Myths, Legends & Fables
advertisement

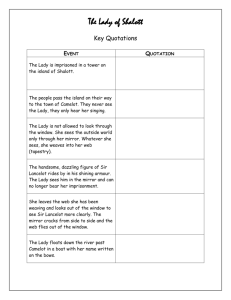
Short Story Unit What are they? Myths, legends & fables are stories that are passed down through many generations, but they all have a different purpose. Most of the time, these stories ARE NOT written down and are told by memory! Fables, Myths and Legends are very important, because this is how we remember past generations. It explains what they believe and give clues to their lives. Myths A myth is a story with a purpose. It tries to explain the way the world is. Myths also try to explain the relationship between gods and humans. Even though the events in a myth are usually impossible, they try to send a message that has an important social or religious meaning. Myths Cont… People have always tried to figure out common questions like who made the universe or questions like what causes a storm. Religion, gods, and myths were created when people tried to make sense out of these questions. For early people, myths were like science because they explain how things work. They also explained other questions that are now answered through modern science. 4 Rules for Myths Story that uses the Supernatural Interprets natural events Explains the nature of humanity (why we do what we do) 4. Expresses a cultures view of the universe 1. 2. 3. Eg. Greek Mythology – Hercules or King Arthur What is Greek Mythology The people of ancient Greece shared stories called myths about the gods, goddesses, and heroes in which they believed. Each god or goddess was worshipped as a deity and ruled over certain areas of the Greeks’ lives. These exciting stories explained natural phenomena that could not be explained by science in the ancient world. Why should we study Greek Mythology? The Ancient Greek culture has been kept alive by the oral and later written stories handed down through thousands of years. Modern plays, novels, television programs, movies and even advertisements refer to Greek gods, goddesses, heroes and their stories. Adventurous and exciting stories delight and entertain us. What is Mount Olympus? Traditionally regarded as the heavenly abode of the Greek gods and the site of the throne of Zeus These gods and goddesses did not actually live upon Olympus, rather the ancient myth can be understood to be a metaphor for the power of the sacred mountain It is believed the Olympians gained their supremacy in the world of gods after Zeus led his siblings to victory in war with the Titans Pantheon The Pantheon is a building in Rome which was originally built as a temple to all the gods of Ancient Rome. Literally translated, pan = all and theon = of the gods. A hole at the dome's top point allows daylight into the majestic main room, a shifting spotlight that slowly fades into twilight and allows no defense against the rain or the occasional Roman snowfall. Pantheon history states that the interior of the roof is intended to symbolize the heavens, and the giant hole above is supposedly the eyes of the gods. Who Were the Gods and Goddesses of the Pantheon on Mount Olympus? Zeus – Leader of the Olympian gods He ruled the Olympians. He was the god of the sky, lightning and thunder carrying a thunderbolt as his symbol. He married Hera, his sister, which was a family habit. He fathered many children with various goddesses and mortals. Hera – Wife of Zeus She was the protector of marriage and the home. She was associated with the peacock, because of her great beauty. She and Zeus were always quarreling. She was called the queen of intriguers, a vindictive and jealous wife, who frequently outwitted her husband, Zeus. Poseidon – god of the sea He built an underwater palace with a great pearl and coral throne. Although he chose Thetis, a beautiful water nymph, as his queen, he, like his brother Zeus, was a great wanderer fathering hundreds of children. He was a difficult god, changeful and quarrelsome, but created many curious forms for his sea creatures. He invented the horse for his sister Demeter, whom he loved. Hades – god of the Underworld He was the jealous brother to Zeus and Poseidon. He made Persephone his wife after stealing her from her mother, Demeter, who was his sister. Because he was a violent god, who was also very possessive of every new soul, he rarely left his underworld domain. Demeter - goddess of Corn and the Harvest She was the goddess of growing things. She was the mother of Persephone, whose father was Zeus. Her daughter was kidnapped by Hades and taken to the Underworld for six months of the year causing the change of seasons. Hestia – goddess of the hearth She was the sister of Zeus and the daughter of Cronos and Rhea. She represented personal and communal security and happiness. She was thought of as the kindest and mildest of the goddesses. She was of little mythological importance, appearing in only a few stories. Athena-Goddess of