Exam 1a
advertisement

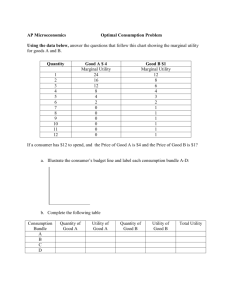
Ag Econ 1041 First Exam, 140 points September 22, 2011 Name ________KEY__________________ 8 a.m. Section True/False – one point each T F 1. Opportunity cost includes both benefits and costs of the foregone alternative. T F 2. Market outcomes are the price and quantity that buyers and sellers agree upon. T F 3. My decision in purchasing a sweatshirt depends on how many sweatshirts are available in Columbia. T F 4. The demand for sunscreen will be increasing now that autumn has arrived. T F 5. People make decisions at the margin rather than average. T F 6. An incentive may persuade people to act differently. T F 7. Supply creates demand. T F 8. Utility measures a consumer’s level of satisfaction. T F 9. The principle of diminishing marginal utility means as more of a product is consumed, the total utility from the good diminishes. T F 10. If marginal utility per dollar spent on good X exceeds the marginal utility per dollar spend on good Y, total utility rises by increasing the consumption of X. T F 11. By maximizing his or her utility, a consumer uses his or her resources efficiently. T F 12. The economically efficient level of pollution is zero. T F 13. Demand is downward sloping because as price falls, we have more purchasing power and the good with the lower price is a better deal. T F 14. The supply of wheat may shift to the right if the weather is poor for producing wheat. T F 15. As Post cereals lower price for breakfast cereals, it expects sales of cereal to decline. T F 16. If the price of hamburger decreases, we expect the price of hamburger buns to fall. 1 T F 17. Our decision about the color of t-shirts is based on the difference in utility we anticipate from the various colors. T F 18. The equilibrium price of bread is the price where buyers and sellers agree on the amount of bread exchanged. T F 19. Demand is the relationship between price and the quantity consumers are willing and able to buy. T F 20. If demand and supply both increase by the same amount for backpacks, then price will increase. T F 21. Production is the combination of inputs to create outputs. T F 22. There is a negative relationship between the price of steel and the quantity supplied of steel. T F 23. Prices are signals that help resources be allocated efficiently in a market. T F 24. A basic assumption made by economists about human behavior is that people try to maximize their utility. T F 25. The true cost of something is what you give up for it. T F 26. The marginal benefit of a good to the buyer must exceed the marginal cost if a purchase is to occur. T F 27. A decrease in price suggests that a good is becoming scarcer. T F 28. Efficient decisions are made at the average rather than the margin. T F 29. The opportunity cost of a purchase is never more than the price paid for the good. T F 30. Markets work best when the government dictates the price. Multiple Choice – two points each ___a___ 31. The income elasticity of demand is a) Positive for a normal good b) Zero for an inferior good c) Less than one for an income inelastic complement d) Only answers A and B are correct e) Answers A, B and C are correct 2 ___a___ 32. If substitutes are easy to find, then demand for the good is likely a) Elastic b) Inelastic c) Unit elastic d) Perfectly elastic e) Substitutes don’t have any effect on elasticity ___a___ 33. Which of the following is a consumer goal? a) Satisfaction or happiness b) Profit c) Increase supply d) Increase quantity supplied e) All of the above ___b___ 34. Researchers have found a hybrid corn that is cheaper to grow. This technological breakthrough a) Increases the demand for corn b) Increases the supply of corn c) Decreases the supply of corn d) Decrease the demand of corn e) Both answers A and B are correct ___b___ 35. Market equilibrium occurs when a) All markets become equal b) The quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied c) Opposing forces pull demand and supply apart d) Demand and supply move in opposite directions e) Demand and supply change so that they are equal at all possible prices ___b___ 36. Which of the following raises the equilibrium price of cement? a) An increase in the supply of cement b) An increase in the demand for cement c) A decrease in the demand for cement d) An increase in the quantity of cement demanded e) An increase in the quantity of cement supplied ___b___ 37. If producers believe the price of leather shoes will increase in a few months, today a) The supply curve for leather shoes shifts rightward b) The supply curve for leather shoes shifts leftward c) There is a movement along the supply curve for leather shoes d) The equilibrium price of leather shoes falls e) The equilibrium quantity of leather shoes increases 3 ___c___ 38. Which of the following represents a quantity demanded of pies? a) $5 per pie b) 6 pies c) 2 pies per week at $5 each d) 8 pies per month e) $5 ___a___ 39. Changes in which of the following factors do not shift the demand curve? a) The price of the good b) Buyers’ incomes c) The number of buyers d) The price expected in the future e) None of the above ___a___ 40. Consumers eat salsa with taco chips. The price of salsa rises. How does the increase in the price of salsa affect the demand for taco chips? a) It decreases the demand for taco chips b) It increases the demand for taco chips c) It has no effect on the demand for taco chips d) It will decrease the demand for taco chips only if taco chips are a normal good e) It could increase, decrease or have no effect on the demand for taco chips, but more information is needed to determine the impact Short answers – five points each 41. Draw a supply curve for copper production and then show what happens to supply if input prices decline. $/Q S S1 0 Q 42. If your marginal benefit from going to a concert were just equal to your marginal cost, would you go? Why? No; no gain 4 43. What does it mean to say there is a negative slope to a demand curve? P ↑ then Q ↓ or vice versa 44. If your marginal utility is greater than the price or marginal cost, why might you not buy the product? There may be a better choice or there may be a constraint like no money 45. Show the result of increased fertilizer, pesticide and seed prices on the supply of flowers. $/Q S1 S P1 P0 D 0 Q1 Q0 Q 46. In economic terms, why does the U.S. President support the military action in Afghanistan? MU ma > MU of not MC MC 47. Why do we often change what we consume after we consume more of that good? Diminishing marginal utility 5 48. Diagram the situation in the pork industry where demand increases and price still decreases. $/Q S0 S1 P0 P1 D 0 Q0 Q1 D1 Q 49. Diagram the current change that is happening in the market for gardening supplies. $/Q S P0 P1 D D1 0 Q1 Q0 Q 50. Diagram the impact on the market for cellular phones of substantially improved technology used by producers to make the phones. $/Q S S1 P0 P1 D 0 Q0 Q1 Q 6 51. Why do reduced cheeseburger prices cause an increase in the quantity demanded of french fries? They are complements 52. What do we call the best option foregone when a decision is made? Opportunity cost 53. Diagram the result of income decreasing on the housing market. $/Q S P0 P1 D D1 0 Q1 Q0 Q 54. How would we measure the impact on the demand for charcoal caused by a change in the price of charcoal grills? Cross-price elasticity 55. Why don’t we always do everything that has MU/MC > 1? There may be better choices or constraints (if they list a constraint like income it is ok) 7 56. Using two diagrams show the difference between an increase in demand and an increase in quantity demanded. Increase in Qd Increase in D $/Q P0 P1 D1 D 0 Q D Q0 Q1 The following question is valued at 10 points 57. What will happen to the market price if a) Input costs increase ↑ b) Utility of consumers decreases ↓ c) Price of a substitute rises ↑ d) Income increases ↑ unless inferior good e) Production technology improvements are implemented ↓ 8