Scaffolding Chart K-4 - Department of Social Sciences
advertisement

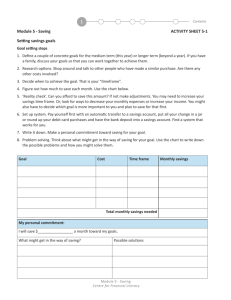
Topics Scaffolding Chart K-4 Kindergarten Earning Income Grade 1 Earning Income Grade 2 Earning Income Grade 3 Earning Income Grade 4 Earning Income What is money? Exchanging Money for Goods and Services Using Interests and Talents in Choosing a Job Service Jobs vs. Production Jobs Importance of Money Why People Choose Particular Jobs (Lesson Plan: What is MoneyIncome: http://www.scholastic.com/browse /lessonplan.jsp?id=370 ) SS.4.FL.1.1 People have many different types of jobs from which to choose. Identify different jobs requiring people to have different skills. How Money is Used (Video: What is a Job? https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=ihhmDFdsUE4) Different Types of Jobs Buyers, Sellers, and Producers (Lesson Plan: Sorting Money http://financeintheclassroom.org/p assport/kindergarten/social_studi es.shtml#sorting ) (Lesson Plan Understanding Money: http://www.practicalmoneyskills.c om/foreducators/lesson_plans/lev _1/4_complete.pdf Earning Money ( i.e. regular allowance or earnings from special household tasks.) Why People Have Jobs (Lesson Plan: We Can Earn Money http://www.econedlink.org/lesson s/index.php?lid=465&type=educa tor ) Topic(s): Choosing A Job Different jobs- Different Skills (Money Instructor Lesson Plan: Earning Money: http://www.moneyinstructor.com/l esson/earnmoney.asp) Employees and Employers (Lesson Plan Jobs: http://tcaassets.org/public/lessonplans/grade-one-jobs.pdf ) Income from Jobs Getting Hired by an Employer SS.4.FL.1.2 People earn an income when they are hired by an employer to work at a job. Explain why employers are willing to pay people to do their work. Topic(s): Why Employers Pay People to Work What Is income? How People Earn Income. Different forms of income. Wages, Salaries, and Commissions. SS.4.FL.1.3 Workers are paid for their labor in different ways such as wages, salaries, or commissions. Explain the ways in which workers are paid. Topic(s): How Waitresses, Teachers, and Realtors are paid Differently Jobs with Commissions Jobs with Commissions vs. Jobs with Salaries XX XX What is interest? Earning Interest Income SS.4.FL.1.4 People can earn interest income from letting other Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Earning Interest Money in the Bank! Grade 3 (Lesson Plan: Money, Kids & Cash- Interest http://financeintheclassroom.org/d ownloads/kidsandcash.pdf ) Grade 4 people borrow their money. Explain why banks and financial institutions pay people interest when they deposit their money at those institutions. Topic(s): Why banks Pay Interest (Lesson Idea-Plan: Introduction to Earning Interest Worksheet http://www.moneyinstructor.com/ wsp/wsp0039.asp ) XX XX What is Renting? Earning Rental Income SS.4.FL.1.5 People can earn income by renting their property to other people. Identify different types of property (such as apartments, automobiles, or tools) that people own and on which rent is paid. Topic(s): Income from Property that Has Rental Value Things I Own Owning a Business What is profit? How Businesses Make a Profit SS.4.FL.1.6 Describe ways that people who own a business can earn a profit, which is a source of income. Topic(s): Business Owners: Expenses; Profit; and Income What is a business? What is an Entrepreneur? Why People Become Entrepreneurs Risks involved in being an Entrepreneur (Lesson Plan: Open for Business – Risks and Rewards of Entrepreneurship http://www.econedlink.org/teache r-lesson/920 ) SS.4.FL.1.7 Entrepreneurs are people who start new businesses. Entrepreneurs do not know if their new businesses will be successful and earn a profit. Identify ways in which starting a business is risky for entrepreneurs. Topic(s): Entrepreneurs: Risk vs. Reward Kindergarten XX Grade 1 XX Grade 2 Grade 3 What is a Tax? Income Tax (Lesson Plan: Taxes Just Aren’t Fair http://teachers.net/lessons/posts/ 3874.html ) The “What” and “Why” of Income Tax (Worksheet: Calculating Mike’s Pay http://fffl.councilforeconed.org/doc uments/978-1-56183-692-5activity-lesson-03.pdf Answer Key http://fffl.councilforeconed.org/doc uments/978-1-56183-692-5visual-lesson-03.pdf ) Grade 4 (Federal Reserve Lesson Plan: Lemonade Stand – Entrepreneurism http://financeintheclassroom.org/d ownloads/kidsandcash.pdf ) SS.4.FL.1.8 