The Sustainable Company and Sustainability Reporting
advertisement

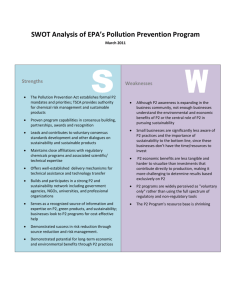
The Sustainable Company and Sustainability Reporting Sigurt Vitols EWPCC WORKSHOP ON ‘FINANCIAL ANALYSIS AND SUSTAINABILITY’ – HAMBURG, 26 – 28 OCTOBER 2011 Agenda for this session ● ● ● ● What is sustainability? What is the sustainable company? What is sustainability reporting? What does sustainability reporting mean for workers? What is your definition of: ● Sustainability ● Durabilité ● Nachhaltigkeit ● Corporate Social Responsibility ● Responsabilité sociale des entreprises (RSE) ● Soziale Verantwortung der Unternehmen (CSR) Corporate Social Responsibility CSR: One Definition The EU definition of CSR is: A concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and in their interaction with their stakeholders on a voluntary basis. -- Commission Green Paper 2001 “Promoting a European Framework for Corporate Social Responsibility” A new definition of CSR: ● ● ● “The responsibility of enterprises for their impacts on society” Respect for applicable legislation, and for collective agreements between social partners, is a prerequisite for meeting that responsibility. To fully meet their corporate social responsibility, enterprises should have in place a process to integrate social, environmental, ethical, human rights and consumer concerns into their business operations and core strategy in close collaboration with their stakeholders -- European Commission Communication, 25.10.2011 Sustainability Sustainability – One Definition "Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". -- UN Brutland Commission, 1983 Dimensions of sustainability: one definition ● Economic Performance ● Environment ● Human Rights ● Labour practices and decent work ● Society ● Product Responsibility -- Categories used by Global Reporting Initiative (G3 guidlines) Battle of the models of corporate governance? Postwar stakeholder model 1950 1960 1970 Shareholder value model The Sustainable Company?? 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 2030 Triple crisis of shareholder value capitalism 25 23 Excluding capital gains Including capital gains 21 19 17 15 13 11 9 7 1915 1925 1935 1945 1955 1965 1975 1985 Share of top 1% in US national income 1995 2005 Shareholder value capitalism: your opinion ● Does it work? ● Do we want an alternative? ● What would an alternative look like? Our opinion Shareholder Value Model of CG ● Core assumption: Share price best measure of company value Three main elements: ● ● ● ● Competitive market for investors Top managers‘ pay tied to share price Gatekeepers: auditors, regulators, independent directors What does Share Price Measure? Failures of Shareholder Value ● Weak correlation between share price and company performance ● Externalities – share price doesn‘t measure social costs ● Sacrifice LT investment for ST performance ● Incentives for fraud by managers ● Conflict of interest of gatekeepers Elements of the Sustainable Company Stakeholder value Sustainability goals and strategy Stakeholder voice The Sustainable Company Long term responsible investors Disclosure of social and environmental performance Remuneration oriented to sustainability The Way Forward: Key Challenges ● Binding legislation ● Sustainability-friendly capital markets ● Extending the role of trade unions Many Initiatives on Sustainability and CSR Allianz SE: International sustainability commitments ● Transparency International ● UN Global Compact ● UN Principles for Responsible Investment ● UN Environment Program: Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) ● World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) ● Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) ● WWF ● EU Corporate Leaders' Group on Climate Change (EU CLG) Sustainability reporting: main types ● ● ● External: published reports Internal: worker information rights Private: rating agencies + index providers Global Reporting Initiative ● Nearly 3,000 participants in about 70 countries ● Stakeholder involvement in governance ● Current consultation on new (G4) reporting guidelines ● Core Goals: Mainstreaming of disclosure on environmental, social and governance performance ● Categories of Performance Indicators ● Economic Performance ● Environment ● Human Rights ● Labour practices and decent work ● Society ● Product Responsibility Participation Rate: Europe vs. rest of world GRI core indicators for labour practices and decent work ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● LA1 Total workforce by employment type, employment contract, and region, broken down by gender LA2 Total number and rate of new employee hires and employee turnover by age group, gender, and region. LA4 Percentage of employees covered by collective bargaining agreements. LA5 Minimum notice period(s) regarding operational changes, including whether it is specified in collective agreements. LA7 Rates of injury, occupational diseases, lost days, and absenteeism, and number of work related fatalities by region and by gender. LA8 Education, training, counseling, prevention, and risk-control programs in place to assist workforce members, their families, or community members regarding serious diseases. LA10 Average hours of training per year per employee by gender, and by employee category. LA13 Composition of governance bodies and breakdown of employees per employee category according to gender, age group, minority group membership, and other indicators of diversity. LA14 Ratio of basic salary and renumeration of women to men by employee category, by significant locations of operation. LA15 Return to work and retention rates after parental leave, by gender. Volkswagen: social partnership in sustainability reporting Important questions ● ● ● ● ● What kind of information do workers want? How can they use this information? Do they want to be involved in developing reporting systems? How aware are workers of current rights and reporting practices? Best strategy for improving rights and practices (internal versus external reporting)? THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!