chap4 seq3
advertisement

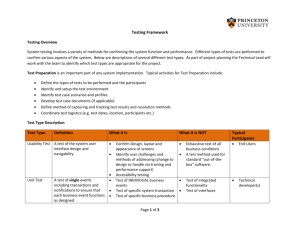
System Analysis and Design System Design - Mr. Ahmad Al-Ghoul Learning Objectives Explain the concept of user interface design and humancomputer interaction Explain the user rights Discuss several types of user interfaces Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 2 Introduction The user interface (UI) is the system which helps users communicate with the computer system and/or the application system UI Consists of all the hardware, software, screens, menus, functions, and features that affect two-way communications between the user and the computer A good user interface provides a unifying structure for finding, viewing and invoking the different components of a system Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 3 User Interface Design Evolution of the User Interface Avicenna In older systems, analysts designed all the printed and screen output first, then worked on the inputs necessary to produce the results In older systems interface mainly consisted of Process-control screens that allowed the users to send commands to a system A process control screen (also known as a dialog screen) is part of the user interface, and enables a user to initiate or control system actions. A process-control screens worked will with traditional systems that simply transformed input data into structured output As information management evolved from centralized data processing to dynamic, enterprise-wide systems, the primary focus also shifted — from the IT department to the users themselves System Analysis and Design System Design 4 User Interface Design Evolution of the User Interface Avicenna In modern systems, the main focus is on users within and outside the company, how they communicate with the information system, and how the system supports the firm’s business operations In modern systems most users work with varied mix of input, screen output, and data queries To perform users day-to-day job, the user interface is a vital element in the systems design phase Requires an understanding of human-computer interaction and user-centered design principles System Analysis and Design System Design 5 User Interface Design Compare the traditional, processing-centered system at the top of the figure to the modern, user-centered information system at the bottom. Notice the change in the role of the IT department. [1] Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 6 User Interface Design Human-Computer Interaction Avicenna A user interface is based on basic principles of human-computer interaction Human-computer interaction (HCI) describes the relationship between computers and people who use them to perform business-related tasks User interface includes all communications and instructions necessary to enter input to the system and to obtain output in the form of screen displays or printed reports Your main objective is to create a user-friendly design that is easy to learn and use System Analysis and Design System Design 7 User Interface Design Human-Computer Interaction Dr. Clare-Marie Karat IBM usability expert, states that “in this new computer age, the customer is not only right, the customer has rights.” The user rights cited by Dr. Karat include Avicenna Perspective: the user is always right Installation: the user has the right to install and uninstall software and hardware systems easily without negative consequences Compliance: the user has the right to a system that performs exactly as promised Instruction: the user has the right to easy-to-use instructions to achieve desired goals and recover efficiently from problem situations Control: the user has the right to be in control of the system and to be able to get the system to respond to a request for attention System Analysis and Design System Design 8 User Interface Design Human-Computer Interaction The user rights cited by Dr. Karat include Avicenna Feedback: the user has the right to a system that provides clear, understandable, and accurate information Dependencies: the user has the right to be informed clearly about all systems requirements for successfully using software or hardware Scope: the user has the right to know the limits of the system’s capabilities Assistance: the user has the right to communicate with the technology provider and receive a thoughtful and helpful response when raising concerns Usability: the user has the right to be the master of software and hardware technology, not vice versa System Analysis and Design System Design 9 User-computer interface design User Interface design: There are various types of user interface designs, each of which has a typical character and ability. The design type is required to be suitable to the system’s duties and to its users who will interact directly with the computers Avicenna Natural-language interfaces Question-and-answer interfaces A menu interface Form-fill interfaces Command-language interfaces Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) System Analysis and Design System Design 10 Interface designs Natural language Avicenna Natural-language interfaces permit users to interact with the computer in their everyday or "natural" language Inputs to and outputs from system are in a conventional speaking language like English Based on research in artificial intelligence Current implementations are tedious and difficult to work with, not as viable as other