
-Supernetting is a bunch of
contiguous classful networks
that is addressed as a single
network.
-To verify that supernets are
being sent and received
#show ip route
#debug ip rip
RIPv2 (Verify and Troubleshoot)
Basic Troubleshooting Steps:
-Check the status of all links
-Check cabling
-Check IP address & subnet mask configuration
-Remove any unneeded configuration commands
Common RIPv2 Issues:
-Version : Check to make sure you are using version 2
-Network statements : Network statements may be incorrectly typed
or missing
-Automatic summarization : If summarized routes are not needed
then disable automatic summarization
Commands used to verify proper operation of RIPv2:
#show ip interfaces brief
#show ip protocols
#debug ip rip
#show ip route
Summary
Routing
Protocol
Distance
Vector
Classless
Routing
Protocol
Uses
HoldDown
Timers
Use of
Split
Horizon
or
Split
Horizon
w/
Poison
Revers
e
Max
Hop
count
= 15
RIPv1
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
RIPv2
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
Auto
Suppor
Summary
t
CIDR
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Support
s
VLSM
Uses
Authen
ticatio
n
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Cisco Public
33
ITE PC v4.0
Chapter 1
© 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Cisco Public
34