Studies in Forensic Psychology
advertisement
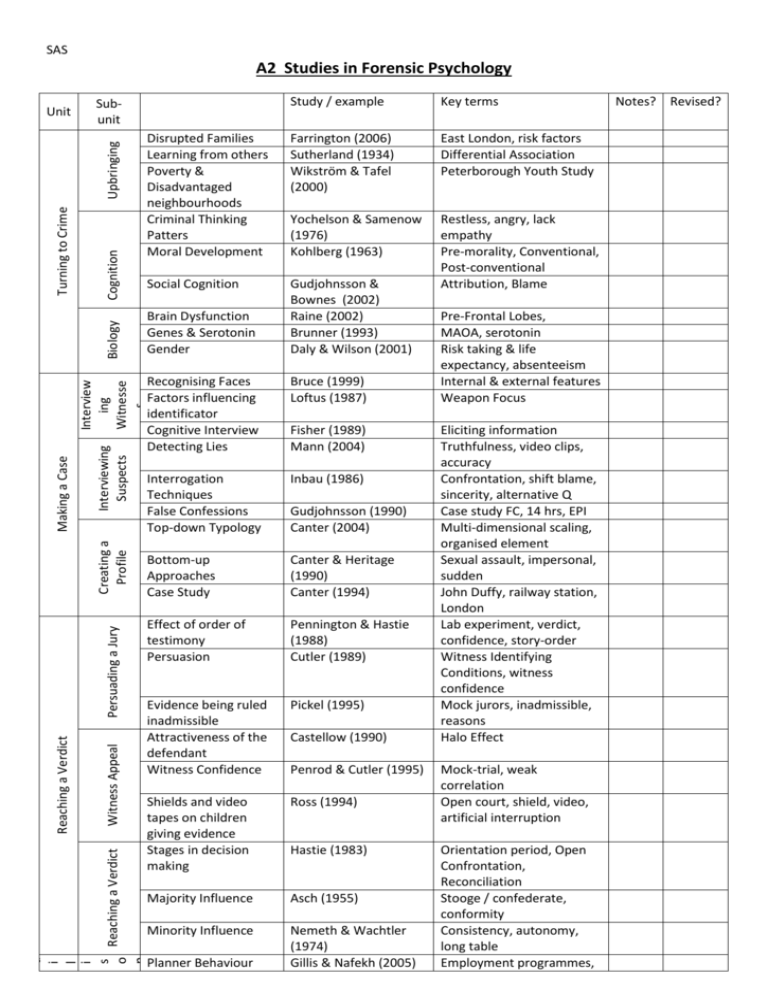
SAS A2 Studies in Forensic Psychology Key terms Disrupted Families Learning from others Poverty & Disadvantaged neighbourhoods Criminal Thinking Patters Moral Development Farrington (2006) Sutherland (1934) Wikström & Tafel (2000) East London, risk factors Differential Association Peterborough Youth Study Yochelson & Samenow (1976) Kohlberg (1963) Social Cognition Gudjohnsson & Bownes (2002) Raine (2002) Brunner (1993) Daly & Wilson (2001) Restless, angry, lack empathy Pre-morality, Conventional, Post-conventional Attribution, Blame Brain Dysfunction Genes & Serotonin Gender Recognising Faces Factors influencing identificator Cognitive Interview Detecting Lies Bruce (1999) Loftus (1987) Interrogation Techniques False Confessions Top-down Typology Inbau (1986) Bottom-up Approaches Case Study Canter & Heritage (1990) Canter (1994) Effect of order of testimony Persuasion Pennington & Hastie (1988) Cutler (1989) Evidence being ruled inadmissible Attractiveness of the defendant Witness Confidence Pickel (1995) Shields and video tapes on children giving evidence Stages in decision making Ross (1994) Majority Influence Asch (1955) Minority Influence Nemeth & Wachtler (1974) Gillis & Nafekh (2005) Cognition Interviewing Suspects Witness Appeal IG m u p i rl it sy Reaching a Verdict o n V m e er n d ti c t Reaching a Verdict Persuading a Jury Creating a Profile Making a Case Interview ing Witnesse s Biology Turning to Crime Study / example Subunit Upbringing Unit Planner Behaviour Fisher (1989) Mann (2004) Gudjohnsson (1990) Canter (2004) Castellow (1990) Penrod & Cutler (1995) Hastie (1983) Pre-Frontal Lobes, MAOA, serotonin Risk taking & life expectancy, absenteeism Internal & external features Weapon Focus Eliciting information Truthfulness, video clips, accuracy Confrontation, shift blame, sincerity, alternative Q Case study FC, 14 hrs, EPI Multi-dimensional scaling, organised element Sexual assault, impersonal, sudden John Duffy, railway station, London Lab experiment, verdict, confidence, story-order Witness Identifying Conditions, witness confidence Mock jurors, inadmissible, reasons Halo Effect Mock-trial, weak correlation Open court, shield, video, artificial interruption Orientation period, Open Confrontation, Reconciliation Stooge / confederate, conformity Consistency, autonomy, long table Employment programmes, Notes? Revised? SAS Treatment programmes Alternatives to Imprisonment once freed from jail Depression / suicide risk in prisons Prison situation and roles Probation Dooley (1990) Restorative Justice Sherman & Strang (2007) Eberhardt (2006) Looking “Deathworthy” Cognitive Skills programme Anger Mangement Ear Acupuncture for Drug Rehabilitation Haney & Zimbardo (1998) Mair & May (1997) Cann (2006) Ireland (2000) Wheatley (2007) conditional release, custody Content analysis, remand, overcrowding Dispositional explanations, supermax cells Self-report, Likert, 88% useful Reductions in violent & property crime Race and Capital punishment Enhanced Thinking Skills Instrumental & Hostile Aggression, WBC, self report Qualitative, coping skills, cravings











