Place
advertisement
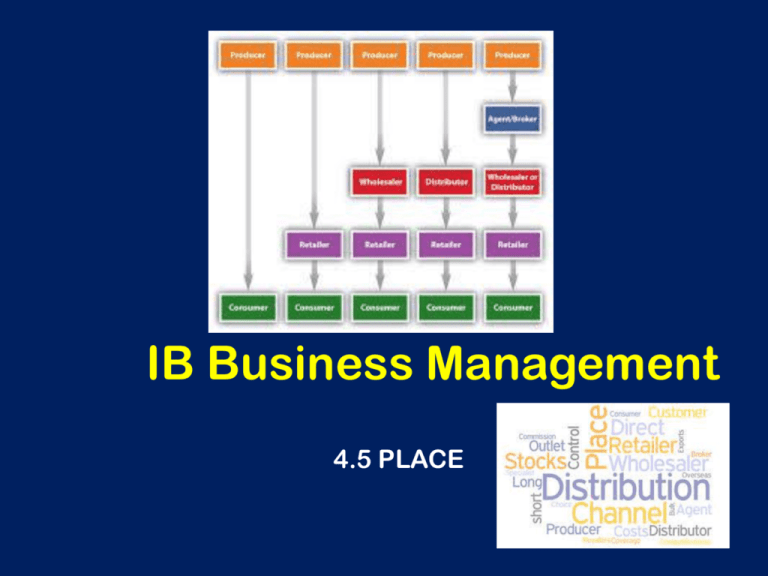
IB Business Management 4.5 PLACE Learning Outcomes • To understand the importance of place in the marketing mix (A02) • To analyse and evaluate the effectiveness of different types of distribution channels (A03) Central Question How does a business decide where to sell and what distribution method is most appropriate? Place (distribution) • How products get from the producer to the consumer. “getting the right products to the right customers at the right price in the right place at the right time” How do these get to the consumer? Channels of Distribution • The method of getting the product to the consumer • Intermediaries are agents or businesses that facilitate this (middle man) • The longer the distribution channel generally leads to higher prices as each intermediary adds a profit margin to their selling price • A long channel of distribution is not suitable for perishable products – why? Distribution channels as levels • A zero level channel – has no intermediaries e.g. service industry • A one level channel – has one intermediary e.g. a retailer • A two level channel - has two intermediaries e.g. wholesaler and retailer How many levels? Types of Intermediaries • Retailer – A business which buys goods from manufacturers and wholesalers and sells them in small quantities to customers • Wholesaler – A business which buys large quantities of goods from manufacturers. They then ‘break the bulk’ and sell them in smaller quantities to retailers • Agent/Broker – An independent company who negotiates between buyers and sellers • Distributor – Specialist , independent businesses that sell products of only a few manufacturers WHOLESALERS – WHY USE THEM? Wholesaler Advantages • Wholesaler takes care of storage o Retailer has less cost & more space • Retailers do not have to purchase such large quantities • Producer’s costs are lower as they are selling in bulk to fewer customers • Producers do not have to deal with distribution issues / problems Wholesaler Disadvantages • Producer loses control of marketing • How do you know the wholesaler will promote like you want them to? • Retailers have higher prices as the wholesaler’s costs must be passed on RETAILERS – WHAT ARE THEY ALL ABOUT? Retailers (shops) • The sellers of products to the final customer What Different types of retailers are there? Some Types of Retailers Superstores/ Hypermarkets Department Stores Supermarkets Multiples/Chains Market Traders Online Retailers Independent stores Distributors • Distributors o Independent, specialist businesses that sell products of only a few manufacturers • Examples include: o o o o Cars Books Movies Electrical equipment Agents or Brokers • Negotiators who act on behalf of buyers & sellers of a product • Usually not employed by the producer, independent • Experts in their field • Often charge either a commission or a fee • Often offer products from a variety of producers • Examples: o Real estate, travel, insurance, financial advisors Agents or Brokers • Often rely on personal selling techniques o o o o Product is complicated Buyer needs education Buyer can ask questions Product may need demonstration Direct Route • What methods could a firm use to sell directly to customers? Can you think of examples of companies which use these methods? Direct Marketing Distribution • Telesales, or telemarketing o o o o Sales people make phone calls Or automated voice or text messaging Expense varies Some people hate it • E-commerce o Websites which accept payment online Credit card PayPal E-check o o Not appropriate for all products Growing in popularity • Direct Mail o o o Send promotional material via the postal service Can be personalized But often considered ‘junk’ • Vending Machines o o o o o Drinks, snacks, cigs Can be placed almost anywhere New machines can accept various payment methods Costs are minimal, i.e., no salespeople needed Vandalism, limited stock, mechanical failures Factors in Choosing Distribution Strategy • Costs & benefits o o Direct selling may reduce costs but retailers may have better access to customers Transportation methods must also be considered, e.g., rail, ship, trucking, air • Product Perishables must have short chains Fast-moving goods need to be moved in large volumes (wholesalers & retailers more app.) o Many products can now be sold directly through the internet (books, dvds, toys, airfare, vacations, clothes) o o Multi-Channel Distribution • Many businesses will use more than one channel • E.G., airlines will sell tickets via: o o o o Travel agencies Airport counters Internet website Internet travel sites Expedia Kayak Orbitz What Distribution Channel/Channels do these manufacturers use? Factors in Choosing Distribution Strategy • Market o Niche markets often directly controlled by producer whereas mass markets often best to use intermediaries • Time o Some items require immediate delivery while others can be ordered and delivered at a later date • Legal Constraints o o Often a nation or community’s laws affect the distribution selection E.g., gambling, alcohol sales, guns & ammunition Channels of Distribution • Channels of distribution are NOT the methods of transport o They are NOT trucking, railroads, shipping etc. • Channels of distribution refer to the intermediaries used to get product to customer such as wholesalers, agents, retailers Place – CUEGIS? CONCEPT CHANGE CULTURE ETHICS GLOBALISATION INNOVATION STRAETEGY RELEVANCE TO PLACE THEORY Quiz Time











