Business Law Chapter One
advertisement

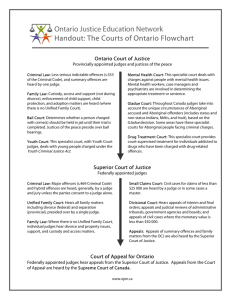
Business Law Chapter One Our Laws p.5-17 Section 1-1 Goals Explain the stages of evolution of law Describe the differences between common and positive law Describe the differences between law courts and equity courts Hot Debate – Page 4 1. Who was at Fault? 2. What arguments would Donna’s Attorney present at the civil trial to determine who was negligent? 3. What arguments would Wilma’s attorney present? Basic Terms Law Enforceable rules of conduct in a society Reflect the culture and circumstances that create them Code Laws grouped into an organized form Criminal, property, business, family, personal injury, labor laws Stages in the Growth of Law 1. Individuals take revenge for wrongs done to them 2. Awards of money or goods are substituted for revenge 3. Court systems are formed 4. A central authority figure (sovereign) intervenes to prevent and punish wrongs Common vs. Positive Common Law Based on current standards or customs Usually pronounced by judges Used to settle disputes Positive Law Dictated from above Usually from a higher central authority figure To prevent disputes before they happen Example: Cigarettes * Laws should be both predictable and flexible English Common Law The Kings Court 1150 by King Henry II Developed to create consistency among regions Appointed Judges Good weather months judges would “ride circuit” Bad weather months judges met in London to hear cases Example: Ox Cart Accident – Page 6 English Common Law Kings Court Established: Jurisdiction The power to decide a case Jurypanel of citizens, to interpret local customs Unique to English Common Law Precedent Use of prior cases as a guide for similar cases Levels of Government Federal State Local Each level consists of Constitutions Statutes Administrative Legislations Case Law Basic Terms Constitution A document that sets forth the framework of a government & its relationship to the people it governs Allocation of power between: People & government – Bill of Rights State & federal government – Fed regulates commerce (intrastate and interstate) Branches of government – checks and balances between the three branches Basic Terms Statutes Laws enacted by state or federal legislature Ordinances Example: What's Your Verdict? Page 9 Laws enacted at the local level Administrative Agencies Government bodies formed to carry out particular laws Social Security Administration Pa Department of Transportation County Zoning Commission Federal State Local Basic terms cont. Case Law Usually is made after a trial has ended and appealed. The decision of that appeal may create a new law Stare decisis READ “IN THIS CASE”…PAGE 10 What Happens when Laws Conflict? Any federal, state or local law that conflicts with the constitution is unconstitutional That law is invalid Turn to page 618 for some constitutional laws Criminal Vs. Civil Law Criminal Law Define and set punishment for offences against society Violates citizen’s right to live in peace Civil Law Define and set punishment for offences against individuals Example: tenant refuses to pay rent; owner can sue •Crime- an offence against society Criminal Vs. Civil Law What’s your verdict? Page 11 Criminal or Civil? Both – running through a stop sign is a crime against society - smashing into Bates is a civil offense Law in the Media?? Read Karla Faye Tucker Case - P.12 Is execution ever justified as a punishment for crime? Why? / Why not? Procedural vs. Substantive Procedural Deals with methods of enforcing legal rights and duties How/when arrests can be made Determine equitable remedies Stare decisis lower courts must follow existing case law in similar cases Substantive Defines rights and duties Rules of conduct Except enforcement Defines offences Murder Theft Vehicular homicide negligence Business Law Covers rules that apply to business situations & transactions Most occur between merchant and consumer Concerned with Civil law Torts Private wrongs against people/organizations Manufactures make defective products Two types of Procedural Law Criminal Procedural Defines the process for enforcing the law when someone is charged with a crime Civil Procedural Used when civil law is violated Concerned with private offences Police & public prosecutors generally do not get involved Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Widely adopted uniform business law Gives consistency between state commercial laws Sales of goods, aspects of banking, leases of goods, credit transactions, etc. Review what you know Think Critically #10 - #12 & 14 Your Legal Vocabulary page 13 #1 - 14 page 14