Lab7-Exploring Cells
advertisement

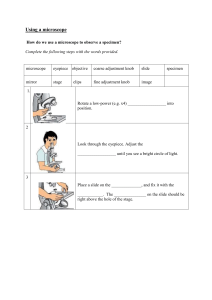
Principles and Methods Lab: Exploring Cells Prelab: 1. What is the major difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What types of organisms are found in each? 2. List three differences between a typical plant cell and a typical animal cell. 3. What do the following parts of a microscope do? Eyepiece Objective lenses Condenser Diaphragm Course adjust knob Fine adjust knob Stage adjust knob Introduction: In this lab, we will use a compound microscope to study cells. Familiarize yourself with the parts shown in the diagram below and their functions before proceeding: When using a microscope, it is important to report the total magnification of any images seen. To do this, you must multiply the magnification of the eyepiece lens (10x for these microscopes) by the power of the objective lenses. They are listed below: Scanning lens = 4x Low Power = 10x High Power = 40x Oil Immersion = 100x We will examine a total of seven slides. They are: Zea root tip Alium epidermis Generalized animal cell Neuron Paramecium Stentor Cheek cell smear Instructions for making a cheek cell smear: 1) Obtain a clean blank slide and a slip cover. 2) Using a toothpick, gently rub the insides of the cheeks. Then rub the toothpick on the blank slide. 3) Add one drop of methylene blue. This will stain cell structures especially the nucleus. 4) Place cover slip on top. Use tissue paper to wick away any excess stain. 5) Observe the slide. Note the cells and their structures. Also, look for the presence of bacteria (small dark specks). FOR THE DATA SECTION OF THE REPORT: - Add drawings for each of the seven slides. For each drawing, label any cell structures seen and write the total magnification used to view the slide. - Show the calculations for total magnification for each objective lens (scanning, low, high, oil). FOR THE OBSERVATIONS SECTION: - Add written observations for which structures are present and what kinds of differences/similarities exist between the slides. Questions: 1. Place each of the slides into one of the following categories: Plant, animal, or protist. What do all of these cell types have in common? 2. What differences did you see between the plant cells and the animal cells? 3. How is the neuron different from the generalized animal cell? How might this relate to the neuron's function? 4. When you increase magnification, does your field of view get bigger or smaller? Why is it important to center your subject before switching to higher magnification?