Rome - Divum
advertisement

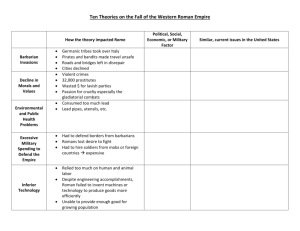
Chapter 10: Ancient Rome Lesson One: Rome’s Beginnings I. Legend a. Roman legend claimed that brothers, Romulus and Remus founded Rome after they were raised by a she-wolf. II. Landforms and Bodies of Water in Rome a. Mountainous (like Greece) b. Longest coastlines i. became a center of trade because of its many harbors and ports with access to the Mediterranean Sea. c. Surrounded by Mediterranean Sea, Tyrrhenian Sea, and Click to edit the outline text format Second Outline Level Third Outline Level Fourth Outline Level Fifth Outline Level III. Connection a. Rome was considered a bridge between Western Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. IV. TRADING a. Tiber River was important because foreign ships could bring goods up the river to Rome. i. Rome became very rich. b. Because of trade, Romans studied new ideas about growing crops and they learned about other Click to edit the outline text format Second Outline Level Third Outline Level Fourth Outline Level Fifth Outline Level V. Etruscans a. Etruscans took over Rome about 600 B.C. b. Romans learned how to build aqueducts. i. aqueductsstructures that carry flowing water to supply water to cities. c. The Romans also Click to edit the outline text format Second Outline Level Third Outline Level Fourth Outline Level Fifth Outline Level The ROMAN AQUEDUCT—built in the 2nd century a.d. Lesson 2 Outline Lesson 2-The Roman Republic I. Nationalism a. Romans were proud of their soldiers and loyal to their homeland. Told many war hero stories to raise pride and nationalism- a strong devotion to one’s country. II. a. b. Two Groups of Citizens patricians – rich and powerful plebeians – all other people, 90% of the people. patricians soldier and slave plebeians farmer/craftsmen III. Republic a. b. c. d. Citizens have the right to vote, or choose their leaders Elected officials represented the people in the Senate (governing body) At first the Senate made up of patricians. Each year two patricians were elected as consuls (officials for the government and army) IV. Citizenship a. b. Slaves and most foreigners were NOT citizens. Women WERE citizens with limited power. i. Women could not vote or hold public office but they had more freedom than Greek women. ii. Women could own property, testify in court and play major roles in government. Patricians V. Tribunes men who were appointed to protect the rights of the plebeians b. set up to protect plebeians from the harsh treatment from patricians c. Over time plebeians gained in wealth and power, but the patricians always had more power. a. VI. Carthage a. City-state located in North Africa. b. Had a large and powerful navy and one of the strongest armies. VII. Rome and Carthage a. Rome and Carthage fought three times in the battles called the Punic Wars. i. Wars lasted a total of 120 years and the Romans won all three wars. b. 1st War of the Punic Wars- fought over land off the coast of Italy c. 2nd War of the Punic Wars- MOST FAMOUS OF THE THREE i. Hannibal (Carthaginian general) took his army across the Alps on elephants and surprised the Romans. ii. The Romans learned of the attack by Hannibal. iii. The Romans were saved when Scipio(Roman General) attacked Carthage and Hannibal had to rush back home to Carthage to help. iv. Carthage was defeated. d. 3rd War of the Punic Wars- Romans captured and destroyed Carthage i. surviving Carthaginians were sold into slavery and Rome controlled the entire Western Mediterranean region. VIII. Conquered Places a. Romans tried to keep people happy and patriotic (loyal to Rome). i. They granted Roman citizenship to people they conquered ii. allowed others to keep local selfgovernment and their leaders remained in power IX. Effects of War on Rome Money came to Rome but only the patricians were wealthier. i. Plebeians lost jobs to wartime slaves ii. farmland and homes were destroyed because of fighting iii. This angered the plebians a. X. Julius Caesar ” Won battle between two other Roman generals and was made a ruler for life. b. The patricians feared that Caesar would take total power, so he was stabbed on the floor of the Senate. i. This lead to a civil war (which is when people from the same country fight one another) as leaders fought for power. c. The Roman Republic came to an end. a. On March 15, Julius Caesar was stabbed on the Senate floor. XI. Advancements of this time a. Romans built