Wisdom, Justice, War, Civilization and Peace She was born full grown out of the head of Zeus. She taught man to use tools and taught his wife to spin and weave. She was the best-loved goddess on Olympus. She hated Ares, god of war, often besting him in battle. The Greek city of Athens is named after her. She was said to have created the spider. Apollo-The Sun God; God of Music, Poetry, Wisdom, Light and Truth He was the twin brother of Artemis and the most handsome of the gods. He was also the god of the healing arts and of medicine. He drove his chariot across the sky to pull the sun each day. His son, Phaethon, drives Apollo’s sun chariot with disastrous results. Artemis- Goddess of the Woods, Moon and the Hunt She was the twin sister of Apollo, whose mother was Leto and father was Zeus. She was a chaste huntress, who always carried a silver bow and arrows. She ruled over the untamed places of the earth. Dionysus-God of Revelry and the Vine He is said to be the only god on Olympus with a mortal parent. His creation of wine brings ecstasy and drunkenness to his revelers. Much of the ancient world’s greatest poetry was created in his honor. Ares - Cruel God off War He was a ruthless and murderous god, who displayed the worst of humanity’s traits. He, along with grief, strife, panic, and terror, roams the earth. Ironically, he was a coward, who fled the field of battle. Hephaestus-God of Fire, Volcanoes and the Forge He was the ugliest of the gods, who was rejected by his mother, Hera, when she hurled him off of Mount Olympus crippling him. He fashioned the armor and tools of the gods on a broken mountain near Mount Olympus. He made beautiful jewelry for the goddesses. Hermes- God of Mischief and Messenger of the Gods He was the precocious son of Zeus and Maia, a Titaness. As a baby, he made a lyre and pipe for his half brother, Apollo. He carried Apollo’s golden staff and flew around the heavens and earth on winged sandals. Aphrodite-Goddess of Love & Beauty She is the goddess of desire born from sea foam. Another myth credits her mother as Dione and her father as Zeus. After all the gods on Mount Olympus courted her, she married Hephaestus, the ugliest of the gods. Because she was judged the most beautiful of all the goddesses on Mount Olympus by Paris, the other goddesses envied her. Paris and the Golden Apple STOP! Read the MYTH, Paris and the Golden Apple. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS! Paris & Apple Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What are Paris’ parents named? What was Hecuba’s dream about? What other story do you know that uses the line, “fairest of them all”? Are there similarities between those stories? What 3 goddesses are in a beauty contest? What does Paris mean when he says, “How can a mortal man succeed when the gods have failed”? Where does Aphrodite tell Paris to go? Who is the most beautiful woman? Who is she married to? Name all of the Kings who agreed to help Menelaus fight Troy. (Hint: There are 6). Who thinks the Greeks are tricking the Trojans? What does Oenone mean when she says, “I died ten years ago”? Paris’ Questions Cont… BY YOURSELF answer these questions: (Value 20) 1. Are there elements of this myth that you find hard to believe? Explain fully. How are these elements an essential part of myths? 2. Would you describe Paris as a hero? Explain your answer. 3. What was the worst mistake made by a character in this story? Have you ever had to make a difficult decision? What helped you? Do you think Paris made the right or wrong choices? Explain. 4. How are the characters in this selection rewarded or punished? Do you think this myth is intended to teach a lesson? What lesson is it trying to teach? Paris Group Work Complete the handout Ms. Williams has given you, to complete a FANTASTIC example for future generations! Must be neat and use lots of color! Worth 30 MARKS! The Iliad The Iliad is a powerful, beautiful, and awe-inspiring work of ancient Greece. It combines the horridness and sometimes mundane part of war into a epic poem filled with art, illustrious descriptions, and a myriad of wonderful literary images. There are 24 books in the Iliad all together! Homer The Iliad was written by a man named Homer (not Simpson!) in 800 B.C.E Homer was a BLIND Greek poet and he probably lived during 800-700 B.C.E! Not a lot is known about Homer, and some scholars doubt that Homer actually wrote this epic poem. They suggest that perhaps a group of poets got together and shared all of the stories that they had been telling and combined them into one story. The Iliad Translated, it literally means The Story of Troy. The Iliad is the story of the battle of Troy. Some scholars believe that this battle never took place, and that the poem, being an oral tradition, was just embellished to make it more exciting. The original Iliad was written in the Greek dialect and has since