DALSA_WPhilbrook
advertisement

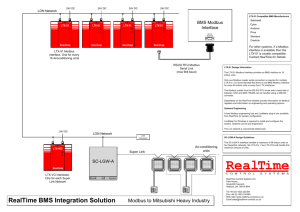
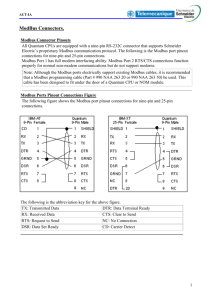
PLCs and Vision Appliance Functions IPD Technical Conference February 19th 2008 PLC Types ModBus PLC EtherNet/IP AB Control Logix GE Fanuc SNP / SRTP Melsec PLC Omron C Motoman MRC / XRC Modbus PLC Modbus connection consists of 2 parties Modbus Slave : Offers register storage which it accesses locally makes available to one or more masters Modbus Master accesses one slave device register set ModBus PLC VA can be added as Modbus Master Modbus Slave VA as Modbus Master TCP/IP Can be a master of multiple slave devices Add a PLC Destination for each IP Address RS232 Only one PLC slave per serial port VA as Modbus Slave Multiple Modbus masters can connect to one VA Modbus Slave. 2 VAs can communicate with each other; One VA as Master, connected to the other VA as a Slave. ModBus-Function/Data Block Four Major Data Blocks From VA perspective, each Data Block has a separate zero-based address space Coil Status – 1 Bit Read/Write Input Status – 1 Bit Read Only Holding Register – 16 Bit Read/Write Offsets specified in 16 Bit Words, but can overlay 32 bit and 64 bit float types Input Register – 16 Bit Read Only ModBus – Data Types Holding and Input Register Data Blocks support following types: Char – single ASCII character Signed 16 bit Unsigned 16 bit Float 32 Double (64 bit float) Offset specified to access register in 16 bit Word Units, e.g., first 3 float 32 registers are: myFloat32[0] , myFloat32[2], myFloat32[4] e.g., first 3 double registers are: myDouble64[0] , myDouble64[4], myDouble64[8] ModBus –Register Attached Vars When ModBus Dest. Defined, Register Attached Variable is created Default Attached Var naming convention “MB[DestID][FuncID][TypeID]” E.g., For IP@192.168.10.175 , Holding Register, signed 16 => MB175HRs16 Can change default attached var name to anything desired. Index attached var to access any register inside the associated ModBus data block. e.g., myFloat32Var[20] , access 11th float32 reg EtherNet/IP VA is the Server to a : Implicit Messaging Client E.g. ControlLogix 5550 Controller PCCC Client E.g. Allen-Bradley SLC5/05 EtherNet/IP – Implicit Message Use RSLogix 5000 SW to configure Add VA ETHERNET-MODULE in I/O Configuration folder. Enter VA IP Address, and Assembly object data, Name Assembly Instance Size Input 2 100 Output 1 100 Configuration 1 0 Add VA for Implicit Messaging with RSLogix 5000 EtherNet/IP – PCCC Client Setup Use RSLogix 500 SW to Configure In Channel Configuration Dialog, Configure Channel 1 (Ethernet) Add Message Instruction to Read or Write to VA. Target Device: PLC5 for VA Data Table Address, writes go to VA Input Assembly Object, reads are from VA Output Assembly Object EtherNet/IP– Data Types SINT – Single ASCII character INT - Signed 16 bit DINT - Signed 32 bit REAL - Float 32 Register Indexing is type size aware e.g., first 3 float registers are: myFloat32[0] , myFloat32[1], myFloat32[2] Definition of EtherNet/IP Dest. of a given type, overlays Input & Output Assembly Objects with that type. EtherNet/IP –Register Attached Variables When EtherNet/IP Dest. Defined, Register Attached Variable is created Default Attached Var naming convention “EIP[TypeID]” E.g., For real float 32 => EIPreal Can change default attached var name to anything desired. Index attached var to access any register inside the Assembly data blocks. Register Write - operates on Input Assembly Object Register Read - operates on Output Assembly Object Control Logix Uses Explicit Messages to: Query Global Scope and Program Scope Tags Read / Write Global Scope Tag variables Read Program Scope Tag Variables Supports user defined types Supported by Control Logix and Compact Logix processors GE Fanuc SNP (Series 90 Protocol) RS232 Serial Protocol for accessing GE Fanuc Series 90 PLCs Protocol defines various Register Sets which the VA can read or write . Add SNP Destination with VA GE Fanuc SRTP An Ethernet Protocol similar to SNP Allows connecting to GE Fanuc Series 90 PLCs with an Ethernet Interface MELSEC/Omron PLC VA is the Master to a : TCP/IP MELSEC Slave RS232 MELSEC Slave MELSEC/Omron - Protocols MELSEC 1C ACPU MELSEC 1C AnACPU MELSEC 2C MELSEC 3C MELSEC 4C OMRON C MELSEC/Omron – Data Types One Data Space supports following types: Unsigned 16 bit ( 1 Register WORD Size) Fixed point ( 4 Register WORD Size) Offset specified to access register in 16 bit Word Units, e.g., first 3 fixed registers are: