2-5 ch3

Warm-up: (9-22-15)
*Ch.3-1 video notes/rubric out for stamp!
• 1. Give 2 pros and 2 cons for using synthetic fertilizer and organic fertilizer.
• 2. Contrast crop rotation and strip cropping.
• 3. Contrast terracing with contour farming.
• *copy hw from the board.
Q/A
What is interdependence?
Which of the 4 spheres of Earth makes up the crust and upper mantle?
Which sphere is the gas layer?
Which sphere is made up of water?
Which sphere is made up of all of the ecosystems and living things?
A greater variety of species describes the _____ of the area.
T/F. Biodiversity tends to be greater in ecotones.
Give one example of an abiotic factor.
In a pond, the interactions between the plants, fish, bacteria, turtles, algae, would describe which level of ecology?
If you were researching the density or distribution of a specific species of turtle, which level of ecology would you be describing?
What is the difference between an ecosystem and a community?
Ch.3-3
Mrs. Boyd
“auto” means …
“troph” means…
Autotroph means…
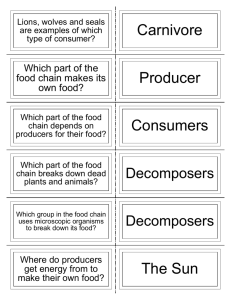
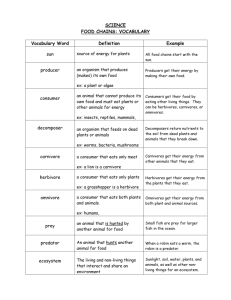
Producers
Producers: Autotrophs. Organisms that make their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Photosynthesis: use sun’s energy to make food.
Chemosynthesis: use energy stored in chemical to make food.
Name the plant organelle involved in photosynthesis.
Do animal cells have this organelle?
Fungi?
Consumers
Consumers: heterotrophs. Organisms that can’t make their own food so they have to consume organic molecules made by other organisms.
Include:
Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, detrivores
How do autotrophs and heterotrophs differ?
Herbivores: eat producers.
Primary consumers
Teeth designed for grinding
Ex. Rabbits, cows
Carnivores: eat consumers.
Secondary consumers
Feed on primary consumers (herbivores)
Teeth designed for tearing (large canines and sharp molars) cats for example
Ex. Lions eats a zebra that eats grass
Omnivores: eat both producers and consumers.
Ex. Grizzly bear: eats both salmon and berries.
Tertiary consumer
Ex. Shark eats a fish that ate another fish that ate plankton.
Give one example of an herbivore.
Give one example of a carnivore.
Give one example of an omnivore.
Detrivores: feed on parts of dead organisms in an ecosystem.
Recently dead organisms
Scavengers – feed on dead organism they did not kill, but found dead
Ex. Vultures, hyenas
Decomposers: bacteria and fungi that break down dead tissue or waste into simpler molecules.
Biodegradable means can be broken down by decomposers
Why are detrivores and decomposers important to any ecosystem?
Food chains to food webs
Food chain: single pathway of feeding relationships (energy transfers) among organisms in an ecosystem.
Ex. Grass mouse eats grass seeds
snake
hawk
Food web: interrelated food chains in an ecosystem. (arrow points in the direction that energy is transferred)
Check for Understanding:
1. Contrast population and community.
2. Give an example of a detrivore and an example of a decomposer.
3. What does the ringed seal eat?