Place
advertisement

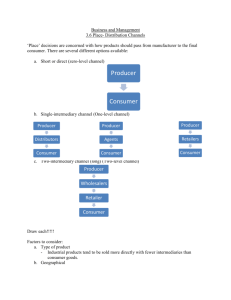
UNIT 4.6 - PLACE PG. 576 What is Place? The distribution of a product ie. How the product gets to the consumer “getting the right products to the right customers at the right price in the right place and at the right time.” Place can be through: Warehouses Agents Retail stores Internet What is Place? Stores have limited space so will only stock products that will sell EX: Cinemas have limited seating so will only show popular movies Marketers must convince stores to stock their product over their rival Businesses use distribution channels (retail, internet) to get their product to customers Traditional Channels of Distribution Since most products are not sold straight from manufacturer to customers so businesses must use intermediaries – middle person in the chain of distribution – manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers A long chain of distribution will raise or lower prices? Types of distribution channels: Zero-level channel One-level channel Two-level channel Types of Intermediaries Wholesalers Between producer and retailer Break large quantities into smaller units for retailers Bear the costs of storage Allow producers more time to focus on production Disadvantage: producer passes responsibility of marketing to wholesaler Distributors Trade products of only a few manufacturers Types of Intermediaries Agents Negotiators on behalf of buyers and vendors Helps sell products EX: real estate agents, insurance agents, door-to-door, telemarketing Charge commission of % of sales made Retailers Sellers of products to consumer (stores) Advantage: can reach large # of consumers Types: Independent – sells small range of products Multiple – several outlets EX: McD’s Supermarkets – sell mostly foods Hypermarkets – superstores; sells food AND consumer durables Department stores – sells furniture, jewelry, clothes, toys Direct Marketing as a COD Direct marketing – direct selling of products to consumers. NO intermediaries Advantages: No intermediaries therefore greater profit Direct control over marketing Boom in internet so direct marketing is more popular Can reach customers who live far from retail outlets Usually cheaper than ATL EX: telesales, e-commerce, direct mail, vending machines Direct Marketing as a COD Telesales (telemarketing) – using telephones to sell products directly to customers Can use sales people, automated voice, text message EX: insurance, satellite tv company Disadvantage: Mass telephone calls can be costly Many people do not like ‘cold calls’ Direct Marketing as a COD E-commerce – trading via internet More businesses are using websites to entice customers all around the world Reduces costs/risks of international marketing However, not all products can be sold online Cars, This jewelry, food is a growing channel of distribution Direct Marketing as a COD Direct Mail – sending promotional material thru the mail system Used by: banks, local restaurants, fast-food Advantages: personalized communication service bc it uses addresses of customers Low costs Detailed info aimed at diff market segments can be used Disadvantages: Low response rate bc people ignore mail Contact info on customers can be out of date Direct Marketing as a COD Vending Machines – specialist machines that stock certain products such as: cigarettes, drinks, snacks Advantages: Can be placed almost anywhere Multiple payment methods – convenient Low maintenance costs Disadvantages: Prone to vandalism Mechanical failures stops sales Can only sell a small range of products Choosing an Appropriate Distribution Strategy An efficient and cost-effective distribution strategy increases likelihood of customers purchasing the products 5 factors affecting distribution decision: Cost and benefits – agents are cheaper but retailers can reach more customers Product – flowers/meats would need shorter COD. DVDs/CDs best sold through internet Market – small markets need no intermediaries Time – urgent delivery of product needs direct COD Legal constraints – license to sell alcohol, anti-gambling laws Place and Business Strategy Marketing managers must deal w/ 2 key issues: The best COD to use How it will ensure that intermediaries will want to stock their products When choosing a COD or which intermediaries to use they must decide on the most suitable TYPE: Intensive distribution – mass produced products Selective distribution – producer chooses suitable intermediaries Exclusive distribution – less common; specially chosen intermediaries given the right to sell a certain product Place and Business Strategy Some companies want as many outlets to sell their products ie. Coca-Cola Others do not want many outlets ie. Rolls-Royce, Tiffany & Co. To ensure an outlet will sell their product, a company can: Open their own store (expensive) ie. Nike, Adidas Company can use franchise agreements – allow other certified people to run the store under business name ie. 7-11, Pizza Hut, Burger King Place and Business Strategy If a company wants complete control over all its marketing activities company can use: Vertical integration – growth strategy that unifies supplier, producer, wholesalers, and retailers Will have more direct control over its supply chain and distribution channels However, this is usually not a realistic option, so businesses will have to go back to competing for floor space Place and Business Strategy Companies can use branding as another strategy Companies of popular brands will have preferential distribution channels. Distributors and retail stores will want to stock their products. Exporting has benefited international trade However, exporting has some complications: Fluctuating exchange rates Government intervention Language barriers Cultural differences Internet has greatly decreased costs. Rising popular distribution method