aqueducts, roads and buildings in conquered land. (Roads were made of concrete—not dirt) i. Most famous of the roads was the Appian Way, which stretched 350 miles east and south of Rome) Lesson 3 Outline The Roman Empire I. Augustus a. Emperor of Rome who stabilized Rome after Julius Caesar’s death and the civil war b. Centralized the government and improved the economy c. Began a long period of peace called Pax Romana (Roman Peace). i. 200 YEARS OF PEACE d. Made people conquered by Rome loyal to Rome i. this united the Roman Empire i. ii. Roman Empire spread eastward and westward ii. on three continents. II. Good and Bad Emperors a. Although there were many good emperors, there were also bad emperors. i. Period of bad emperors lasted for thirty years until Marcus Aurelius. b. “Five Good Emperors” i. more stable leadership led to 84 years of peace and prosperity ii. Marcus Aurelius was the last and greatest emperor of this time. IV. Conquered People (the people the Romans took over) a. All spoke their own language and Latin b. The conquered people also had citizenship c. Local leaders were allowed to remain in power i. This led to the empire being united! V. Roman Law (similar to U.S. Law) that all a. couldhave follow: Allpeople free people equal rights. b. A person is innocent until he or she is proven guilty. c. Accused people should be allowed to face their accusers and defend themselves. d. Judges must interpret the law and make decisions fairly. e. People have rights that no government can take The Twelve Tables were laws away. engraved on tablets and put on display in the Forum in Rome for everyone to see, so they could be understood by all of the citizens of Rome. VI. Roman Culture a. The Colosseum is the most famous Roman arena. It held the following events: i. gladiator fights (most important), plays and religious ceremonies b. Built aqueducts that brought fresh water. c. Roman rule led to the growth of many cities in the Empire. Lesson 4 Outline The Rise of Christianity I. Christianity a. A religion based on the teaching of Jesus (who was a Jewish man). II. Jesus’ beliefs (monotheistic) a. believed that God loved everyone b. wanted people to be kind to one another c. he preached about forgiveness and mercy III. Jesus is Crucified a. Jesus was crucified because local leaders thought his message would upset Roman rulers. b. After his death disciples spread Jesus’ teachings and Christianity continued to spread. c. Peter and Paul were the most famous disciples. IV. Persecution of Christians a. At first Christians were persecuted (being punished for religious beliefs) because they refused to worship the emperor as a god. b. Emperor Constantine made Christianity equal to all other religions and outlawed the persecutions. Lesson 5 outline Rise and Fall Emperors for Sale I. Emperors a. Most Emperors after Marcus Aurelius cared about increasing their wealth and power not the welfare of the Roman Empire. II. Choosing a New Ruler a. Roman Army began to fight each other to get their favorite person as an Emperor. b. The Roman Army spent so much time fighting within Rome (Romans fighting Romans) The Empire Divided III. Restoring Order a. To restore order and bring money to the empire, Emperor Diocletian divided the empire. b. Diocletian and a co-emperor ruled the eastern portion, while two co-emperors ruled the western portion. The city of Constantine/ Christianity Divides IV. Emperor Constantine a. Constantine united the empire again b. He made a new capital city in the eastern part of the Empire, Byzantium (later known as Constantinople). Constantinople c. Constantinople became the center of the Byzantine Empire. V. Differences among the empires a. Eastern part of the empire was strong and rich; capital city was Constantinople. i. Emperor was the head of the church-Byzantine Orthodox Church. b. Western part of the empire was weak and poor; capital city was Rome. i. Pope was the head of the church-the Roman Catholic Church. Western Empire Eastern Empire The Final Days of Rome/ The Fall VI. Visigoths (German Tribe) a. Attacked the eastern Empire b. Alaric, leader, reached the gates of Rome. c. He surrounded the city, cutting off its food supply. i. He pillaged (robbed) the homes of the wealthy in Rome and burned what he could not take. VII. Rome Falls a. As Rome declined, the Byzantine Empire became even more prosperous. b. When Rome fell, the Byzantine Empire became the center of Roman Power.