been translated into hundreds of languages. Sample of the Iliad “Sing, O goddess, the anger of Achilles son of Peleus, that brought countless ills upon the Achaeans. Many a brave soul did it send hurrying down to Hades, and many a hero did it yield a prey to dogs and vultures, for so were the counsels of Jove fulfilled from the day on which the son of Atreus, king of men, and great Achilles, first fell out with one another.” Book I Summary 3 goddesses are fighting over a golden apple – because each one thinks they are the most beautiful and should have the apple Zeus, being smart enough to know not to pick one, asks Paris to chose the goddess who is the most beautiful Each goddess bribes Paris, but in the end, he chooses Aphrodite, who promises to give him the most beautiful bride in the land This angers the other two goddesses who vow revenge on him and the Trojans forever Summary Cont… Unfortunately, the most beautiful woman in the world, Helen, is already married to the Spartan King, and he will not let her be taken without a fight. When Paris visits Sparta, he steals away with Helen and some of the Spartan King’s money to Troy and doesn’t tell the King! The King of Sparta is very angry and gathers thousands of people to go to Troy and get Helen back. The Iliad opens in the 10th year of this war! Troy STOP! Let’s watch Troy! You will complete a quiz as you watch the movie! Also, look for major themes in the movie. We will discuss these themes after the movie is finished. Troy Major Themes Revenge – The revenge of Achilles – wants to punish anyone who has wronged him – Greeks seek revenge on the Trojans Glory and Honor – The war begins because another man’s wife left with someone else! The war goes on for 10 YEARS! Paris gives the sword of Troy to a boy leaving the city, because as long as the sword reminds in the hands of a Trojan, there is a future for Troy. Respect – Priam says, “Even enemies can show respect” when talking to Achilles about giving Hectar’s body back for a proper burial. Themes Cont… Persistence – Even though the war goes on for 10 years, the Greeks don’t give up. They have lost many men AND they haven’t seen their wives OR children! Love/Women – Women play an important role in shaping how these men act. Briseis loves Achilles and at one point, Achilles wants to go home and not fight anymore. The Trojan war starts because Helen leaves her husband. Also, the goddesses are the ones who cause the war (Paris and the Golden Apple)! Writing Assignment Write a ¾ page on the topic of one of the above themes we discussed. Use other examples from the movie to support your choice of theme. You can also relate this back to your life: have you ever tried to take revenge? Has a girl drove you crazy enough to do something you regret? GOOD COPY AND ROUGH COPY PLEASE! Value: 20 MARKS!!! Gods/Goddesses Project Now that you know all about the heavenly powers controlling everything in our world, it’s time for you to take control and learn about a god or a goddess of your choice! See handout and plan to have 3 days in the computer lab to complete the task… don’t leave your fate to the gods, get the work done! What's a Legend? Similar to a myth, a legend is a narrative told as a true story. Sometimes the details are difficult to confirm, but usually the story names people and identifies locations. The person telling the story usually does not claim to be an eyewitness to the events, but heard it from someone who knows someone who heard it from someone who was really there... Legends often contain a moral or a lesson and are told to uphold the values of the community. They often involve supernatural or religious elements. King Arthur King Arthur was a legendary king in England in the Middle Ages. His life has been retold many times over the centuries; hence, most of the incidents in his life have several versions. He established a brilliant court at Camelot, where he gathered around him the greatest and most chivalrous warriors in Europe, the Knights of the Round Table. Lancelot, Galahad, Percival and Gawain were notable knights. Other characters associated with the legends were Merlin, Morgan le Fay and Queen Guinevere. Legend of King Arthur King Arthur was a king who ruled England. He brought peace to the land because no enemy could defeat him and many backed away from his deadly sword. Arthur owned a special sword that was given to him and that could kill anyone. The scabbard, or the sword’s case, could instantly heal any disease. This sword was called Excalibur. When King Arthur was ruling England, he grew restless and the legend goes that he soon conquered France. He then formed Camelot and the Round Table. Camelot was Arthur’s royal castle and the place where the Round Table was located. Legend Cont… King Arthur and the knights were semi-fictional characters that protected England for over a century. The debate over