Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Alpha Particles
advertisement

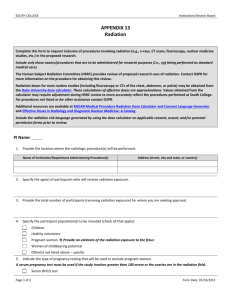
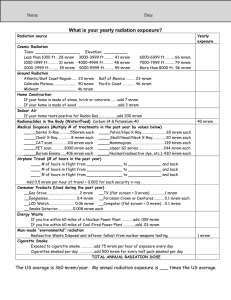
Ions and Isotopes Ions have charge – Cations + – Anions - Isotopes vary in mass – Neutrons – Radioisotopes Unstable nuclei Emit energy -radiation Medical uses as tracers and treating disease Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Alpha Particles Alpha Particles: 2 neutrons and 2 protons They travel short distances, have large mass Only a hazard when inhaled Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Beta Particles Beta Particles: Electrons or positrons having small mass and variable energy. Electrons form when a neutron transforms into a proton and an electron or when a proton transforms into a positron and a neutron: Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Gamma Rays Gamma Rays (or photons): Result when the nucleus releases Energy, usually after an alpha, beta or positron transition Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: X-Rays X-Rays: Occur whenever an inner shell orbital electron is removed and rearrangement of the atomic electrons results with the release of the elements characteristic X-Ray energy Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation: Neutrons Neutrons: Have the same mass as protons but are uncharged They behave like bowling balls Four Primary Types of Ionizing Radiation Alpha particles Beta particles Gamma rays (or photons) X-Rays (or photons) Neutrons Ionization Ionizing radiation is produced by unstable atoms. Unstable atoms differ from stable atoms because they have an excess of energy or mass or both. Unstable atoms are said to be radioactive. In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation. Types or Products of Ionizing Radiation neutron or X-ray DNA and Radiation Ionizing Radiation at the Cellular Level Causes breaks in one or both DNA strands or; Causes Free Radical formation Commonly Transported Radioisotopes Americium-241= Diagnose thyroid disorders, smoke detectors. Cesium-137= Cancer treatment. Iodine-125,131= Diagnosis & treatment liver, kidney,heart, lung and brain. Technetium-99m=Bone and brain imaging; thyroid and liver studies; localization of brain tumors. rad 1 rad = 1 Roentgen rem Roentgen Equivalent Man The unit of dose equivalent for any type of ionizing radiation absorbed by body tissue in terms of estimated biological effect - Unit of dose equivalent Dose in health record is in units of rem 1 rem = 1 Roentgen 1 Sievert (Sv) = 100 REM 1 mSv = 100 mREM Quality Factor (Q) The specific value that accounts for the ability of different types of ionizing radiation to cause varying degrees of biological damage – X-rays, gamma rays, & beta particles – Neutrons & High energy protons – Alpha Particles 1 10 20 Units of Radioactivity Curie (Ci) = 2.22 E12 dpm or 3.7E10 dps Becquerel (Bq) = 1 dps Maximum Dose/year = 5 REM or 50 mSv Maximum Dose/year for Declared Pregnant Woman & Minors= 0.5 REM or 5 mSv Half Life Calculation Annual Dose Limits External/Internal Exposure Limits for Occupationally Exposed Individuals Adult ($18 yrs) Minor (< 18 yrs) Whole body* 5000 mrem/yr 500 mrem/yr Lens of eye 15000 mrem/yr 1500 mrem/yr Extremities 50000 mrem/yr 5000 mrem/yr Skin 50000 mrem/yr 5000 mrem/yr Organ 50000 mrem/yr 5000 mrem/yr Dose Response Relationships 0-150 rem—No or minimal symptoms 150-400 rem—Moderate to severe illness 400-800 rem—Severe illness deaths start above 500 rem Above 800 rem—Fatal ***Acute whole body doses Your Annual Exposure Activity Smoking Typical Dose 280 millirem/year Radioactive materials use in a UM lab <10 millirem/year Dental x-ray Chest x-ray Drinking water Cross country round trip by air Coal Burning power plant 10 millirem per xray 8 millirem per xray 5 millirem/year 5 millirem per trip 0.165 millirem/year Effective doses of ionizing radiation from medical procedures Subjects Total Subjects undergoing more subjects (n) than 1 procedure (%) Mean annual effective dose from procedures (mSv) All subjects 952 420 68.8 2.4 •Males •Females •18–34 y •35–39 y •40–44 y •45–49 y •50–54 y •55–59 y •60–64 y 453 078 57.9 2.3 499 342 78.7 2.6 233 586 49.5 1.0 118 365 65.7 1.6 144 728 72.1 2.0 146 703 74.9 2.6 131 209 78.2 3.3 115 520 79.5 4.1 62 309 85.9 5.2 Fazel R et al. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 849-57. Medical imaging procedures with largest contribution to cumulative effective dose Procedure Average effective dose (mSv) Proportion of the total effective dose from all study procedures (%) Myocardial perfusion imaging CT of abdomen CT of pelvis CT of chest Diagnostic cardiac catheterization Radiography of the lumbar spine Mammography CT angiography of the chest (noncoronary) Upper gastrointestinal series CT of head or brain PCI 15.6 8 6 7 7 1.5 0.4 15 22.1 18.3 12.2 7.5 4.6 3.3 3.1 3.1 6 2 15 2.4 2.0 1.8 Fazel R et al. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 849-57. Estimated Exposure To The National Population Between 320 – 360 mr/yr