Visual Aids
advertisement

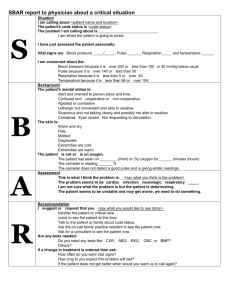
Allied Healthcare: Critical Reading & Application Exercise How well do you understand Visual Aides? Directions: With your study group, answer the following questions as they relate to the diagrams and charts. Write T for True, F for False, CT for can’t tell or fill-in the blank using the information given. Grahpic A: Diagram Skeletal System: McCall & Tankersley, Phlebotomy Essentials, 5th ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkin, 129. The muscular system “gives the body the ability to move, maintain posture and produce heat. It also plays a role in organ function and blood circulation.” Where as, “the skeletal system is the framework that that gives the body shape and support, protects internal organs.” 1. The Clavicle and Scapula are not components of the skeletal system. 2. The metatarsals and phalanges are bones in the hands. 3. The vertebral column starts at the pelvis. 4. The ilium is part of which skeletal structure? ________________ 5. The humerus is attached directly to the ribs. Graphic B: Table Classification of Bones by Shape 1. Which are the shortest bones? ___________________________ 2. What shape are most of the cranial bones? _______________________ 3. The most regular shaped bones in the body are the vertebrae. 4. In comparing the table with the diagram, it is easy to see why the skull and rib bones are considered flat. Graphic C: Table Cross Section of Skin. Phlebotomy Essentials, 133. 1. How many main layers of skin is there? __________ 2. Which layer contains the pore opening? __________ 3. Which layer houses the glands? _________________________ 4. In which section does the hair follicle initiate? _________________ 5. Nerve endings are found in which layer? _______________ Graphic D: Table NORMAL PULSE RATES (BEATS PER MINUTE, AT REST) Adult Infants and Children Adolescent 11 to 14 years School age 6 to 10 years Preschooler 3 to 5 years Toddler 1 to 3 years Infant 6 to 12 months Infant 0 to 5 months Newborn 60 to 100 PULSE QUALITY SIGNIFICANCE/POSSIBLE CAUSES 60 to 105 70 to 110 80 to 120 80 to 130 80 to 140 90 to 140 120 to 160 Rapid, regular and full Exertion, fright, fever, high blood pressure, first stage of blood loss Rapid, regular and thready Shock, later stages of blood loss Slow Head injury, drugs, some poisons, some heart problems, lack of oxygen in children No pulse Cardiac arrest (clinical death) Infants and Children: A high pulse in an infant or child is not as great a concern as a low pulse. A low pulse may indicate imminent cardiac arrest. Emergency Care, Chapter 12 Vital Signs and Monitoring Devices, 293 1. A patient has lost a lot of blood, what would you expect the quality of his heart rate to be? 2. An adult’s pulse has slowed down greatly, what are some possible causes for this? 3. What is a normal pulse rate of an infant in contrast to an adult’s? 4. A child who is 12 months old has a pulse rate of 155; should you be concerned with this situation? 5. A preschooler was climbing up a tree and fell. His pulse rate was 72 what might be the cause of this?