IB 2 Karyotypes
advertisement

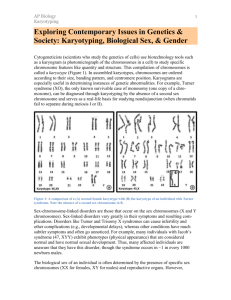
Errors in Meiosis Karyotypes & Chromosomal Abnormalities Karyotype • A photograph of an organism’s chromosomes • Homologous chromosomes are grouped together • Based on size, banding pattern, and location of centromere Arranged from largest smallest, sex chromosomes at the end Karyotype • Helpful in finding chromosomal abnormalities • Will NOT show genetic traits or disorders • Can NOT tell if baby has blue eyes • Can NOT tell if baby has cystic fibrosis • Can tell if baby has too many chromosomes or pieces missing Chromosomal Abnormalities • Nondisjunction • Chromosome (or chromosome pair) fails to separate during meiosis • Results in an incorrect number of chromosomes for daughter cells Chromosomal Abnormalities • Problems with meiotic spindle causes errors • Homologous chromosomes do not separate properly during Meiosis I • Sister chromatids do not separate properly during Meiosis II • Results in too many or too few chromosomes 2n nn-1 nn+1 error in Meiosis 1 error in Meiosis 2 all with incorrect number 1/2 with incorrect number Nondisjunction • Trisomy • Cells have three copies of a chromosome • Monosomy n-1 n • Cells have one copy of a chromosome n+1 n trisomy 2n+1 monosomy 2n-1 Nondisjunction in Humans • High frequency in humans Polyploidy = nondisjuction of ALL chromsome pairs -occurs in plants -fatal in animals • Most embryos spontaneously abort • Alterations are too disasterous • Developmental problems result from biochemical imbalance • Regulatory molecules? • Hormones? • Transcription factors? • Certain conditions are tolerated • Smaller chromosomes or sex chromosomes = survivable • Have a characteristic set of symptoms = syndrome Down Syndrome • Trisomy 21 • 3 copies of chromosome 21 • 1 in 700 children born in the U.S. • Chromosome 21 is the smallest human chromosome • But still has severe effects • Frequency of Down’s Syndrome correlates with mother’s age Mother’s age Incidence of Down Syndrome Under 30 <1 in 1000 30 1 in 900 35 1 in 400 36 1 in 300 37 1 in 230 38 1 in 180 39 1 in 135 40 1 in 105 42 1 in 60 44 1 in 35 46 1 in 20 48 1 in 16 49 1 in 12 Rate of miscarriage due to amniocentesis: 1970s data 0.5%, or 1 in 200 pregnancies 2006 data <0.1%, or 1 in 1600 pregnancies Genetic Testing • Amniocentesis in 2nd trimester • Sample of embryo cells • Stain & photograph chromosomes • Usually in metaphase • Analysis of karyotype Sex Chromosome Abnormalities • Human development more tolerant of wrong numbers in sex chromosomes • Still produces a variety of distinct syndromes in humans • XXY = Klinefelter’s Syndrome (male) • XXX = Trisomy X Syndrome (female) • XYY = Jacob’s Syndrome (male) • XO = Turner’s Syndrome (female) Klinefelter’s Syndrome • XXY male • 1 in every 2000 live births • Have male sex organs, but are sterile • Feminine characteristics • Some breast development • Lack of facial hair • Tall • Normal intelligence Jacob’s Syndrome • XYY male • 1 in every 1000 live male births • Slightly taller than average • More active • Normal intelligence, possible reading disabilities • Delayed emotional maturity • Normal sexual development Trisomy X • XXX female • 1 in every 2000 live births • Produces healthy females • Why? • Barr bodies • All but 1 X chromosome becomes inactivated Turner’s Syndrome • Monosomy X or XO female • 1 in every 5000 live births • Varied degree of effect • Webbed neck • Short • Sterile error of replication Changes in Chromosome Structure • deletion • loss of a chromosomal segment • duplication • repeat a segment error of crossing over • inversion • reverses a segment • translocation • move segment from one chromosome to another Any Questions??