whether they really existed is still a hot topic with historians. Most agree that he did rule England around 500 A.D. Since he lived before the middle ages, he was not the medieval knight that many think he was. Most believe that he did rule England for a short while, but not in the style of greatness that the stories make him out to be. Some historians believe that he did live in Camelot with his Round Table. No matter what the real facts are, it is true that King Arthur probably did exist. Legend Cont… Many people wonder if the Round Table was a round table, a group of men, or just a figure of speech. It was actually a real table created to seat over 150 knights in King Arthur’s castle, Camelot. It was made of very valuable wood and by its size would have been worth A LOT of money. It was created by Merlin as a wedding present when Arthur married Guinevere. There are rumors that said that Merlin enchanted the table to make it invincible when Arthur was alive. This is of course only a rumor. The round table was a majestic and powerful table. King Arthur and the Sword STOP! Read the story King Arthur and the Sword adapted from a story written by Sir Thomas Malory and hear how Arthur pulled Excalibur from a ROCK! King Arthur Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Who is Sir Ector? Why did Arthur’s father send him away? In your own words, tells me what the words on the sword meant. Why did Arthur pull the sword from the stone the 1st time? What happened when Sir Kay found out about the sword? What did Sir Ector ask Sir Kay to do with the sword? Why did Arthur have to pull the sword from the stone multiple times? What is the relationship like between Arthur and Sir Ector and Sir Kay? Give an example to prove your answer. Lord Alfred Tennyson Tennyson was the most popular poet of the Victorian age. He expressed the period’s moral earnestness, religious doubts, and fears & hopes about science and democracy more completely than his peers did. He was a great lyrical poet: he had an impressive ability to express emotion, especially melancholy emotions of grief and loss & loneliness, in a musical and memorable way. Tennyson Bio Father was a clergyman, but it “drove him to drink”. People tried to explain his behavior by saying he had epilepsy, and also said some of the children had it, but, really, he was an alcoholic and the entire family was rather “eccentric”. There were 12 children in his family. At Cambridge, he formed a close friendship with Arthur Henry Hallam, whose death he mourned in his famous elegy, “In Memoriam” (1850). Arthur Hallam introduced him to Emily Sellwood, the love of his life. Hallam himself became engaged to Alfred’s sisters. They didn’t marry, but when she married someone else, she named her son Arthur Henry Hallam Tennyson Jesse. Tennyson Bio Cont… The same year Arthur Henry Hallam died, Alfred’s brother was admitted to a mental asylum, where he stayed until his death. Hallam’s death (combined with a hostile review in 1830) sent him into severe melancholy. For ten years, he published nothing. In 1839 Alfred and Emily were officially engaged. By 1840, they were officially unengaged because her father had put a stop to it – supposedly because Alfred was too poor to marry. He was also unhappy because his other daughter, Louisa, was very unhappily married to Alfred’s brother Charles (who was an opium addict). Tennyson Bio Final! In 1842 Tennyson decided that his health was bad and he let his doctors talk him into not writing for two years. He always had hypochondriac tendencies, but chain-smoking and a bottle of port every day didn’t help. He died in 1892, peacefully, apparently of gout, with his wife and son by his side. He’d outlived most of the great writers of his time. At his request, his poem “Crossing the Bar”, an epitaph of sorts, is always printed last in any collection of his works. The Lady of Shalott Lord Alfred Tennyson The Lady of Shalott is a magical being who lives alone on an island upstream from King Arthur's Camelot. Her business is to look at the world outside her castle window in a mirror, and to weave what she sees into a tapestry. She is forbidden by the magic to look at the outside world directly. The farmers who live near her island hear her singing and know who she is, but never see her. Summary The Lady sees ordinary people, loving couples, and knights in pairs reflected in her mirror. One day, she sees the reflection of Sir Lancelot riding alone. Although she knows that it is forbidden, she looks out the window at him. The mirror shatters, the tapestry flies off on the wind, and the Lady feels the power of her curse. Summary An autumn storm suddenly arises. The lady leaves her castle, finds a boat, writes her name on it, gets into the boat, sets it adrift, and sings her death song as she drifts down the river to Camelot. The locals find the boat and the body, realize