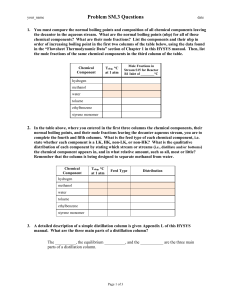
Mole Fractions in Stream S14 for Reactor R1 Inlet of ______°C
advertisement

Problem SM.4 Questions your_name date 1. As with column C3 in Problem SM.3, you must first compare the normal boiling points and composition of all chemical components leaving the decanter in the organic stream. What are the normal boiling points (nbp) for all of those chemical components? What are their mole fractions? List the components and their nbp in order of increasing boiling point in the first two columns of the table below, using the data found in the “Flowsheet Thermodynamic Data” section of Chapter 1 in this HYSYS manual. Then, list the mole fractions of the same chemical components in the third column of the table. Chemical Component Tnbp, C at 1 atm Mole Fractions in Stream S14 for Reactor R1 Inlet of ________°C hydrogen methanol water toluene ethylbenzene styrene monomer 2. Furthermore, you are to complete the fourth and fifth columns in the above table. What is the feed type of each chemical component, i.e. state whether each component is a LK, HK, non-LK, or non-HK? What is the qualitative distribution of each component? State which stream or streams (i.e., distillate and/or bottoms) the chemical component appears in, and in what relative amount, such as all, most or little. If necessary, refer to the Problem SM.3 handout to refresh your memory about the concept of key and non-key components. Remember that the column is being designed to separate the reactants from the products. Chemical Component Tnbp, C at 1 atm Feed Type Distribution hydrogen methanol water toluene ethylbenzene styrene monomer 3. Column C1 is depicted on the next page. What is the functional form for the HYSYS simulation algorithm for this column, based on knowing the mole fraction of the heavy-key component in the distillate stream? Define each of the variables in this functional form (HINT: Refer to the Problem SM.3 assignment). V , D , B , QPC , QR rcolumn____ F , PPC , PPC , PR , PR , N S , N FS , R, z D , HK , VRPC where QPC is the ____________ energy rate or heat duty, Q R is the ____________ energy rate or heat duty, Pu is the pressure of the partial ____________ or ____________ unit, Pu is the pressure drop across the partial ____________ or ____________ unit, N S is the number of Page 1 of 2 your_name Problem SM.4 Questions date ____________ stages, NFS is the ____________ stage number, R is the ____________, z D , HK is the total mole fraction of the ____________ in the distillate, and VRPC is the vent ratio for the partial ____________. The vector i is a short notation to represent the temperature, pressure, flow rate, and molar composition (i.e., total mole fractions) of Stream i. 4. How might the value for the vent ratio be estimated? vent ratio flow rate sum of all non-condensables in the feed total flow rate of the feed vent ratio ________ kgmol / h in Stream S 22 ________ kgmol / h in Stream S 22 A value one-hundred times greater like 1×10-2 should be used for the vent ratio of the condenser vapor stream, because this value is less likely to constrain the iterative process that converges the material and energy balances of the distillation column. A stricter vent ratio like 1×10-3 will lead to an iteration error of “two liquid phases were found on the condenser stage.” Using 1×10-2 eliminates this error. What are the composition profiles of just the LK and HK in the distillation column? Use the Performance/Plots page to print these profiles. Note that toluene is the light key and ethylbenzene is the heavy key in this problem. Below is the composition profile of toluene and ethylbenzene for a reactor inlet temperature of ________°C. Use Snipping Tool to copy and paste graph here. Page 2 of 2