myFixed[0] , myFixed[4], myFixed[8] MELSEC/Omron–Register Attached Variables When MELSEC Dest. Defined, Register Attached Variable is created Default Attached Var naming convention “MLS[StationNum]_[ProtoId][TypeID]” E.g., For Station 1 Protocol 1C ACPU/Format2 fixed point register => MLS1_1CAF2fp Can change default attached var name to anything desired. Index attached var to access any register inside the MELSEC data block. e.g., myFixed[20] , access 6th (20/4+1)fixed point reg Index is always 16 bit WORD offset of register Motoman MRC/XRC Protocol RS232 Serial Protocol to access Motoman Robot Controllers Offers variables which controller can: Read with LOADV command Write with SAVEV command Supports types: BYTE, INT, REAL, Robot Axis in XYZ form VA Functions Event Driven Functions User Functions Internal Functions Event Driven Functions Solution Initialize Pre-Image Process Post-Image Process Periodic Functions Call with user specified frequency Input State Change Function Called when GPI rising/falling Event Driven Functions(cont.) Delayed Event Functions Called specified delay after an event Image Received Image Processed PLC Variable Change of State Called when associated register changes value, actual register must reside on VA Ethernet/IP Modbus Slave User Functions Function a user defines to be called by other functions passed parameters returns a value Internal Functions Math Functions String Functions Acquisition/ IO Control Logging History Control Misc Math Functions sin(radians) cos(radians) tan(radians) asin(x) arcsine of x in the range -p/2 to p/2 radians, where: -1 <= x <= 1. acos(x) arccosine of x in the range -p/2 to p/2 radians, where: -1 <= x <= 1. atan(x) arctangent of x in the range -p/2 to p/2 radians atan2(y,x) arctangent of y/x in the range -p to p radians exp(x) the exponential value of x. logn(x) the natural logarithm of x sqrt(x) square root of x pow(x,y) x raised to the power y String Functions find(substring, inString) finds first substring in the input inString, returns index of first character. Returns -1 if no match. Example: idx = find("00", "SM WRA 0057 4321") returns 7, or sets idx = 7. substring(string, startIndex, length) forms a sub-string from the input string, beginning at startIndex (zero-based) of length characters. Example: s2 = substring("SM WRA 0057 4321" , 9, 0) returns string "57 4321" in s2. strlen(string) returns the number of characters in a string. getchar(string, index) returns the character located at index (zero-based) in the string. setchar(string, index, char) sets the character in string, located at index (zero-based), to char. int(string) converts the input string (of numbers) to an integer value. Example: x = int("33") sets x = 33 float(string) converts the input string (of numbers) to a floating point value. Example: x = float("57.499") sets x = 57.499 char( int ) Converts integer to a character type Acquisition/ IO Control Functions pulse(activeVal, offsetMillisec, durationMillisec) generates a pulse output. The pulse function can only be assigned to Global Outputs GPO4 through GPO7 on VA40 For Example, the statement: Global.GPO[4] = pulse(1,5,10) outputs on GPO4 an active-high pulse of 10 ms duration and offset 5 ms after the statement executes. trigger() generate an image trigger signal. The Sensor Trigger must be set to "Inspection Trigger" when using this function. triggersource(source) set the trigger source / mode to: freerun, internal timer, external trigger, or software Logging/History Control logstart(fileName, onClient) Start logging the processed frame data to the specified CSV file. For Example, logstart(C:\Logs\iHistlog78.csv,0) logstop() Stop logging data that was started by a logstart call. logimage( fileName ) Explicitly specify the file name for the next image logged on the server. resethistory() clears the history log of stored images and data. resetstatistics() clears the pass/recycle/reject counters. Misc. Internal Functions copy(source, dest, numElements) Copy numElements from source (an array of elements) to dest (an array of elements. The copy function can be used to cause multiple PLC registers to be updated in a single transaction. For Example (update 3 Modbus registers): print(string, endOfFile) Send a string of data to the default printer. timemillisec( ) cmd[0] = x cmd[1] = y cmd[2] = z copy (cmd, MB92HRs16, 3) returns current time in milliseconds getkey( ) Returns a new keyboard input if available, otherwise immediately returns 0.