who she is, and are saddened. Lancelot prays that God will have mercy on her soul. The Lady of Shalott STOP!!! Lets read this poem together. While reading, please HIGHLIGHT any words you don’t know. Make note of the RHYME SCHEME for PART II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bUuZBXNw0O 8&feature=related Lady of Shalott Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. What is in the fields next to the river? Name two trees that grow on the river bank. Who heard the Lady of Shalott signing? What does the Lady of Shalott do all day? Why can she not go out or look out her window? How does the Lady of Shalott know what is going on outside? What picture does she weave in her web? Who did she see in the mirror riding through the “barley sheaves”? What picture was on his shield? What color is his hair? Why did the mirror crack and the web fly out the window? Where did the Lady of Shalott find her boat? Why did the Lady of Shalott die? What did Sir Lancelot say when he saw her dead body? Who wrote the poem? Choose 5 vocabulary words, write out the sentence it is found in in the poem and then DEFINE it. Lady of Shalott Group Now that you have finished reading the “Lady of Shalott,” it is time to summarize in your own words, that is going on. Summarize the Part you are given, and then draw it in a 6 pane cartoon. Summary – Part I The poem begins with a description of a rvier and a road that pass through long fields of barley and rye before reaching the town of Camelot. The people of the town travel along the road and look toward and island called Shalott, which lies further down the river. On the island, a woman known as the Lady of Shalott is imprisioned within a building made of “four gray walls and four gray towers.” Only the reapers who harvest the barley hear the echo of the Lady of Shalott’s singing. Summary – Part II The Lady weaves a magic, colorful web. She has heard a voice whisper that a curse will befall her is she looks down to Camelot, so she concentrates solely on her weaving, never lifting her eyes. However, a mirror hangs before her and in the mirror, she sees the “shadows of the world,” including the highway. She sees different people walking on the road, and she enjoys her solitary weaving, but she is frustrated with the world of shadows when she glimpses a newlywed couple. Summary – Part III A knight in brass armor comes riding through the fields of barley beside Shalott and the sun makes him sparkle and glitter like the stars. He has a bugle hanging from his waist, which makes noises as he gallops on his horse. He is very handsome, and as he gallops past the island of Shalott he sings out “tirra lirra.” When the Lady hears the knight, she stops weaving her web and abandons her loom. The web flies out from the loom, and the mirror cracks and the Lady announces the arrival of her doom. Summary – Part IV As it starts to rain, the Lady of Shalott descends from her tower and finds a boat. She writes the words, “Lady of Shalott” around the boat’s bow and looks downstream to Camelot. She lies down in the boat, and the stream carries her to Camelot. She sings her last song as she sails to Camelot, her blood them freezes, her eyes darken and she dies. As the boat sails into Camelot, all the knights, lords and ladies or Camelot emerge from the halls to behold her. They read her name on the bow and “cross themselves for fear.” Only the great knight Lancelot is bold enough to push aside the crowd, look closely at the dead maiden, and remark, “She has a lovely face; God in his mercy lend her grace.” King Arthur STOP! Now that you know about the legend of King Arthur, Sir Lancelot and others, let’s watch the movie about the REAL King Arthur! Pay close attention similarities between the legend and the movie King Arthur. Take notes on major conflicts, themes and storylines in the movie. King Arthur Movie Review You are going to write a movie review for King Arthur. Make sure you mention that similarities or non-similarities between the legend of King Arthur and the real King Arthur. When writing a movie review keep the following things in mind: Movie Review Guidelines Paragraph 1: Create a GOOD LEAD. Start with a quote, refer to the director, etc. Grab the reader’s attention. Paragraph 2: RECAP very quickly. Keep it brief and don’t give away the ending! Paragraph 3: Give your OPINION. Make sure you back your opinion up with examples from the movie. (Eg. Movie too long? Actors believable?) In this paragraph, mention any similarities or non-similarities to King Arthur the legend. Paragraph 4: Give the film a RATING. Rate the film out of 5 stars (5 being the best). Movie Review Cont… Value: 30 MARKS! You will be marked on: Content (10 marks) – Did you cover all points thoroughly with examples? Creativity (10 marks) – Were you thoughts original? Did you put time into your planning? Organization/Conventions (10 