Information systems and strategic management
advertisement

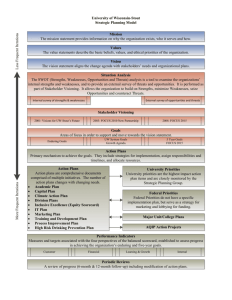
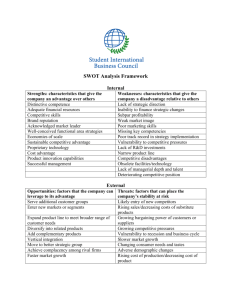
Definition of an Enterprise System • An enterprise system is an interrelated set of information systems (technologies) working together for the purpose of facilitating planning, control, coordination, and decision making in businesses and other organisations to aid in achieving the vision and mission of the organisation Environment Organisation Input Processing Feedback Output Enterprise Systems: Decision Support Systems Basic I.S. Activities • Basic activities: – Input: capturing or collecting raw data from inside or outside the organisation – Processing: converting the raw data into a more appropriate or useful form – Output: transferring the processed data to the people or business activities that need it – Feedback: output used to refine input • Basic Components – Organisations: consist of specialised units with a clear-cut division of labour, e.g. sales, manufacturing, personnel, finance – People: use information from I.S. in their jobs – Technology: the means by which data are transformed and organised for business use • Hardware, Software, Storage technology, Communications technology The Organisation Organisational Problem Organisational Level Strategic Senior Management General or Middle Management Tactical Knowledge or Data Workers Knowledge Operations Production Workers P ro duct io n Fin an ce/ Sales/ Hum an acco un t in g m ark et in g Reso urces Strategic Management – Defined Art & science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating, cross-functional decisions that enable an organization to achieve its objectives Strategy Formulation Vision & Mission External Opportunities & Threats Internal Strengths & Weaknesses Long-Term Objectives Alternative Strategies Strategy Selection Strategy Implementation Annual Objectives Policies Employee Motivation Resource Allocation Strategy Implementation Action Stage of Strategic Management – Most difficult stage Mobilization of employees & managers Interpersonal skills critical Consensus on goal pursuit Strategy Evaluation Internal Review External Review Performance Metrics Corrective Actions Strategy Evaluation Final Stage of Strategic Management Subject to future modification Today’s success no guarantee of future success New & different problems Complacency leads to demise Strategic Management • Integrating Intuition and analysis – objective, logical, systematic approach for making major decisions in a way that allows effective decisions to be made under conditions of uncertainty. • Adapting to change – organizations should continually monitor internal and external events and trends so that timely changes can be made as needed. – The rate and magnitude of changes that affect organizations are increasing dramatically. Strategy Formulation Vision & Mission External Opportunities & Threats Internal Strengths & Weaknesses Long-Term Objectives Alternative Strategies Strategy Selection Key Terms Vision Statement – What do we want to become? Mission Statement – What is our business?: Mission statements are “enduring statements of purpose that distinguish one business from other similar firms. A mission statement identifies the scope of a firm’s operations in product and market terms.” It addresses the basic question that faces all strategists: “What is our business?” It should include the values and priorities of an organization. Mission state examples • Microsoft vision: A personal computer in every home running Microsoft software. • Microsoft is to create software that empowers and enriches people in the workplace at school and at home. Key Terms Opportunities and Threats (External) Largely beyond the control of a single organization Process of conducting industrial analysis: research, gathering and assimilating external information Key Terms Opportunities & Threats (External) Analysis of Trends: • Economic • Social • Cultural • Demographic/Environmental • Political, Legal, Governmental • Technological • Competitors Take advantage of External Opportunities Avoid/minimize impact of External Threats Key Terms Strengths & Weaknesses (Internal) An organisations controllable activities that are performed especially well or poorly Key Terms Strengths & Weaknesses (Internal) Analysis of performance in in functional areas such as: • Management • Marketing • Finance/Accounting • Production/Operations • Research & Development • Computer Information Systems Long-term Objectives: Objectives or specific results that an organization seeks to achieve in pursuing its basic mission. Essential for ensuring the firm’s success • • Provide direction • Aid in evaluation • Create synergy • Focus coordination • Basis for planning, motivating, and controlling The objectives should be at least measurable, consistent clear and reasonable. Key Terms Strategies:Means by which long-term objectives are achieved Some Examples 1. Geographic expansion 2. Diversification 3. Acquisition 4. Market penetration Annual Objectives:Short-term milestones that firms must achieve to attain long-term objectives Policies:Means by which annual objectives will be achieved Some benefits of SM • Its benefits can be financial and non financial : – enhanced awareness of external threats, – an improved understanding of competitors’ strengths, – increased employee productivity, – reduced resistance to change, – and a clearer understanding of performancereward relationships. Impact upon enterprise structure • Scott Morton’s 5 levels of organisational restructuring Impact upon enterprise structure • evolutionary levels: • localised exploitation within individual business functions. The primary objectives addressed are local efficiency and effectiveness; • internal integration between different systems and applications, generally involving not just automation, but also rationalisation, and using a common IT platform. Efficiency and effectiveness are enhanced by coordination and cooperation within the enterprise; • Impact upon enterprise structure • revolutionary levels: • business process redesign, involving more thorough re-evaluation of the enterprise value-chain and the production process, and more far-reaching change. • business network redesign, the reconfiguration of the scope and tasks of the business network involved in the creation and delivery of products and services. Coordination and cooperation extend, selectively, beyond the enterprise's boundaries. • business scope redefinition, involving migration of functions across the enterprise's boundaries, to the extent of changing the organisation's conception of the business it is in. Questions on the class • Discuss which stage(s) of the strategic formulation process are the most suitable to the utilisation of Enterprise information systems. • Discuss how you, as head of the school of computing would derive strategies for increasing the popularity of DT211 “degree in computing”; this can not include altering module syllabi…