ICS321 / IBM205 Management Information Systems
advertisement

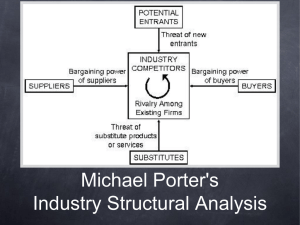
ICS321 / IBM205 Management Information Systems Dr. Kenneth Cosh Lecture 3 Review • What is MIS? • What types of information system are we dealing with? • How has the role of information systems changed? – Business Pull factors – Technology Push factors • What distinct era’s has IS been through? Today’s Topic • Strategic Information Systems • Five Forces • How IS drives alternative strategies Strategic Information Systems • No longer is IS an afterthought when considering corporate strategy, now it is often either the ‘cause’ or the ‘driver’ of strategy. – Cause; • Taking advantage of some core competency within the organisation’s IT. – Driver; • Using IT to realise the organisation’s strategy. Strategic Information Systems • A strategic information system is any information system which helps an organisation gain any kind of competitive advantage. • Michael Porter’s model of competitive strategy suggests that any business which wants to survive and succeed has to develop strategies to counter 5 key forces. – – – – – Rivalry of Competitors Threat of New Entrants Threat of Substitutes Bargaining power of Customers Bargaining power of Suppliers Porter’s 5 Forces Threat of New Entries Bargaining Power of Suppliers Intensity of Rivalry Threat of Substitutes Bargaining Power of Buyers Bargaining Power of Customers • • • • • • • • • Buyer concentration vs Firm Concentration Buyer Volume Buyer switching costs Ability to backward integrate Price Sensitivity Product Differences Brand Identity Impact of quality / performance Buyer Profits Bargaining Power of Suppliers • • • • Differentiation of Inputs Switching costs of suppliers Supplier Concentration Ability to forward integrate Threat of Substitutes • Impact on Supplier & Buyer Power Threat of New Entries • • • • • • • • Economies of Scale Brand Identity Switching costs Capital Requirements Access to Distribution Cost Advantages Government Policy Expected Retaliation Intensity of Rivalry • • • • • • Industry Growth Product Differences Brand Identity Switching Costs Diversity of Competitors Exit Barriers Determining Strategy • Combine Porter’s Analysis with SWOT – Reduce Costs – Raise Barriers to Market Entrants – Establish High Switching Costs – Create New Products or Services – Differentiate Products or Services – Enhance Products or Services – Establish Alliances – Lock-in Suppliers or Buyers Reduce Costs • Gain advantage by selling more units at a lower price while maintaining/increasing it’s profit margin – Automation • Production using robots • Web based customer service – FAQs – Convert task from being labour intensive to being technology intensive. Raise Barriers to Market Entrants • Deters competition, thus increasing market potential – Gaining legal protection • Intellectual Property – Amazon.com owns a patent for one-click online purchasing until 2017 – It also owns a patent for techniques to predict what the customer may buy in the future. • Expense of entering market – Essential, but bespoke software. Establish High Switching Costs • Economically infeasible for customers to switch to a new supplier – Direct • Contracts which are expensive to break (e.g. mobile phone contract). – Indirect • Time and money expense of learning how to use Open Office. – Consider printers! Cheap printer, but expensive ink catridges. Create New Products / Services • Gain first mover advantage – Be the first to deliver a new product (that the customers want) • Lotus 1-2-3 Spreadsheet program – But how long did this advantage last? • E-Bay – the first online auction – But how long will it last? • Netscape? Differentiate Products or Services • Persuading customers my product is better than anyone elses. – Skype • Not the first internet telephone service, but better than competitors • Differentiated by adding video and other features such as mobile… Enhance Products / Services • Add value to existing products / services – Perhaps by adding information / help to a web portal – Offering traditionally physical transactions via the internet Establish Alliances • Focus on our core competency, but work closely with experts in symbiotic markets. – Strategic Alliances allow the tourism industry to offer complete vacation packages; • Combining flights, hotels, car rental, restaurant, mobile phones etc. – Affiliate programs? • The web allows anyone to create an alliance with another service provider or retailer. Lock-in Suppliers / Buyers • Depends entirely on bargaining power. – Walmart has power to influence its suppliers, such that they are locked in to them – Software industry • often customers fear high switching costs, and if the software provider continues to improve their product… – Flash • Free to download, but buy the development tool. The more people who download the player, the more companies are willing to invest in the development kit – and the more companies who invest, the more people download… Competitive Strategies • 5 key strategies (and some others) have been developed to counter the threats of competitive forces. – Cost Leadership – Differentiation – Innovation – Growth – Alliance Cost Leadership • Become the low-cost producer of products, by finding ways to lower our costs, lower our customers and suppliers costs or increase our competitors costs. – IT can drive cost reduction, such as reducing labour costs. – SCM systems can assist reducing suppliers costs (Walmart). – Online Price adjustment, to match best match competitors prices. Differentiation • Develop ways to make our product different from our competitors (or reduce our competitors differentiation). Focus on a niche or market segment. – IT can assist by introducing IT features to a product such as a camera on a phone. – Reduce competitors by integrating their differentiated ideas (adding a camera to our phone too!) – Ross Operating Valves, allows customers to design their desired valves online. Innovation • Find new ways of doing business, developing new markets or unique products. Making changes to business processes to change the way business is done within the industry. – Create new products which include IT, e.g. online stock trading – Amazon constantly innovates introducing new products / services – Paypal introducing a system for making payments online. Growth • Increasing capacity to produce more goods and services, expanding into global markets or diversifying into new products. – Using IT to manage global business, such as by using a global intranet – Using technology to increase capacity, through automating processes. Alliance • Building alliances with suppliers, customers, competitors, consultants etc. Creating links through mergers, acquisitions or joint ventures. Creating ‘virtual’ organisations – Use technology to improve communication channels between alliance partners – Walmart links with supplier to enable automatic inventory replenishment – a win win alliance. – Online inventory management for supplier, with shipment tracking for customer.