Income earned from working and most other sources of income are taxed. Describe ways that the revenue from these taxes is used to pay for government provided goods and services. Topic(s): Goods and Services Provided by Tax Money Taxes and Government Services Benefits of Tax Revenue (Lesson Plan Taxes: Cowboy Bob Builds a Community http://www.econedlink.org/lesson s/index.php?lid=665&type=educa tor# ) Buying Goods and Services Buying Goods and Services Buying Goods and Services Buying Goods and Services Buying Goods and Services Wants vs. Needs What Do You Want to Buy? What are “Goods?” What are “Services?” Goods and Services- What is the difference? Buyers Economic Wants Consumers Use Goods and Services Buying Goods and Services SS.4.FL.2.1 Explain that economic wants are desires that can be satisfied by consuming a good, a service, or a leisure activity. Understanding “Wants” (Lesson Plan: All I Really Need http://www.uen.org/Lessonplan/pr eview?LPid=25968 ) Spending Money on Leisure Activities How Buyers and Sellers Interact Topic(s): Ways to Satisfy Economic Wants (Lesson Plan: Goods and Services http://www.econedlink.org/lesson s/index.php?lid=642&type=educa tor ) What Do You Want? Choosing What I Want Most Money is Limited: Choose Carefully Things to Think About Before Spending Money Thoughtful Money Choices vs. Later Regret Goals Help Us Make Choices Be Careful: You Can Only Spend that Money Once SS.4.FL.2.2 Explain that people make choices about what goods and services they buy because they can’t have everything they want. This requires individuals to Kindergarten Grade 1 (Lesson Plan: Yard Sale – Spending Decisions http://www.moneymanagement.or g/Budgeting-Tools/Credit-LessonPlans/Yard-Sale.aspx ) Grade 2 (Scholastic Spending Goals Activity Sheet: http://content.scholastic.com/cont ent/collateral_resources/pdf/08/T EANOV08_022.pdf ) Grade 3 Grade 4 prioritize their wants. Topic(s): Prioritize Your Wants Narrow that Shopping List (Lesson Plan: Spending Decisions http://www.practicalmoneyskills.c om/foreducators/lesson_plans/lev _1/1_complete.pdf ) What Do I Want? Not Everyone Wants a Baseball What’s at the Top of Your List? Identify Wants and Rank Them in Order of Importance People Have Different Needs and Wants Why People Spend Money Class “Wants” Survey SS.4.FL.2.3 Identify some of the ways that people spend a portion of their income on goods and services in order to increase their personal satisfaction or happiness. Topic(s): Buying Goods and Services for Personal Satisfaction or Happiness. Different People- Different Spending Choices Making Choices – You Can’t Have Everything! Giving Up One Thing for Another What is Opportunity Cost? Opportunity Cost: Weigh the Alternatives (Lesson Plan: What Pet Should I Get? http://www.econedlink.org/teache r-lesson/1263 ) (Lesson Plan: Opportunity Cost http://www.econedlink.org/teache r-lesson/1289 ) (Lesson Plan Opportunity Choice: Everyday Opportunities http://www.econedlink.org/lesson s/index.php?lid=738&type=educa tor# ) SS.4.FL.2.4 Discuss that whenever people buy something, they incur an opportunity cost. Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a person makes a choice. Topic(s): Opportunity Cost: Choosing the Best Alternative Good Choice: But What is the Cost? (Lesson Plan – Opportunity Cost: Uncle Jed’s Barber Shop file:///C:/Users/Sharon/Downloads /UncleJedsBarbershop.pdf ) Kindergarten What does it Cost? Grade 1 Benefits of Spending Grade 2 Comparing Costs and Benefits (Lesson Plan: Every Penny Counts http://www.econedlink.org/teache r-lesson/461 ) Grade 3 Consider the wider consequences of economic decisions Explore Economic Decisionmaking Grade 4 SS.4.FL.2.5 Explain that costs are things that a decision maker gives up; benefits are things that a decision maker gains. Make an informed decision by comparing the costs and benefits of spending alternatives. Alternate Choices Topic(s): Components of Informed Economic Decision Making Comparing Costs and Benefits of Spending Alternatives Not Everything Costs the Same Different Goods or Services have Different Prices. How Price Affects Spending Choices How Advertising Affects Spending Choices Which Costs More? Peer Pressure Spending (But Mom, Everyone I Know Has One) SS.4.FL.2.6 Predict how people’s spending choices are influenced by prices as well as many other factors, including