marks) – Did you use paragraphs? Is your spelling/grammar fairly done? King Arthur Important Information 2004 Touchstone Pictures Actors/Actresses: Clive Owen – Arthur Ioan Gruffudd – Lancelot Keira Knightley – Guinevere Rating – PG13 Length – 142 mins Setting - In 400 AD, the Roman Empire extends to Britain and the Romans become impressed with the fight skills of the warrior Sarmatian people. Fables A fable is a very short story that tells us how to behave or that teaches us a lesson. Usually, but not always, fables are stories about animals that talk like people. The lesson that a fable teaches us is called a moral. Eg: The Boy who cried wolf – moral of the story, if you continue to lie, people won’t trust you anymore Grimm’s Fairytales Looking for a sweet, soothing tale to waft you toward dreamland? Look somewhere else. The stories collected by Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm in the early 1800s serve up life as generations of central Europeans knew it—unpredictable and often cruel. The two brothers, patriots determined to preserve Germanic folktales, were only accidental entertainers. Grimm’s Cont… Once they saw how the tales bewitched young readers, the Grimms, and editors aplenty after them, started "fixing" things. Tales gradually got softer, sweeter, and primly moral. Yet all the polishing never rubbed away the solid heart of the stories, now read and loved in more than 160 languages. Who are the Grimm Brothers? JACOB LUDWIG GRIMM 1785-1863 WILHELM CARL GRIMM 1786-1859 Just the Facts • Grimm’s primary method for collecting tales was by inviting story tellers to their homes and writing the information down • Story tellers consisted of young educated woman from middle class to aristocracy • The Grimm’s wanted the people to know the basic truths about the customs and practices of the German people and on preserving their authentic ties to the oral tradition Grimm’s Kinder-und Hausmarchen • English translation Children’s and Household Tales • 1812 1st volume was published. Consisted of 86 stories and folktales • 1814 2nd volume is published. Consisted of 70 stories and folktales • All together the Kinder-und Hausmarchen saw 8 editions • The final contained 200 stories and folktales, including 10 children's legends Grimm Brother Achievements • The Grimm brothers produced a significant amount of books during their lifetime • Jacob Grimm publishes 21 • Wilhelm Grimm publishes 14 • Together the brothers published 8 The Frog King Stop! Read the Brothers Grimm’s tale, The Frog King. Once done, with a partner, come up with the “moral of the story.” The Brothers Grimm STOP! With a partner, read your assigned Grimm’s fairytale. How is it different from the Disney version you may have heard of before? Once done, YOU WRITE 15 questions for teaching this fairytale. Who was Aesop? Aesop was a Greek folk hero who is supposed to have lived in the 6th century BC, and made up stories to make life easier. He gained a great reputation as a teller of animal fables. Through these many fables, Aesop showed the wise and foolish behavior of men, and taught a lesson in the form of a moral. Aesop Not much is known about the life of Aesop. It is believed Aesop was born in Thrace, Greece, as a slave. It is said that his wisdom so delighted one of his masters that the slave was given his freedom. According to one tradition, Aesop lived for a while as a slave on the island of Samos, after being freed he traveled widely, then was murdered while visiting Delphi Aesop’s Fables There are no records that Aesop ever wrote down his fables or published them. His fables were not meant to entertain children. He told them as moral lessons for adults, who in turn passed them on to others. Not until 200 years after his death did the first written collection of fables appear! Aesop’s Fables Aesop's fables later served as an inspiration for the writings of Jean de La Fontaine, a 17thcentury French writer Since then Aesop's Fables have been translated into almost every language in the world. The Man and the Serpent A Countryman's son by accident trod upon a Serpent's tail, which turned and bit him so that he died. The father in a rage got his axe, and pursuing the Serpent, cut off part of its tail. So the Serpent in revenge began stinging several of the Farmer's cattle and caused him severe loss. Well, the Farmer thought it best to make it up with the Serpent, and brought food and honey to the mouth of its lair, and said to it: "Let's forget and forgive; perhaps you were right to punish my son, and take vengeance on my cattle, but surely I was right in trying to revenge him; now that we are both satisfied why should not we be friends again?" The Man and the Serpent STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! Why did the man bring honey and food to the snake? 