Rivers revision sheet
advertisement
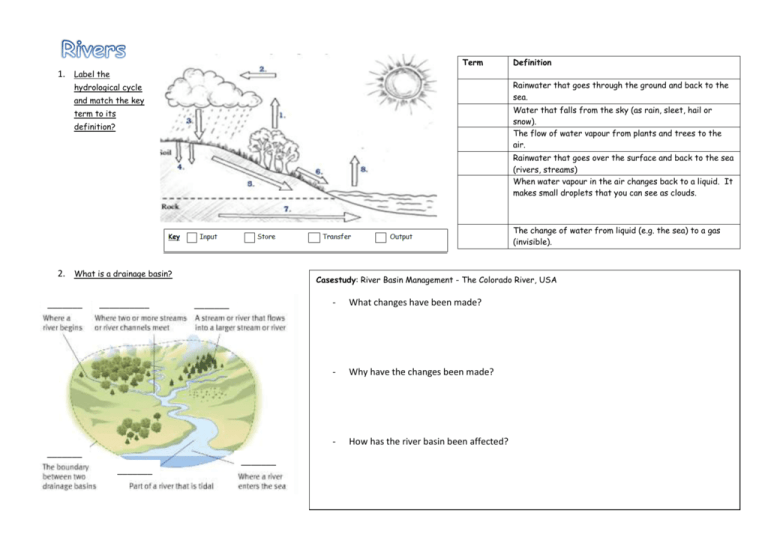
Term 1. Label the Definition Rainwater that goes through the ground and back to the sea. hydrological cycle and match the key Water that falls from the sky (as rain, sleet, hail or snow). The flow of water vapour from plants and trees to the air. term to its definition? Rainwater that goes over the surface and back to the sea (rivers, streams) When water vapour in the air changes back to a liquid. It makes small droplets that you can see as clouds. The change of water from liquid (e.g. the sea) to a gas (invisible). 2. What is a drainage basin? _______ __________ __ Casestudy: River Basin Management - The Colorado River, USA _______ - What changes have been made? - Why have the changes been made? - How has the river basin been affected? __ _______ _______ _______ 3. What are the processes that affect river? Weathering and Erosion What is freeze-thaw weathering? Abrasion or corrasion Attrition Hydraulic Action ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Transport Solution or corrosion Draw and label diagram to show the processes of transportation. Deposition Why does deposition occur? it. _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ____ Can you draw 2 places on a river you would expect to find _______________________ Upper, middle and lower - Draw, label and describe UPPER 4. What are the features of a river? Feature Description Floodplain Plunge pool A bend in the river An area of land that floods when the river bursts its banks. A narrow steep-sided valley formed by vertical erosion A hollow at the base of a waterfall A crescent shaped lake A vertical drop of water Ox-bow lake Waterfall Meander V-shape valley MIDDLE Upper / Middle / Lower? LOWER the formation of a feature located along the river. 5. How are precipitation and runoff linked? Title: ___________________________________________ What is a storm hydrograph? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Graph definitions Base flow – Rising limb – Peak discharge Falling limb – Lag time – The shaded area is known as the ___________ ___________ Different factors can affect the shape of a storm hydrograph. Vegetation: Soil (Rock type) Steepness: Your own: How did the river Eden react in Carlisle 2005? Why are storm hydrographs important? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ _____________ Your example: _________________ 6. How can flooding be managed? Case study: MEDC - Case study: LEDC - Bangladesh What were the causes of the floods? What were the causes of the floods? Physical (Natural) Causes Human made causes Physical (Natural) Causes What were the effects of the disaster? What were the effects of the disaster? Short term: Short term: Long term: Long term: Human made causes Bangladesh flood responses – What are they and are they an effective method? How did the area respond and protect themselves for the future? Preparedness Programme (supported by Oxfam) Dhaka Integrated Flood protection project ($100 million government project )