interaction methods System Analysis and Design System Design 11 Interface designs Question-and-answer interfaces The computer displays a question for the user on the screen The user enters an answer via the keyboard The computer acts on that input information in a preprogrammed manner New users may find the question-and-answer interface most comfortable Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 12 Interface designs A Menu Interface A menu interface, which provides the user with an onscreen list of available selections A specific command is invoked by user selection of a menu option Two common placement methods A nested menu is a menu which can be reached through another menu The advantages of nested menus are Avicenna Pop-up Drop-down Nested menus eliminate menu options which do not interest a user Nested menus allow users to move quickly through the program System Analysis and Design System Design 13 Interface designs Guidelines for Menu Design Avicenna Wording: meaningful titles, clear command verbs, mixed upper/lower case Organization: consistent organizing principle Length: all choices fit within screen length Selection: consistent, clear and easy selection methods Highlighting: only for selected options or unavailable options System Analysis and Design System Design 14 Interface designs Graphical User Interface (GUI) Menus GUI menus guidelines The main menu is always on the screen The main menu uses single words The main menu should have secondary menus grouped into similar features The secondary drop-down menus often consist of more than one word Secondary options perform actions or display additional menu options Menu items in gray are unavailable for the current activity Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 15 Interface designs Form: Filling in the form is a popular type of dialogue on data and data processing. Form-fill interfaces are onscreen forms displaying fields containing data items or parameters that need to be communicated to the user Forms are displayed on the screen similarly to the way tables are arranged. The screen also displays form name, field name and instruction information. Form-fill interfaces may be implemented using the Web Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 16 Interface designs Advantages of using a Web-based form User enters the data Data may be entered 24 hours a day, globally Disadvantages of a Web-based form Avicenna The user may not know what to enter if the form is not clear User might be nervous about using a credit card over the Internet System Analysis and Design System Design 17 Interface designs Command-Language Interfaces: This is a wide but simple area consisting of both simple commands and grammatically complicated commands. Allow the user to control the application with a series of keystrokes, commands, phrases, or some sequence of these A command will result in a move of the system when it is entered by the user. The most significant advantage of command-language is that its flexibility is limited by the language’s grammar only. it takes time for users to learn by heart the commands and users are required to have a background knowledge of the system in case there are no information displayed on the screen. command-language asks for great efforts while developing it. It is suitable for users who are professionals. Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 18 Interface designs Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) GUIs provide a strong metaphor of the application Allow direct manipulation of the graphical representation on the screen Can be accomplished with keyboard input, joystick, or mouse Requires more system sophistication than other interfaces Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 19 Sequence Summary In older systems interface mainly consisted of Process-control screens that allowed the users to send commands to a system In modern systems most users work with varied mix of input, screen output, and data queries A variety of user interfaces can be used, some interfaces are particularly well suited to inexperienced users, such as natural language, question and answer, menus, form-fill and webbased form-fill. Command language is better suited with experienced users Combinations of interfaces can be extremely effective Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 20 Sequence Summary In this Sequence we have Avicenna Defined the term user interface Discussed the evolution of the user interface Defined and discussed the term human-computer interaction (HCI) Explained the user rights cited by Dr. Karat Explained the concept of user interface design and humancomputer interaction Discussed several types of user interfaces include: Natural-language interfaces Question-and-answer interfaces A menu interface Form-fill interfaces Command-language interfaces Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) System Analysis and Design System Design 21 Reference [1] System Analysis and Design, Sixth Edition Authors: Gary B. Shelly, Thomas J. Cashman and Harry J. Rosenblatt Publisher: SHELLY CASHMAN SEWIES. [2] system analysis and design, sixth edition Authors: Kenneth E. Kendall and Julie E. Kendall Publisher: Prentice Hall [3] Modern Systems Analysis and Design Third Edition Authors: Jeffrey A. Hoffer , Joey F. George, Joseph S. Valacich Publisher: prentice hall Avicenna System Analysis and Design System Design 22