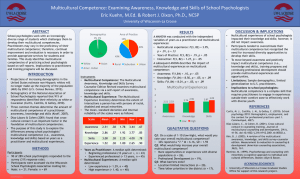
The following figure is one way (not the only way) to factor analyze
advertisement

The following figure is one way (not the only way) to factor analyze the Alliant’s Institutional Objectives and I-MERIT Competencies. Using this grouping as a preliminary structure (can be changed), the following is a mapping of different definitions and conceptualizations of what an integration of international and multicultural competence might look like: 4 factors in 4 Factors in Institutional I-MERIT Objectives Competencies Networks & Professional Collaboration service skills 11/21/11 meeting brainstorming - Ability to change generate better solutions and - Ability to be at ease in increase our chances of unfamiliar surroundings Multicultural personality - Multicultural friendships - Multicultural competence - Expanded Social Networks - Humor - Coping Ability - Hardiness - General SelfEfficacy - Resiliency Continuous Learning. A Understand: major component of - Etic/emic perspectives effectiveness is the extent to - Ecological models which we can continuously - Time, place, historical context expand our knowledge and - What one doesn’t know awareness both individually (metacognitive) and collectively. - Power dynamics - Authority perceptions - Broaden concept of mental illness - Interest in how things work - Power distance (diff in hierarchy respect) - High/Low context - Uncertainty avoidance - Short vs. long-term - Racial/Ethnic Identity - Prejudice levels 7 Alliant Values Partnership. We can success by collaborating across differences. Knowledge Multicultural (Hays) vs. Intercultural (Sinicrope et al.) - Multicultural comptncy-Ability to: o Examine beliefs / attitudes o Exercise culturally appropriate professional practice - Tolerance for ambiguity - Global competence - World citizenship - Cross-cultural adaptation - Intercultural competence (“ability to think / act in interculturally appropriate ways”) - Skills of interpreting and relating (ability to interpret, explain, relate events/documents from other culture to own culture) - Skills of discovery and interaction (ability to acquire “new knowledge of culture/cultural practices) - Critical cultural awareness (ability to use perspectives, practices, products in own & in other cultures to make evaluations.) - Power / oppression / privilege - Social justice - Aversive racism/bias - Discrimination / Prejudic e/ “isms” o Blatant & micro-aggressions - Race/Ethnicity - Intersections of culture o Sexual orientation, religion, disability, immigration, gender. SES, health, age, etc… Intercultural sensitivity (“ability to discriminate and experience relevant cultural differences”) - Ethnorelativity - Pluralinguism - Biculturalism orientation - Variance in cultural norms Awareness & Attitudes Respect. We respect and value diverse ways of learning, knowing, and accomplishing goals. Responsibility. Each of us benefits when we take responsibility, personally and collectively, for building a more inclusive community. Humility. No one person or perspective has the whole answer. Commitment. Building inclusion is a long-term process and requires ongoing commitment. - Communication Dialogue and Skills Engagement. We can foster individual and collective growth and adaptation by listening to many voices, re-examining assumptions, and working through conflict. Patience Curiosity Empathy Int’l-2nd nature Neutrality Openness to experience w/o judgment Experience w/o comparison Flexibility Adjust one’s boundaries Basics of being polite Learn rather than promote US ideals Openness to diff. prof. degrees Relativistic/Int’l worldview Respect across SES o Comm skills: o Knowing 2+ languages o Follow up to confirm mutual understanding o Pause & breathe o Excellent observat’l skills o Read & adjust own body language (facial exp.) o Read non-verbal cues o Talk/listen across own field’s paradigms o Translate field’s language for others o Respond / mend crosscultural ruptures - Cultural empathy - Appreciate other norms/ value systems Openmindedness - Aware of own values / biases Flexibility - Understand other worldviews Adventurousness Interest in Int’l careers Emotional stability Extroversion Social initiative Communication: We can foster individual and collective growth and adaptation by listening to many voices, re-examining assumptions, and working through conflict. - Communication skills: - Knowing 2+ languages - Follow up to confirm mutual understanding - Pause & breathe - Excellent observational skills - Read & adjust own body language (facial exp.) - Read non-verbal cues - Talk/listen across own field’s paradigms - Translate field’s language for others - Respond / mend crosscultural ruptures - - - Effective intergroup communication - Transcultural communication - Transnational cooperation - Quality of Life - Psychological Well-Being - Life Satisfaction - Physical Health -