2. Why did the snake refuse the food and honey from the man? 3. What do you think the moral is? 1. The Lion and the Mouse Once when a Lion was asleep a little Mouse began running up and down upon him; this soon wakened the Lion, who placed his huge paw upon him, and opened his big jaws to swallow him. "Pardon, O King," cried the little Mouse: "forgive me this time, I shall never forget it: who knows but what I may be able to do you a turn some of these days?" The Lion was so tickled at the idea of the Mouse being able to help him, that he lifted up his paw and let him go. Some time after the Lion was caught in a trap, and the hunters who desired to carry him alive to the King, tied him to a tree while they went in search of a wagon to carry him on. Just then the little Mouse happened to pass by, and seeing the sad plight in which the Lion was, went up to him and soon gnawed away the ropes that bound the King of the Beasts. "Was I not right?" said the little Mouse. The Lion and the Mouse STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! 1. 2. 3. 4. Why did the lion let the mouse go? How did the mouse help the lion? Why? Who learned something in this fable—the mouse or the lion? What did he learn? What do you think the moral is? The Hares and the Frogs THE HARES, oppressed with a sense of their own exceeding timidity, and weary of the perpetual alarm to which they were exposed, with one accord determined to put an end to themselves and their troubles, by jumping from a lofty precipice into a deep lake below. As they scampered off in a very numerous body to carry out their resolve, the Frogs lying on the banks of the lake heard the noise of their feet and rushed helter-skelter to the deep water for safety. On seeing the rapid disappearance of the Frogs, one of the Hares cried out to his companions: Stay, my friends, do not do as you intended; for you now see that other creatures who yet live are more timorous than ourselves. The Hares and the Frogs STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! 1. 2. 3. 4. Why did the hares want to drown themselves? Why did they decide not to? What animals might the frogs see that would make them say the same thing the hares said? What do you think the moral is? The Fox and the Mask A Fox had by some means got into the store-room of a theatre. Suddenly he observed a face glaring down on him and began to be very frightened; but looking more closely he found it was only a Mask such as actors use to put over their face. "Ah," said the Fox, "you look very fine; it is a pity you have not got any brains." The Fox and the Mask STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! Why was the fox afraid when he first saw the mask? 2. What did the fox mean when he said, “It’s a pity you haven’t got any brains?” 3. What do you think the moral is? 1. One fine day it occurred to the Members of the Body that they were doing all the work and the Belly was having all the food. So they held a meeting, and after a long discussion, decided to strike work till the Belly consented to take its proper share of the work. So for a day or two, the Hands refused to take the food, the Mouth refused to receive it, and the Teeth had no work to do. But after a day or two the Members began to find that they themselves were not in a very active condition: the Hands could hardly move, and the Mouth was all parched and dry, while the Legs were unable to support the rest. So thus they found that even the Belly in its dull quiet way was doing necessary work for the Body, and that all must work together or the Body will go to pieces. The Belly and the Members STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! 1. What did the other body parts want the belly to do? How did they try to force the belly to do what they wanted? What did the body parts learn? What do you think the moral is? 2. 3. 4. ONCE UPON A TIME a Wolf resolved to disguise his appearance in order to secure food more easily. Encased in the skin of a sheep, he pastured with the flock deceiving the shepherd by his costume. In the evening he was shut up by the shepherd in the fold; the gate was closed, and the entrance made thoroughly secure. But the shepherd, returning to the fold during the night to obtain meat for the next day, mistakenly caught up the Wolf instead of a sheep, and killed him instantly. Harm seek. harm find. The Wolf in Sheep’s Clothing STOP! Read the above fable and then answer the following questions! 1. 2. 3. 4. How did the wolf trick the lamb? Why did the lamb think the wolf was one of the sheep? 3 What are some examples of things that look safe but may be dangerous? What do you think the moral is? Aesop’s Final Project Now that you’re a Fable expert, it’s time to put that knowledge to the test! See the project sheet and get to work! The Brothers Grimm STOP! Let’s watch the movie “Brothers Grimm” to finish off the unit, “Myths, Legends and Fable.” Be ready for a test in the next few days.