4 - Uniform Motion Lab
advertisement

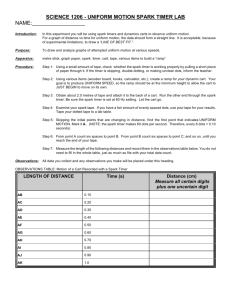
S10 Unit B – Physics: Uniform Motion Lab Name: ____________ Date: ____________ Question: What are the qualities of the uniform motion of a dynamics cart? What is the shape of a distance vs. time graph? What information can be determined from these graphs? /22 Hypothesis (Answer the 3 questions above) (3 marks) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… Design: A spark timer is used to determine the distance traveled by a dynamics cart over set time intervals. Graphs of distance vs. time is constructed and analyzed. Variables: (1 mark) Controlled: (variable that does not change)……………………………………………………… Manipulated: (variable the experimenter changes)……………………………………………… Responding: (variable that is measured)………………………………………………………… Materials: dynamics cart ramp (a few textbooks, with one opened to make the ramp works well) metre stick / ruler spark timer sticky tape Procedure: Calibrating the spark-timer: 1. Place the spark-tape in the spark-timer and pull on the tape for a measured length of time (between 3 and 5 seconds is good). Record the length of time. 2. Count the number of intervals (spaces between dots, N) present on the spark-tape. Take the number of intervals and divide by the time to get the number of intervals per second for the timer (t). 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 again to ensure the t remains constant. Measuring Uniform Motion: 1. Create a ramp out of books, with one open book used as the ramp surface. 2. Place the spark-timer on the top of the ramp (on the flat portion). Place the spark tape through the meter and fasten it onto the end of the cart. 3. Turn the spark-timer on and release the cart, allowing it to roll to a stop (try to ensure it travels in as straight a line as possible). 4. Examine the spark tape. Look for intervals in the middle of the tape that are roughly equally spaced. Starting from the first equally spaced interval, begin recording measurements of distance and time. Set this interval as the starting time and starting distance. Use the previously recorded values of t to determine time. Measure distance with a metre stick. Data Table: (1 mark) N1 - N2 Time between dots (s) Distance between dots (m) N2 – N3 N3 – N4 N4 – N5 N5 – N6 N6 – N7 N7 – N8 N8 – N9 Graph: Construct a graph of distance vs. time (2 marks) Analysis: Sample spark-timer calibration calculation: (1 mark) Slope calculation of distance vs. time graph (include proper units): (2 marks) Evaluation: Briefly summarize the lab, answer the question, state whether the hypothesis was correct and why, state the meaning of the slope from the distance vs. time graph, discuss why dots in the middle of the spark tape were used instead of at the beginning or end, state any sources of error or improvements to the lab. (6 marks) ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………… Sample Data for “Uniform Motion” Lab Average # of intervals per second = 100 (approximately) t = 0.0100 s Time between dots (s) Distance between dots (m) N1 - N2 N2 – N3 N3 – N4 N4 – N5 N5 – N6 N6 – N7 N7 – N8 N8 – N9 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.0090 0.019 0.029 0.039 0.048 0.059 0.068 0.074 Slope = velocity = 0.98 m/s