Intorduction to Project Management
advertisement

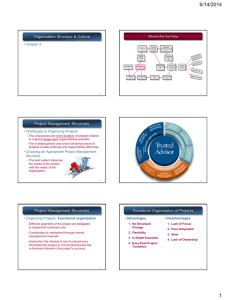
Project Management Human Resource Management* Dr. Lotfi Gaafar * This Presentation is uses information from PMBOK Guide 2000 Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 1 Project Organization Structure Uses information from Project Management: The Managerial Process. Gary and Larson Project Management Functional Organizations – Different segments of the project are delegated to respective functional units. – Coordination is maintained through normal management channels. – Used when the interest of one functional area dominates the project or one functional area has a dominant interest in the project’s success. Project Management Functional Organization of Projects Advantages – No Structural Change – Flexibility – In-Depth Expertise – Easy Post-Project Transition Project Management Disadvantages – Lack of Focus – Poor Integration – Slow – Lack of Ownership Dedicated Teams – Teams operate as separate units under the leadership of a full-time project manager. – In a projectized organization where projects are the dominant form of business, functional departments are responsible for providing support for its teams. Project Management Dedicated Team Advantages Disadvantages – Simple – Expensive – Fast – Internal Strife – Cohesive – Limited Technological Expertise – Cross-Functional Integration – Difficult Post-Project Transition Project Management Matrix Structure – Hybrid organizational structure (matrix) is overlaid on the normal functional structure. Two chains of command (functional and project) Project participants report simultaneously to both functional and project managers. – Matrix structure optimizes the use of resources. Allows for participation on multiple projects while performing normal functional duties. Achieves a greater integration of expertise and project requirements. Project Management Matrix Structure Advantages – Efficient – Strong Project Focus – Easier Post-Project Transition – Flexible Project Management Disadvantages – Dysfunctional Conflict – Infighting – Stressful – Slow Project Management Structures Challenges to Organizing Projects – The uniqueness and short duration of projects relative to ongoing longer-term organizational activities – The multidisciplinary and cross-functional nature of projects creates authority and responsibility dilemmas. Choosing an Appropriate Project Management Structure – The best system balances the needs of the project with the needs of the organization. Project Management Choosing the Appropriate Project Management Structure Organization Form Considerations – How important is the project to the firm’s success? – What percentage of core work involves projects? – What level of resources (human and physical) are available? Project Management Choosing the Appropriate Project Management Structure (cont’d) Project Considerations – – – – Size of project Strategic importance Novelty and need for innovation Need for integration (number of departments involved) – Environmental complexity (number of external interfaces) – Budget and time constraints – Stability of resource requirements Project Management Project Human Resource Management “project human resource management includes the processes required to make the most effective use of the people involved in the project. It includes all the project stakeholders-sponsors, customers, partners, individual contributors, and others.” Processes include –Organizational planning –Staff acquisition –Team development Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 12 Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 13 Planning Acquisition Development Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 14 Responsibility Matrix Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 15 Keys to Managing People Psychologists and management theorists have devoted much research and thought to the field of managing people at work Important areas related to project management include – motivation – influence and power – effectiveness Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 16 Motivation Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy of needs to illustrate his theory that people’s behaviors are guided by a sequence of needs Maslow argued that humans possess unique qualities that enable them to make independent choices, thus giving them control of their destiny Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 17 Organizational Planning Organizational planning involves identifying, documenting, and assigning project roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships Outputs and processes include – – – – project organizational charts work definition and assignment process responsibility assignment matrixes resource histograms Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 18 Staff Acquisition Staffing plans and good hiring procedures are important in staff acquisition, as are incentives for recruiting and retention Some companies give their employees one dollar for every hour a new person they helped hire works Some organizations allow people to work from home as an incentive Research shows that people leave their jobs because they don’t make a difference, don’t get proper recognition, aren’t learning anything new, don’t like their coworkers, and want to earn more money Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 19 Rewards and Recognition • • Reward and recognition systems are actions taken by project management in order to promote and achieve desired behavior and outcomes. The link between project performance and reward must be made clear and achievable. Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 20 Rewards and Recognition Considerations for Reward and Recognition • • • • • • • • Size of the project Project cost budget must be met Desired quality of products Scheduled date of completion must be met Health and safety targets Improved sales margin Ideas that make a difference ( employee suggestions) Recognition of outstanding performance Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 21 Training: • Definition: “ A planned process to modify attitude, knowledge or skill behavior through learning experience to achieve effective performance in an activity or range of activity. In order to satisfy the current and future needs of a project” • Distinction between training and development. (A different definition) Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 22 Considerations to be taken: • Is training a solution for the problem? • Are the goals clear and realistic? • Is it a good investment? • Will it work? Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 23 Training Process Needs Assessment Phase • Organization needs. • Task needs. • Person needs. Development and Training Conduct • Location. On Job (OJT) Off Job • Presentation Slides and video tapes. Computer Simulation Virtual reality • Types. Skills Retraining Cross Functional Training Team Training Creativity Training Evaluation Project Management Gaafar 2006 / 24