Earth Science Week 26
advertisement

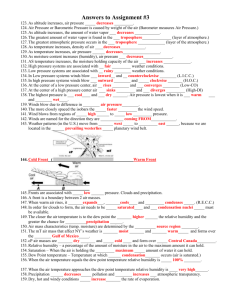
Earth Science Week 26 Weather and Climate Monday Warm Up (125) • Describe air pressure as high or low at the following: – North Pole and South Pole – 60 degrees North latitude and South Latitude – 30 degrees North latitude and South Latitude – Equator Wind Brochure 1. 2. 3. 4. Diagram of pressure belts p. 459 Diagram of global winds p. 461 Diagram of land and sea breezes p. 462 Description of winds: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Polar Easterlies Westerlies Trade Winds The Doldrums The Horse Latitudes The Jet Stream Land Breeze Sea Breeze Tuesday Warm Up (125) • • • • • What causes land and sea breezes? Which direction do land breezes blow? Which direction do sea breezes blow? When do land breezes blow? When do sea breezes blow? www.explorelearning.com • Coastal Winds and Clouds Gizmo • Complete the student guide • Take the assessment. Air Pressure, Wind and Air Movement Lab • Work through all three activities • Record all observations in IAN Making Weather Instruments • Make barometer (See p. 472 – 473) • Make wind vane Wednesday Warm Up (125) • Why do drops of water form on the outside of a glass of cold liquid? • Do they form on glasses with warm liquid in them? Why or why not? Cornell notes p. 482-489 Section Review p. 489 • • • • • • • • • Weather Humidity Relative humidity Psychrometer Condensation Dew point Cloud Cumulus cloud Cumulonimbus cloud • • • • • • • • • • Stratus cloud Nimbostratus cloud Cirrus cloud Cirrocumulus cloud Fig. 6 p. 487 (clouds) Precipitation Rain Sleet Snow hail Thursday Warm Up (125) • What type of cloud is usually associated with thunderstorms? Why? Dew Point Lab • Follow directions completely. • Record observations in IAN. Friday Warm Up (125) • Compare and contrast humidity and relative humidity. Video: Understanding Weather