topic 4 cc606 2
advertisement

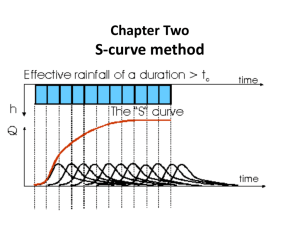
NATURAL HYDROGRAPH Base flow separation technique, Qb: a. Empirical formula b. Master depletion curve c. Simple straight lines Topic 4 EXPLAIN HYDROGRAPH ANALYSIS CONSTRUCT CALCULATE CONCEPT OF UNIT HYDROGRAPH UNIT HYDROGRAPH Volume Of Direct Runoff From Direct Runoff Hydrograph. DETERMINE The Change Of Unit Hydrograph Duration Using: a. S-curve b. Superposition Concept. HYDROGRAPH • A hydrograph is a graph showing the rate of flow (discharge) versus time past a specific point in a river, or other channel or conduit carrying flow. The rate of flow is typically expressed in cubic meters or cubic feet per second (cms or cfs). DEFINITION OF NATURAL HYDROGRAPH • A natural hydrograph is one recorded at a stream gauging site and is a finger-print of the upstream drainage area’s response to rainfall CONCEPT OF UNIT HYDROGRAPH • A Hydrograph is a graph showing changes in the discharge of river over a period of time. • It can also refer to a graph showing the volume of water reaching particular outfall or location in a sewerage network, graph are commonly used in the design of sewerage,more specillcally, the design of surface water sewegare systems and combination system. A hydrograph consists of: a) A rising limb or concentration curve b) A peak or crest segment c) Falling limb or recession curve • The properties or characteristics of a unit hydrograph are a) the volume under a unit hydrograph is equal to 1 unit (1cm or 1in) rainfall excess b) If the duration of two rainfall excess events is equal, without regard to their respective rainfall intensities, they must result in the same hydrograph time base. c) The unit hydrograph results in a linear system whereby the direct runoff for a storm of a specified duration is directly proportional to the rainfall excess amount or volume d) Rainfall distribution for all equal duration storms is identical in space and time. Calculate direct runoff from stream flow & base flow data • Direct runoff = stream flow – base flow Schedule below shows observation data from stream flow with base flow depth in catchment's area 250 km2. from that data , get direct runoff magnitude. example Time (hour) Stream flow, Q (m3/s) Base Flow, (m3/s) 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 1.37 1.25 1.12 5.00 12.00 15.60 17.15 14.40 8.80 6.80 5.50 4.10 2.75 2.00 1.20 0.65 0.15 0.32 0.62 1.25 1.28 1.35 1.42 1.65 1.82 1.88 2.05 2.55 1.91 1.53 1.15 0.28 Calculate Direct Runoff Depth Base On Volume DRO And Cathment Area. • DRO Depth,rd = DIMANA; Vd A Qn Δt Vd A = RUNOFF VOLUME = Qn Δt = CATCHMENT WIDE = HYDROGRAPH ORDINATE = HYDROGRAPH TIME INTERVAL Calculate runoff volume and excess rain depth to a 7 acres catchment's area. Schedule below show a direct runoff data resultant from one precipitation EXAMPLE Time (minute) 0 2 4 6 8 10 Flow, Q (cfs) 0 0 9 21 17 13 Convert the duration of unit hydrograph from short to long (superposition) Convert The Duration Of Unit Hydrograph From Short To Long (Superposition Method)- graphic Time 4hr-UH (Hour) (m3/s) 0 0 4 3 8 33 12 96 16 63 20 35 24 25 28 12 32 6 36 3 4j-UH (m3/s) The following are the ordinates of a 4-hour unit hydrograph. Derive the ordinates of a 12 - hour unit hydrograph 250 Combined 4hr-UH 200 Lagged 150 4hr-UH 4hr-UH 100 12hr-UH 50 0 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 Time (Hour) 28 32 36 40 44 Convert The