warm_up_3
advertisement

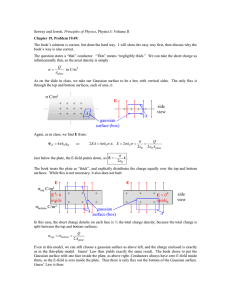
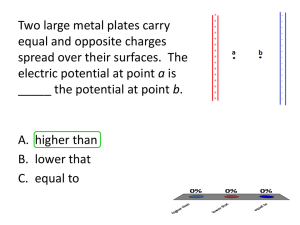
Warm Up 3 Question 1. HRW7 23.CQ.01. [406131] A surface has the area vector A = (6 i +3 j) m2. (a) What is the flux of an electric field through it if the field is E = 4 N/C i? (b) What is the flux of an electric field through it if the field is E = 4 N/C k? Answer: (a) (b) E A (6i 3 j 0k)m (4i 0 j 0k)N / C (24i 0 j 0k)Nm2 / C 24Nm2 / C 2 E A (6i 3 j 0k)m (0i 0 j 4k)N / C 2 (0i 0 j 0k)Nm2 / C 0Nm2 / C Question 2. HRW7 23.CQ.05. [406128] The figure shows, in cross section, three solid cylinders, each of length L and uniform charge Q. Concentric with each cylinder is a cylindrical Gaussian surface, with all three surfaces having the same radius. Rank the Gaussian surfaces according to the electric field at any point on the surface, greatest first (use only the notation > or =, for example b=c>a). Answer: a=b=c Gaussian surfaces are affected only by total charge enclosed, which is the same for all three. The charge is distributed evenly, and so the total charge may be considered to originate at the center, making the electric field equal at all points on all three surfaces.