advertising, the spending choices of others, and peer pressure. Topic(s): Do Role Models Affect Spending Choices? Factors That Influence Spending Choices How Shopping Lists Help Consumers Planning Helps People Make Choices About Spending What is a budget? Balancing Income and Expenses: Make a Plan Budgets and Planning What is a Balanced Budget SS.4.FL.2.7 Planning for spending can help people make informed choices. Develop a budget plan for spending, saving, and managing income. Topic(s): Create a Spending Plan Managing Income Wisely Saving Saving Saving Saving Saving Now and Later (Concept) Importance of Saving Money Benefits and Costs of Saving Saving for Future Needs and Wants SS.4.FL.3.1 Identify ways that income is saved, spent on goods and services, or used to pay taxes. Saving Money Benefits and Costs of Spending Spend Now or Save for Later Saving in Case of Emergency Kindergarten Spending Money (Lesson Plan: Using Money Wisely – Saving for Freckles http://www.moneyinstructor.com/l esson/savingfreckles.asp ) Grade 1 Grade 2 (Lesson Plan: Introduction to Saving and Spending http://www.tdbank.com/wowzone/ lessons/GrK-1Lesson1.pdf Grade 3 Saving vs. Spending Grade 4 Topic(s): Income: Saved or Spent, or Used to Pay Taxes Benefits of Saving Explaining the Difference Between Saving and Spending Saving for Something I Want Choosing to Save Money Reasons for Saving Money Waiting to Buy What We Want (Lesson Plan: Why We Save http://ecedweb.unomaha.edu/less ons/saveK-2.pdf ) Giving Up to Save for the Future SS.4.FL.3.2 Explain that when people save money, they give up the opportunity to buy things now in order to buy things later. Topic(s): Buy Now or Buy Later: The Cost of Future Purchases What You Give Up to Put $50 in a Savings Account A Safe Place to Keep My Savings at Home Keeping My Savings in a Safe Place Keeping My Savings in a Bank Where Shall I Keep My Savings (Lesson Plan: Checking Accounts and Alternative Banking Methods http://www.tdbank.com/wowzone/ lessons/Gr2-3Lesson3.pdf ) SS.4.FL.3.3 Identify ways that people can choose to save money in many places—for example, at home in a piggy bank or at a commercial bank, credit union, or savings and loan. Topic(s): Savings Options: Home; Bank; Credit Union; Savings and Loan Identify Different Places Where People Can Save Their Money (Interactive Site: Hands On Banking for Kids http://www.handsonbanking.org/h tdocs/en/k/ ) Setting Goals Can You Think of Savings Goal? Why Savings Goals are Important How to Set Your Savings Goals Create a Savings Plan SS.4.FL.3.4 Identify savings goals people set as incentives to save. One savings goal might be to buy goods and services in the future. Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Topic(s): Savings Goals: Incentives to Save Step By Step: Planning to Reach My Savings Goal What is a Bank? Keeping Your Money Safe Why Put Your Savings in a Bank Putting Savings in a Bank Banks and Financial Institutions Keep Your Money Safe (Lesson Plan: Savings Accounts and Interest http://www.takechargeamerica.or g/wpcontent/themes/tca/pdfs/teachingresources/grade-one-savingsaccounts-and-interest.pdf ) Different Financial Institutions for Saving Banks and Financial Institutions Help Your Savings Grow (Lesson Plan: Saving http://www.takechargeamerica.or g/wpcontent/themes/tca/pdfs/teachingresources/grade-three-saving.pdf ) SS.4.FL.3.5 Explain that when people deposit money into a bank (or other financial institution), the bank may pay them interest. Banks attract savings by paying interest. People also deposit money into banks because banks are safe places to keep their savings. Topic(s): Banks and Financial Institutions Pay Interest on Your Savings Advantages of a Savings Account Using Credit Using Credit Using Credit Using Credit Borrowing Borrowers and Lenders What is Interest? Advantages and Disadvantages of Borrowing Money Returning What You Borrow Borrowing Has Responsibilities Paying Interest on Borrowed Money Cash vs. Credit (Discovery Education Lesson Plan: Money: Kids and Cash – Interest http://www.discoveryeducation.co m/teachers/free-lessonplans/money-kids-and-cash.cfm ) Examples of Borrowing Being a Good Borrower Making Purchases Without Cash What is credit? Savings Account or Piggy Bank: Which is the Better Way to Save? (Lesson Plan Big Banks, Piggy Banks http://www.econedlink.org/lesson