bioinfo_2014_2a
advertisement

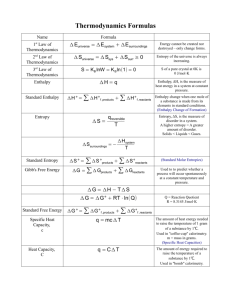
covalent interactions + non-covalent interactions = structural stability of (bio)polymers in the operative molecular environment Energy, entropy and reaction coordinate (Q) of molecular folding process 1 covalent interactions in proteins: disulfide bridges non-covalent interactions not dependent on solvent influenced by solvents Van der Waals Rotational Vibrational electrostatic solvent dependent interactions hydrogen bonds hydrophobic Interactions direct interations with solvents 2 3 in proteins: non-covalent interactions not dependent on solvent influenced by solvents Van der Waals Rotational Vibrational electrostatic solvent dependent interactions hydrogen bonds hydrophobic Interactions direct interations with solvents 4 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 5 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 6 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 7 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 8 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 9 energy contribution not dependent on molecular environment 10 influenced by solvent • electrostatic interactions • dipolar interactions • hydrogen bonding 11 hydrogen bond 2a. enthalpy and entropy in protein folding 12 hydrogen bond 2a. enthalpy and entropy in protein folding 13 hydrogen bond 2a. enthalpy and entropy in protein folding 14 electrostatic interactions 15 16 solvent dependent • hydrophobic interactions • direct interations with solvents 17 The accessible surface of a protein is defined as the van der Waals envelope of the molecule expanded by the radius of the solvent sphere about each atom center (Lee, B and Richards, FM. The interpretation of protein structure: estimation of static accessibility. J. Mol. Biol., 55, 379-400 (1971) The vdW surface of a molecule (shown in red) is defined as the surface of the union of balls representing all atoms, with radii set to the vdW radii. The accessible surface of the same molecule (shown in green) is the surface generated by the center of a sphere rolling on the vdW surface. The radius of this sphere is usually set to 1.4 Angstroms, the radius of a water molecule. The molecular surface (shown in magenta) is the lower envelope generated by the rolling sphere. It differs from the vdW surface in that some areas are inaccessible to the rolling sphere. 18 19 20 TOTAL CONFORMATIONAL ENERGY E=Ea+Er+Ees+El+Et+Ef+EH+EHf Ea Er Ees El Et Ef EH Ehf attractive repulsive electrostatic potential bond lenght changes bond angle changes torsional potential hydrogen bond hydrophobic interactions FORCE FIELD 21 thermodynamics of protein folding from http://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/olhydrophobprot.html from http://www.lanl.gov/bmsi/Individual%20Research/Werner/WernerFolding.html 2a. enthalpy and entropy in protein folding 22 2a. enthalpy and entropy in protein folding 23