Lesson 6.3 Ecosystems
advertisement

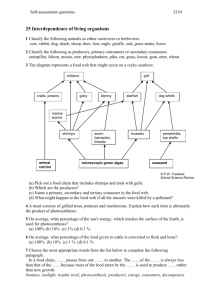
*Refer to Chapter 16 in your Textbook Learning Goals: 1. I can differentiate between an autotroph and heterotroph. 2. I can label organisms in a food web as primary producers and 1st, 2nd, and 3rd level consumers. 3. I can describe the energy flow through an ecosystem. Energy Table: Type of Organism Energy Source Example Autotroph/Producer Photosynthesis Phytoplankton Autotroph/Producer Chemosynthesis Mussel in a hydrothermal vent Heterotroph/Consu mer Cellular Respiration Great White Shark Autotrophs: Autotrophs are organisms capable of producing their own food, also known as producers They can accomplish this two ways: 1. Photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight = oxygen + sugar 2. Chemosynthesis: Carbon dioxide + water + hydrogen sulfide = oxygen + sugar + sulfur Photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Autotrophs: The primary producers of the ocean are phytoplankton “plant plankton” (92% of all producers in the ocean) Heterotrophs: Heterotrophs are organisms that must consume their energy, also known as a consumer All heterotrophs accomplish this one way: 1. Cellular Respiration: Converts food and oxygen into energy Oxygen + sugar = carbon dioxide + water + energy (the opposite of photosynthesis) Types of Consumers: 1. Herbivore: eats plants (ex. Manatee) 2. Carnivore: eats meat (ex. Great White Shark) 3. Omnivore: eats plants & meat (ex. Sea Turtle) 4. Decomposer: break down dead/decaying material and release energy back into the ecosystem (ex. Marine Bacteria) 5. Detritivore (or Scavenger): feed on broken down dead/decaying material to consume energy for themselves (ex. Sea Star) Food Chains: A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. *An example from the Everglades is shown. Food Webs: A food web is a network of feeding interactions through a series of connected food chains Ecological Pyramids: Ecological Pyramids show the amount of energy contained within each trophic level within a food chain or web • Primary producers will always make up the 1st level • Various consumers will make up the next levels