s/index.php?lid=455&type=educa tor# ) Using Credit SS.4.FL.4.1 Discuss that interest is the price the borrower pays for using someone else’s money. Topic(s): Borrowing Money: Terms and Conditions The Cost of Borrowing Money Advantages and Disadvantages of Buying with Credit Repaying the Lender Over Time Credit Buying Has Risks SS.4.FL.4.2 Identify instances when people use credit, that they receive something of value now and agree to repay the lender Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 (Lesson Plan with Interactive story covering- loans, interest, credit card debt: Giving Vicki Credit http://financeintheclassroom.org/p assport/second/social_studies.sht ml#vicki ) Grade 3 Goods and Services Often Purchased with a Loan (Lesson Plan: Debt http://www.takechargeamerica.or g/wpcontent/themes/tca/pdfs/teachingresources/grade-three-debt.pdf ) Grade 4 over time, or at some date in the future, with interest. Topic(s): Buy Now – Pay Later Buying with Credit Costs Money Buying with Credit Has Responsibilities Financial Investing Financial Investing Financial Investing Financial Investing Financial Investing XX XX What is Investing? Benefits of Investing SS.4.FL.5.1 Explain that after people have saved some of their income, they must decide how to invest their savings so that it can grow over time. Different Ways to Invest Money (Investor.gov Suggested Activities: How To Save and Invest http://investor.gov/outreach/teach ers/classroom-resources/howsave-invest ) Topic(s): Choosing the Best Investment Saving vs. Investing: What’s the Difference (Lesson Plan Saving and Investing: http://www.practicalmoneyskills.c om/foreducators/lesson_plans/lev _2/3_comp.pdf ) XX XX Financial Investments Investing in the Stock Market Reasons for Investing How the Stock Market Works (Investor.gov Suggested Activities: Why Save and Invest http://investor.gov/outreach/teach ers/classroom-resources/whysave-invest ) Different Types of Financial Investments SS.4.FL.5.2 Explain that a financial investment is the purchase of a financial asset such as a stock with the expectation of an increase in the value of the asset and/or increase in future income. Topic(s): Investments: Making Your Money Work for You Financial Investments Have Risks Risk vs. Reward Kindergarten Protecting and Insuring Grade 1 Protecting and Insuring Grade 2 Protecting and Insuring Grade 3 Protecting and Insuring Grade 4 Protecting and Insuring What is a Risk? Safe and Unsafe Risks Consequences of Risk-Taking Strategies to Lower Risk SS.4.FL.6.1 Explain that risk is the chance of loss or harm. Choices That Lower Risk Topic(s): Activities With Risks: How to Stay Safe (Sunny Money Ideas and Activities Correlated to NGSSSSS Financial Literacy Protecting and Insuring 6.1-6.4 http://sunnymoney.weebly.com/pr otecting-and-insuring.html ) Accidents Safe Choices Help Avoid Accidents Accidents and Unexpected Events Daily Risks Natural Disasters SS.4.FL.6.2 Explain that risk from accidents and unexpected events is an unavoidable part of daily life. Topic(s): How Accidents and Unexpected Events Affect People Staying Safe Why Wear a Bicycle Helmet? Staying Safe When Crossing Streets Staying Safe at Home Be Careful: Ways to Protect Yourself Planning Helps Avoid Risks Potential Harm From Risk-Taking Think Before You Act! (Ways for Kids to Play it Safe: http://www.tdi.texas.gov/kids/kids safety.html ) What is an Emergency? Losses from Emergencies and Unexpected Events Topic(s): Choices: Accept Risk or Protect Yourself Avoiding or Reducing risk. Saving For Emergencies Loss of Ability to Earn Income Cost of Accidents and Unexpected Events Loss of Personal Property (What is a Disaster? http://www.tdi.texas.gov/kids/kids disaster.html ) SS.4.FL.6.3 Describe ways that individuals can either choose to accept risk or take steps to protect themselves by avoiding or reducing risk. SS.4.FL.6.4 Discuss that one method to cope with unexpected losses is to save for emergencies. Topic(s): Saving for “A Rainy Day” Coping with Unexpected Losses Emergency Savings Help People Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Deal With Unexpected Losses (Lesson Plan- Understanding and Managing Risk http://www.pwc.com/us/en/aboutus/corporateresponsibility/corporateresponsibility-report2011/community/financialliteracy-curriculum-pdfs/8-riskmanagement-3-5/1-pwc-riskmanagement-3-5-lesson.pdf )