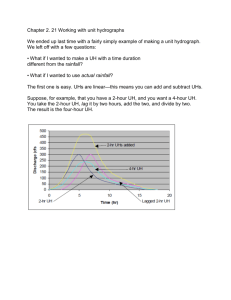
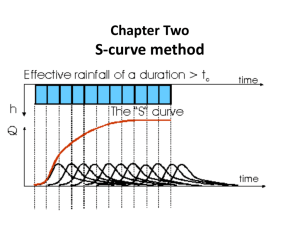
unit hydrograph 2
advertisement

ERT 246 Hydrology & Water Resources Engineering Siti Kamariah Md Sa’at School of Bioprocess Engineering, UniMAP Unit Hydrograph Cont. More Example: Two storm each of 6-hr duration and having rainfall excess values of 3.0cm and 2.0 cm respectively occur successively. The 2-cm ER rain follows the 3-cm rain. The 6-hr UH for the catchment is the same as given in previous example. Calculate the resulting DRH. Unit Hydrograph of Different Durations Under condition where lack of adequate data in developement of unit hydrograph D-hour unit hydrograph is used to develop unit hydrographs of differing durations nD Two method available: 1. Method of superposition 2. The S-Curve Method of superposition If a D-h unit hydrograph is available, and its desired to develop unit hydrograph of nD, its is easily accomplished by superposing n unit hydrographs with each graph separated from the previous on by D-h. D = 2-Hr Unit Hydrograph Adjusted Net Rainfall one inch over basin Qp Change UH Duration Consider 1 hr UH Add and Lag two UH by one hour Sum and divide by 2 Results in 2 hr UH Example Given the ordinates of a 4-hr unit hydrograph as below derive the ordinates of a 12-hr unit hydrograph for the same catchment Time (hr) 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 Ordinates of 4-hr UH 0 20 80 130 150 130 90 52 27 15 0 5 Equilibrium Hydrograph Uniform Rain Inflow = Outflow Equiv to summing n hydrographs in T One Hydrograph Produces S curve S-Curve Also known as S-hydrograph Hydrograph produced by continous effective rainfall at a constant rate for infinite period. Curve obtained by summation of an infinite series of D-h UH spaced D-h apart. S-Curve Construction Obtained by adding a string of D-h UH each lagged by D-hours from one another. If Tb= base period of the UH, addition of only Tb/D UH are suffcient to obtained S-curve U(t) = S(t)-S(t-D) or U(t) = S(t)+S(t-D) Where S(t-D)= S-curve addition at time t S(t) = Ordinate of D-h UH at time t S-Curves for UH S-Curves S-curve • Convert 2 hr Unit hydrograph to 3-hr • Lag each 2-hr UH by Duration D • Add to produce S-curve Lag S Curves in time, subtract them, and multiply by D/D’ Lag by D’ and subtract both curves 3 hr. Unit Hydrograph from a 2 hr. UH (D/D’) 3 HR UH Example Solve previous example with S-curve method: Hydrograph Convolution 1 2 Add and Lag Method 3 1 2 STORM HYDRO 3 Add up the ordinates of all three to produce storm hydrograph Multi-Period Storm • Pg - F = Net Rainfall NET RF UH • RF units = UH duration (i.e. 1 hour) • Adjust UH by Net RF • Add and Lag UH • Produce Storm Hydrograph STORM Development Effects on UH Natural Partial Fully Developed Synthetic UH •Developed for basin that were ungaged •Based on data from similar gaged basins •Most methods are very similar in nature •Revolutionized ability to predict hydro response Synthetic UH Methods •Methods to characterize ungaged basins •Use data and relationships developed from gages •Variety of approaches but most based on Tp and Qp •England and U.S. led the efforts to standardize UH Synthetic UH Methods • Snyder’s Method (1938) • Clark Method (1945) • Nash (1958) • SCS (1964, 1975) • Espey-Winslow (1968) • Kinematic Wave (1970s) Snyder’s Method Synder (1938)- based on study of large catchment in eastern US developed a set of empirical equation for synthetic UH. The equation are use in USA and with some modification in many other countries. Lag time The most important characteristic of basin due to storm- basin lag (lag time) Lag time- time difference between the centroid of the input (rainfall excess) and the output (DRH) Represent time of travel of water from all parts of watershed to the outlet during a given storm. Snyder’s Method 5 to 7 points SCS Method Dimensionless UH Based on a study of large number of UH Developed by US Soil Conservation Services (SCS) SCS Methods Triangular UH Dimensionless UH SCS Triangular UH Example 1 inch of RF over 1.6 hr duration 2-hr Duration UH Example Qp at 400 cfs at 10 hr with 24 hr Tb 400 300 Six Hours of Uniform Rainfall = 0.25 in/hr 1.5 Inches Total Rain 200 100 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 30 Time in Hours SCS RAINFALL RUNOFF CURVES Unit Hydrograph Applications Land Use 1 Land Use will alter UH Peak and Timing Land Use 2 Unit Hydrograph Changes Kinematic Wave Overland Collector Channels Main Stream Manning’s Eqn Kinematic Wave Basin hydrographs- routed & combined to produce storm hydrograph