Duration Of Unit Hydrograph From Short To Long (Superposition Method)- table Time 4j-UH (Hour) (m3/s) 0 0 4 3 0 8 33 3 12 96 16 Lagged Lagged (+) 4j-UH 12j-UH 0 0 3 1 0 36 12 33 3 132 44 63 96 33 192 64 20 35 63 96 194 64.67 24 25 35 63 123 41 28 12 25 35 72 24 32 6 12 25 43 14.33 36 3 6 12 21 7 3 6 9 3 3 3 1 40 44 Example : • The following are the ordinates of a 3-hour unit hydrograph. Derive the ordinates of a 6-hour unit hydrograph and plot the graph. Solution Time (Hour) 0 4j-UH (m3/s) 0 3 1.5 6 (+) 4j-UH 12j-UH 0 0 0 2 0.75 4.5 1.5 6 3.00 9 8.6 4.5 13 6.55 12 12.0 8.6 21 10.30 15 9.4 12.0 21 10.70 18 4.6 9.4 14 7.00 21 2.3 4.6 7 3.45 24 0.8 2.3 3 1.55 0.8 1 0.40 27 30 Lagged 25 20 15 3hr-UH lagged 3hr-UH Combined 3hr-UH 6hr-UH 10 5 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 Question 1: • Determine the 4hr-UH from the 2hr-UH given in the table using the superposition principle method Changing a Short Duration Unit Hydrograph to Long Duration using S-Curved method Example • The ordinates of a 4-hour unit hydrograph for a particular basin are given below. Determine the ordinates of the S-curve hydrograph and there from the ordinates of the 6-hour unit hydrograph Solution Time 4hr-UH (Hour) 0 0 2 25 4 100 6 160 8 190 10 170 12 110 14 70 16 30 18 20 20 6 22 1.5 24 0 S- Curve Addition S- Curve Ordinates Lagged S- Curve S- Curve difference 6hr - UH Time (Hour) 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 4hr-UH 0 25 100 160 190 170 110 70 30 20 6 1.5 0 S- Curve S- Curve Lagged S- Curve 6hr - UH Addition Ordinates S- Curve difference 0 25 100 185 290 355 400 425 430 445 436 446.5 436 0 25 100 185 290 355 400 425 430 445 436 446.5 436 446.5 436 0 25 100 185 290 355 400 425 430 445 436 446.5 0 25 100 185 265 255 215 135 75 45 11 16.5 -9 10.5 -10.5 0.00 16.67 66.67 123.33 176.67 170.00 143.33 90.00 50.00 30.00 7.33 11.00 -6.00 7.00 -7.00 Question 1 • Determine the 3hr-UH from the 1hr-UH given in the table using the S-curve method. Time (Hour) 3hr-UH 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 0 66 134 266 534 466 400 334 266 200 134 66 0 0 0 S- Curve Addition S- Curve Ordinates 0 66 134 266 600 600 666 934 866 866 1068 932 866 1068 932 Lagged S- Curve S- Curve difference 1hr - UH 0 66 134 266 600 600 666 934 866 866 1068 932 866 1068 0 66 68 132 334 0 66 268 -68 0 202 -136 -66 202 -136 0 198 204 396 1002 0 198 804 -204 0 606 -408 -198 606 -408 Changing a Long Duration Unit 0 Hydrograph66 to Short Duration using 134 S-Curved method 266 600 600 666 934 866 866 1068 932 Question • The following are the ordinates of a 4hr – UH. Derive the ordinates of a 3hr-UH Derive the S-curve for 4hr-UH Hydrograph Unit from Stream Discharge Data Example • Table below show runoff from hydrograph data, for a 50km2 catchment . Calculate the unit hydrograph (UH)10mm. Assume that the basic flow is 5.0m3/s Solution Mendapatkan Hidrograf Jumlah • Penggunaan UH10 bagi kawasan tadahan yang sama dengan contoh 1. • Diberikan ribut yang lain dengan tempoh yang sama bagi kawasan tadahan yang sama iaitu 50km2. Anggapkan aliran dasar 7 m3/s Latihan • Cerapan kadaralir bagi satu kejadian hujan berkesan 12 jam bagi kawasan seluas 1150km2 adalah seperti yang ditunjukkan. Dapatkan hidrograf unit (UH)10mm untuk kawasan ini. • Diberi UH 4jam dan dapatkan UH -12jam dengan menggubakan kaeadah tindihan REFERENCES • http://www.ce.utexas.edu/prof/mckinney/c e374k/Overheads/12-RunoffProcesses.pdf